Toenail fungus (onychomycosis, tinea unguium) is a fungal disease of the fingernails and toenails. More than 12 percent of all Germans suffer from it. Men and the elderly are affected more often. Read more about: How can nail fungus be recognized? How do you treat it most effectively? How is it created and what are the risk factors?
Nail fungus: short overview
- Treatment: long-term and consistent treatment with antifungals (antifungals) as nail polishes, creams or sticks, possibly also in tablet form. In addition, laser therapy, in severe cases, possibly surgical nail removal
- Typical symptoms: Depending on the type of fungus discoloration from the edge or nail root, complete discoloration or staining, thickening and dissolution of the Nageslstruktur or chipping the upper layers. Also often pain, redness of the nail fold, inflammation of the nail bed.
- Causes: Infection via shared towels, carpets, beds; damp environment in closed shoes (“sweaty feet”), use of shared showers (sauna, sports club, swimming pool), metabolic and immune diseases (for example diabetes mellitus, HIV infection), circulatory disorders, smoking
- diagnosis: Consultation and physical examination, microscopic and infectiological examination (fungal culture) of a sample of the diseased nail
- Forecast: good chance of recovery with early started and consistently carried out long-term treatment
Nail fungus: treatment
The nail fungus treatment depends mainly on the nature and severity of the symptoms. In all stages of nail fungus local treatment is recommended. The most effective is an antifungal nail polish, because it penetrates well into the nail tissue.
The following table provides an overview of the most important methods and remedies for nail fungus. Before treatment, it may be useful to gently remove infected nail material. For this purpose, a urea ointment is usually applied once a day, which softens the horn substance of the nail. It can be scraped off carefully.
However, a self-treatment of nail fungus should not be performed if the nail is already heavily affected by the fungus. In such cases, the doctor often prescribes additional tablets against the infection.
|
Method / means |
application, Advantages and disadvantages |
Remarks |
|
Antifungal nail polish (water soluble) |
– uncomplicated and fast application – must be applied once a day – after application, the nail must not be in contact with water for 6 hours – After the 6 hours paint residues can be washed off with water – Antifungal drug Ciclopirox also has antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties |
Active ingredient: ciclopirox; available over the counter never use cosmetic nail polish at the same time! |
|
Antifungal nail polish (waterproof) |
– uncomplicated and fast application – Active substance Amorolfin: Apply once or twice a week – Active substance Ciclopirox: every 2nd day in the 1st month, at least twice a week in the 2nd month, at least once a week in the 3rd month – Paint residues can only be removed with alcohol or nail polish remover – Ciclopirox also works antibacterial and anti-inflammatory, Amorolfin not |
Active substance: Ciclopirox or Amorolfin; available over the counter never use cosmetic nail polish at the same time! |
|
Antifungal cream / ointment |
– contains the active substance bifonazole (and sometimes urea): applied once a day (duration: several weeks) – in any case pretreatment with urea ointment makes sense (for detaching the nail) – Bifonazole is also antibacterial and anti-inflammatory |
suitable for thickened nails and fungal infections under the nail plate; available over the counter |
|
Nail fungus-pen |
– uncomplicated and fast application – apply once or twice a day depending on the product |
different active ingredients; available over the counter never use cosmetic nail polish at the same time! |
|
Tablets with terbinafine |
– Continuous intake every day or with treatment breaks (for example, taking for 1 week, then 3 weeks break) – Application duration: max. 4 months – Less interaction with other medicines than itraconazole and fluconazole, therefore particularly suitable for older patients |
Standard anti-dermatophyte drugs (most common toenail fungus pathogens); prescription |
|
Tablets with itraconazole |
– Continuous intake every day or with treatment breaks (for example, taking for 1 week, then 3 weeks break) – Application duration: max. 3 months – numerous interactions with other drugs possible |
helps against the specific nail fungus pathogens against which terbinafine and fluconazole are not effective; prescription |
|
Tablets with fluconazole |
– Take once a week – Application period: 6 to 12 months – less effective than terbinafine and itraconazole, but well tolerated, therefore particularly suitable for children – numerous interactions with other drugs possible |
Applied when other agents are not or should not be taken. prescription |
|
surgical nail removal |
– fast result, but not more promising than other treatments – high risk of relapse – often pain and temporary disability after the procedure |
Will hardly be done. Gentler is the nail removal with urea ointment. |
|
laser treatment |
– hardly any side effects, uncomplicated and effective – expensive and only available in a few dermatological practices |
Statutory health insurance companies do not pay for the laser treatment. Private insurers demand proof of medical necessity. |
Antifungal nail polish, cream and stick
A local nail fungus treatment with Antifungal nail polish, cream or stick Every patient can perform independently at home. In lighter cases, this self-treatment may be sufficient, that is, if:
- only one nail is affected,
- a maximum of half of the nail area is affected and
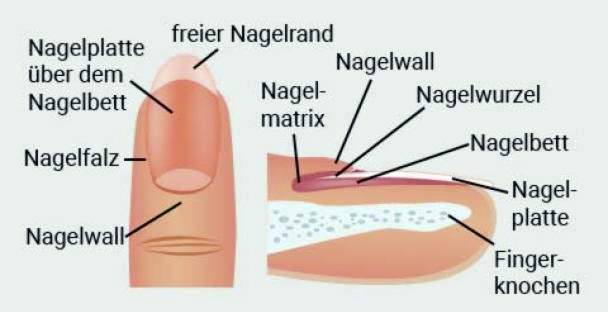
- the nail root (nail matrix) is not infected (this is the area where the nail plate is formed).
If you are unsure about whether these points apply to you, you should consult a doctor or medical podiatrist.
Antifungal nail polish, cream and stick are an uncomplicated help with nail fungus. However, they must be used as long as possible until the fungus is safely killed. To recognize this is not easy for laymen. Then also applies here: If in doubt, go to the doctor!
Nail fungus treatment with tablets
Go to the doctor if an independent nail fungus treatment does not succeed or many nails or larger nail surfaces are affected. The local nail fungus therapy then usually has to be supplemented by a systemic therapy – that is, by taking antifungal tablets, which develop their effect from within and throughout the body.
When choosing a suitable drug (terbinafine, itraconazole, fluconazole), the doctor will consider the exact type of agent and other factors. For example, women should not use terbinafine as much as possible during pregnancy, even if this is the most suitable ingredient against filamentous fungi (the most common exciters of nail fungus). Instead, the doctor may prescribe clotrimazole or miconazole, for example.
Older patients, on the other hand, should preferably be treated with terbinafine. The risk of drug-drug interactions is much lower than that of itraconazole and fluconazole. This is particularly important for older people because they usually have to take several different medications (such as blood pressure medication).
Patients should also inform the doctor conscientiously about all possible illnesses and health complaints. For some diseases, some antifungals may not be given, for example terbinafine in liver function disorders.
Nail fungus treatment by surgery
In the past, the question of “What to do in case of fungal nail in severe / stubborn cases?” Was often called the possibility of surgical nail removal. Due to the side effects (such as pain) and the high risk of relapse, this procedure is hardly performed today. In addition, surgical removal of diseased nails in nail fungus treatment is not more successful than other methods.
Nail fungus treatment by laser
A new treatment option for nail fungus is laser irradiation. In several sessions, this can kill the fungal infection, even if you do not know exactly how it works.
Another advantage of laser therapy in nail mycosis is that it causes little adverse effects when properly performed. The patients report at most a feeling of warmth or slight stinging in the irradiated toes.
However, the lasering of a nail fungus infection is very expensive and is not paid by the statutory health insurance.
Learn more about the laser therapy for onychomycosis in the article nail fungus laser.
Nail fungus: homeopathy
Many sufferers ask themselves the question “What helps against nail fungus except conventional medicine?” They want to treat onychomycosis with alternative healing methods. So some rely on essential oils or Schüßler salts. Still others rely on homeopathy. However, nail fungus is rarely treated exclusively with alternative medicine. Instead, alternative healing methods are often used as an adjunct to conventional medical treatment.
By the way: To the question “What helps with nail fungus?” Homeopaths call means such as Acidum hydrofluoricum, Silica, Antimonium crudum or sepia, Aromatherapy uses about the essential oils of Eucalyptus globulus, Origanum vulgare or Thymus vulgaris (Chemotype thymol) at. As suitable Schüßler salts against nail fungus the number 5 apply Potassium phosphoricum and the number 8 Sodium chloratum, Which remedy is best for a particular case should be discussed with an experienced therapist.
Nail fungus: home remedies
“Better of course than chemical,” many people think and prefer home remedies in the fight against nail fungus. For example, vinegar or acetic acid, lemon, marigold and aloe vera and tea tree oil are used. Such natural remedies are considered gentle help against the fungal infection. They are mainly used externally directly on the diseased nail.
However, it has not yet been scientifically proven that vinegar, tea tree oil & Co. are really effective on nail fungus. Some doctors advise against it. At least the home remedies should not be used as a substitute, but only as an adjunct to conventional medical treatment.
More about the use of home remedies for fungal infections of the nails read in the article nail fungus home remedies.
Nail fungus: symptoms
Generally, nail fungus can infect fingernails and / or toenails. The latter are affected much more often. There are two reasons for this:
First, the feet are exposed to a greater mechanical stress. This is more likely to result in tiny injuries that are used by fungi (and other pathogens) as entry ports. On the other hand, mushrooms love a warm and moist environment, and this is more likely to be found on the feet, such as barefoot running in the pool or in shared showers and foot sweat in closed shoes.
The toenail fungus often grows on the big toe, but it can also affect one of the other toes or spread over several nails. In severe cases, all nails of a foot or a hand are affected.
The nail fungus symptoms vary in the various forms of onychomycosis, as described below. In all but applies: If the infection is not treated or too late, eventually the whole nail can be affected by the fungus and be completely destroyed by this (total dystrophic onychomycosis).
Distolateral subungual onychomycosis (DSO)
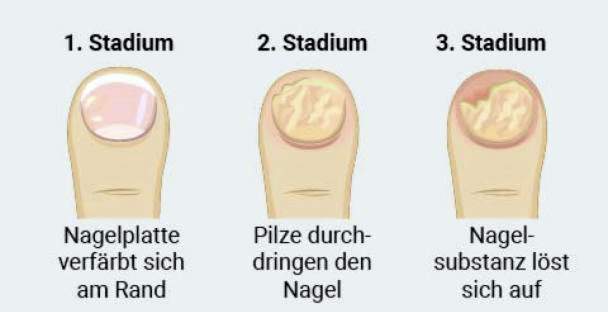
About 82 percent of all patients show this type of nail fungus. The pathogen is usually the filamentous fungusTrichophyton rubrum, It penetrates at the free (distal) end of the nail under the nail plate and spreads on its underside in the direction of nail root. This typically results in the following symptoms of nail fungus (without treatment):
At first she sees Nail plate dull and dull out before they turn discolored white-yellowish, Other symptoms (pain etc.) are usually missing in this phase of nail fungus.
Excessive keratinization under the nail plate (subungual hyperkeratosis) the nail thickens gradually and begins to break away from the nail bed replace, In some patients, the thickened nail plate may painfully press on the underlying delicate nail bed. This can be particularly noticeable when wearing tight shoes and when walking.
In addition, there is a risk that (in addition to nail fungus) bacteria settle in the damaged tissue and a Nail bed inflammation cause. Pain is also possible, and the entire nail is very sensitively sensitive.
Finally, the afflicted Nail cracked, brittle and crumbly.
Proximal subungual onychomycosis (PSO)
This form of nail fungus is usually made from filamentous fungus Trichophyton rubrum triggered. It penetrates the nail wall, where the nail grows out, over the skin into the nail plate and the nail bed. The nail shows one whitish discoloration and opacity, This onychomycosis occurs almost exclusively in people with a weakened immune system.
White superficial onychomycosis (WSO)
This nail mycosis is also called Leukonychia trichophytica. The trigger is usually the filamentous fungus Trichophyton interdigital (T. mentagrophytes). It penetrates directly into the surface of the nail plate. As a result, they form white spots in the nail.
Onychia et Paronychia candidosa (Candida Paronychia)
Here, the proximal nail wall (where the nail grows out) and later also the lateral nail wall are chronically inflamed by an infection with yeasts (usually Candida albicans). Typical nail fungus symptoms are here Redness and swelling of the nail wall.
Later, the nail plate discolors in the border area, where the nail grows out and on the sides. The color varies depending on an additional bacterial infection of yellowish over brownish to greenish, Without treatment, the fungus also spreads to the nail matrix and the nail bed.
This nail mycosis develops preferentially on the fingernails of people who often work with their hands in damp or wet environments.
Edonyx onychomycosis
For this very rare form of nail fungus are usually filamentous fungi of the genus Trichophyton responsible. They penetrate directly between the layers of the nail plate and spread inside. The lackluster, whitish nail plate fragmented thereby lamellar. The nail bed remains mostly intact in this nail mycosis. In addition, there is no thickening and detachment of the nail plate from the nail bed.
Nail Fungus: causes and risk factors
Nail fungus mostly caused by filamentous fungi (dermatophytes). Sometimes molds or yeasts are responsible for the infection. The latter affect especially the fingernails.
In principle, the fungi can infest all keratinized parts of the body (skin, nails and hair). They feed there from the main ingredient keratin.
Is nail fungus contagious?
The nail fungus comes through fungal spores onto the skin. Spores are microscopic particles of fungi that can survive for a very long time and are used to spread them. The most common transmission path is from person to person.
In addition, fungal spores can also be transferred from contaminated objects to humans. These include, for example, towels, bath mats, carpets and beds.
Risk factors for nail fungus
Mushrooms prefer to grow in warm and humid places – so for example sweaty feetEspecially if they are in shoes that are unable to dissipate heat and moisture to the outside. The resulting heat and moisture accumulation promotes fungal growth.
The same is true if you do not clean the toe spaces properly and dries. This is especially true for people who have a physical disability or, for example, a cast leg. You can more easily get a foot and nail fungus. Incidentally, experts suspect that nail fungus on the feet often as Consequence of an athlete’s foot infection developed. So many people suffer from both infections at the same time.
Other factors that could favor nail mycosis are:
- Frequent contact with toenail fungus pathogens, for example in the swimming pool, in shared showers or in the sauna
- Injuries to the nails
- certain skin diseases like psoriasis
- Circulatory disorders in the legs, for example due to diabetes, peripheral arterial disease (PAD) or smoking
- weakened immune system, for example, in some diseases (such as HIV) or in the intake of drugs that suppress the immune system (such as cortisone)
- familial predisposition
By the way: Diabetics are more susceptible to fungal diseases because of the high amount of sugar in their blood – the sugar is used by the mushrooms as food.
For nail fungus on the hands are especially prone to people who often work wet / wet hands to have. These include, for example, cleaners.
As general risk factors for nail fungus (and also skin fungus) are also vitamin deficiency (Vitamin A, B1, B2 and K) as well Lack of zinc and folic acid In the suspicion.
Nail fungus: examinations and diagnosis
The first contact person in the investigation of nail fungus is the family doctor. You can also contact a dermatologist (dermatologist).
Survey of the medical history
The doctor will first raise the medical history (anamnesis). He will ask you about your symptoms, possible underlying diseases and other factors that are important for the diagnosis. Possible questions include:
- Since when do the nail changes (thickening, discoloration) exist?
- Are you familiar with chronic diseases (such as diabetes or psoriasis)?
- What do you do for a living?
- Does or did anyone in your family have a fungal infection?
Physical examination
After the interview follows the physical examination: The doctor examines the affected nails and surrounding tissue. Thickened, discolored nail plates are often a clear indication of nail fungus. However, there are other possible explanations for supposed nail fungus symptoms, which the doctor must exclude (differential diagnosis):
So a psoriasis can extend to the nails and look like a mushroom (nail psoriasis). It can also contribute to a nail involvement eczema (“Eczema”) and other skin diseases like Knötchenflechte (Lichen planus), which may resemble a fungal infection.
In people with chronic varicose veins The toenails are often thickened and grayish-green discolored. This can also fake a nail mycosis. The same applies nail injuries like a bruise and pinching of the nail.
Other differential diagnoses include rare chronic nail changes that can be found in, for example, Circulatory disorders, thyroid disease, Iron, calcium or vitamin deficiency develop.
Detection of toenail fungus pathogens
In clarifying the nail changes helps the doctor Nail fungus test: He disinfects the nail in question with alcohol and then scrapes some of the nail plate. The tiny nail chips can be stained with a special dye and examined under the microscope for fungal spores. If he finds some, that speaks for a nail fungus.
Under the microscope, you can not tell what kind of fungus it is. However, the doctor must know this if he wants to prescribe anti-nail fungus tablets to the patient. Depending on the type of agent, certain active substances are better suited than others. To identify the exact type of pathogen, this is grown from the tissue sample in the laboratory (fungal culture). That takes three to four weeks.
With a strong nail fungus, however, the doctor can already begin an antifungal therapy with an active ingredient that works against a whole range of fungi (broad-spectrum antifungal).
In rare cases, other tests on nail fungus are performed. For example, the nail tissue in the laboratory can be examined more accurately (histologically).
What you should consider before visiting the doctor
So that the doctor can diagnose nail fungus correctly, you should not wear colored nail polish during the examination.
If you have already tried a local nail fungus treatment in the run-up (such as with antifungal nail polish), you should have completed these two to four weeks before the doctor’s visit. Otherwise, the result of fungal culture may be erroneously negative due to possible remnants of the nail.
Nail fungus: disease course and prognosis
Nail fungus does not heal by itself, but must be treated. Where: The sooner nail fungus is treated, the better, In early stages, it is usually painless and easier to treat.
In contrast, advanced nail mycosis can cause significant pain, such as when wearing shoes or walking, and the ingrowth of deformed nails. The skin around the nail or the nail bed can become inflamed. In addition, fungus from the toenail fungus can develop and spread even further.
If the fingernails are affected by the fungal infection, the instinct can change so that the fine motor skills are impaired.
Last but not least, toenail fungus is an aesthetic problem that can greatly affect the affected psychologically. That’s why you should definitely treat him early.
It is essential to hold on to therapy!
A nail fungus treatment is tedious and requires a lot of patience and consistency from those affected. Even in mild cases, it extends over weeks to months. In severe, the toenail fungus therapy lasts for up to a year and longer. The reason: The diseased nail area must first be completely outgrown, before the patient is considered cured. Some patients discontinue the antimycotics treatment early, when no more infestation is visible. It can then be infected but still a part of the nail plate. Starting from these places, the nail fungus can repeatedly spread to healthy areas.
Incidentally, with infected fingernails, the treatment usually leads to success faster than with toenails.
Prevent nail fungus
A nail fungus can be prevented. Although the fungus spores are found everywhere in our environment – the mushrooms feel well, especially in humid, warm surroundings. The most important measure is therefore to deprive him of the breeding ground.
Right footwear
You should wear as few closed shoes (as sneakers) in which your feet sweat a lot. Instead, prefer more breathable shoes (such as sandals or light loafers). Do not put on wet or damp shoes.
After each wearing you should ventilate your shoes well. If you sweat a lot, stuff your footwear with paper after wearing it and allow it to dry completely. In addition, you can also disinfect the shoes regularly.
Do not walk barefoot in public swimming pools, sauna facilities, solariums and changing rooms.
Socks and stockings
When choosing socks, you should prefer materials such as wool, cotton or cotton blends and refrain from using synthetic materials. Change the socks daily or, if you sweat a lot, several times a day. Shoes and socks should never be shared with other people to prevent the transmission of nail fungus in this way.
Proper foot care
After washing and bathing, you should dry your feet well before putting on socks and shoes. Pay special attention to the toe gaps when drying!
A regular and thorough foot care is especially important for people who are particularly prone to nail fungus. These include, for example, diabetics and people with immunodeficiency, but also athletes and seniors. Often it makes sense to visit a medical chiropodist (podiatrist) on a regular basis.
Change laundry and wash properly
Towels and sheets should be changed regularly. If you already have nail fungus, you should even change the towel every day – as well as socks and stockings. Wash them as well as shower rugs at a minimum of 60 degrees Celsius. Use heavy-duty detergents or special detergents that kill fungal spores. These are available in pharmacies and drugstores.
For nail fungus patients: prevent spread
People with nail fungus should not walk barefoot indoors or in the home so as not to spread the robust fungal spores in the area and potentially infect other people.
When sleeping, people with nail fungus should wear socks. This way they can prevent the fungal spores from spreading in the bed and eventually reaching other parts of the body or the partner and triggering a new infection there.
Additional information
- Guideline “Onychomycosis” of the Association of Scientific Medical Societies, Guidelines of the German Dermatological Society and the German-speaking Mycological Society (as of 2006)