Chickenpox (varicella) is a highly contagious viral disease transmitted by droplet or smear infection. The most obvious symptom is an itchy rash with blisters. Most children and adolescents suffer from chickenpox, but adults can be affected. Chickenpox is usually without complications. Pregnancy and a weakened immune system can complicate the course of the disease. Read more about the infection and symptoms of chickenpox, duration of the disease, treatment and prevention.
Quick Overview
- What are chickenpox? An infectious disease caused by the highly contagious varicella-zoster virus (belongs to the herpesviruses). Chickenpox is a childhood disease, but can occur at any age – but only once in a lifetime. After a persistent infection you are immune to chickenpox for life.
- Infection: Often by inhalation of small, virus-containing saliva droplets, the sick give off when coughing, sneezing or exhaling in the air (droplet infection). Sometimes also by contact with the virus-containing liquid in the skin blisters of the patients (smear infection).
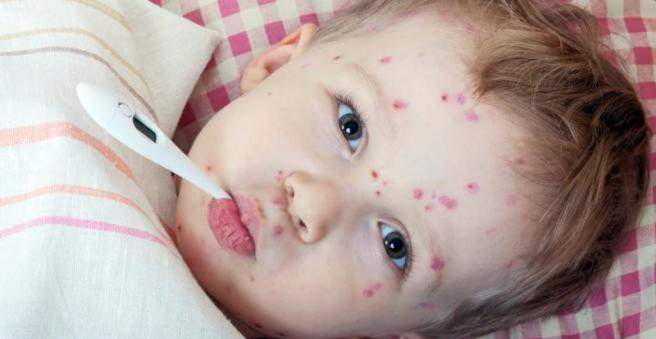
- symptoms: Initially, general symptoms such as malaise, headache and body aches, fatigue and occasional fever. Then the typical rash occurs with fluid-filled, itchy blisters (first on the trunk and face, later on other parts of the body).
- Treatment: especially treatment of the symptoms (e.g., skin care, antipruritics, analgesics). In severe cases and at increased risk of complications additionally virus-inhibiting drugs (antivirals).
- Forecast: Chickenpox usually heal easily. Rarely, complications such as an additional bacterial infection of the skin, pneumonia, encephalitis or meningitis develop. Especially in adults, varicella is often more severe than in children.
- Second condition: After a chickenpox disease, the pathogens remain in the body. You can become active again later and trigger a shingles (zoster).
- Prevention: Especially by chickenpox vaccine. Those who are not vaccinated should avoid contact with patients.
Chickenpox: contagion
Are responsible for a chickenpox infection Varicella-zoster virus, These are highly contagious herpesviruses that occur exclusively in humans. The risk of chickenpox infection is particularly high in the winter and spring months. During this time, the varicella infections accumulate.
The pathogens are transmitted mostly through Droplet or smear infection:
- In a droplet infection tiny, virus-containing saliva droplets of infected people by exhaling, speaking, sneezing or coughing into the ambient air and are then inhaled by healthy people.
- The smear infection occurs by direct contact with the virus-containing fluid from the characteristic skin lesions of the patient – for example, if one touches the patient with his hand and then unconsciously grasps the mouth or nose. Once the viruses reach the mucous membranes, they can easily penetrate inside the body.
Just one to two days before the typical rash becomes visible, there is a risk of infection! It only ends when all the bubbles are encrusted. This is usually the case five to seven days after the appearance of the first bubbles.
Very rarely, varicella from a pregnant woman to the unborn child transmitted via the mother cake (placenta). Such a chickenpox infection in the womb may be called fetal varicella syndrome to lead. Also possible is one Chickenpox infection in newbornsif the mother herself has varicella shortly before or after birth.
A source of infection also pose Shingles patients Shingles is the second disease that can trigger varicella viruses – even years after the chickenpox infection has passed through. Patients can transmit the pathogens to healthy people from the onset of the rash until full blistering (usually five to seven days after onset of rash). If they are not vaccinated against varicella and have not had chickenpox, they can get sick – chickenpox, not shingles. However, shingles patients are less contagious than chickenpox patients.
Chickenpox: incubation period
Chickenpox can present with first symptoms 8 to 28 days after infection. On average, this incubation period is 14 to 16 days. The disease breaks out only if you have never had the chickenpox and not vaccinated against it. After a living infection you are immune to chickenpox viruses for life.
Protection against infection
Those who have not yet undergone chickenpox infection and are not vaccinated against it, is considered unprotected against chickenpox viruses. The risk of infection is very high: In nine out of ten cases, unprotected people also contract chickenpox after contact with patients. Unprotected should therefore the Avoid contact with patients, Especially if somebody has varicellae in the home environment, you should stay as far away as possible and not stay in the same room with the patient for a long time. This is especially true for People with a weak immune system.
Otherwise, no special precautions are generally needed. Sometimes, however, in consultation with the doctor, a so-called post-exposure vaccination against chickenpoxmakes sense: It is suitable, for example, for pregnant women, immunocompromised people and newborns who had contact with patients and (possibly) got infected. By “contact” is meant, for example, that those affected live in the same household as sick or have been in the same room for at least one hour or have come very close to the patient (“face-to-face”) ). You may receive the active chickenpox vaccine within five days of such contact or up to three days after the occurrence of the typical rash. This can prevent an outbreak of the disease or weaken its course.
Instead of the active vaccination, ready antibodies against varicella can also be administered as postexpositional vaccination. If possible, this passive vaccination should be given within three days (maximum of ten days) after the possible infection.
If hospital patients who have chickenpox, they are isolated from other patients. This should prevent the spread of the infectious disease. The same goal is pursued in case of a disease outbreak in Shared facilities like schools and kindergartens: All who suffer from chicken pox have to stay at home for the time being. The others are sometimes given precautionary vaccination against varicella when they are unprotected (locking vaccine). Patients may not visit the facilities until one week later, when the risk of infection has largely disappeared. A medical certificate is not necessary.
Chickenpox is notifiable. Physicians must pass the names of all patients to the health department who are suspected of having chickenpox or who have actually contracted the disease. Even the death of chickenpox must be reported.
Chickenpox vaccine
The Standing Vaccination Commission (STIKO) recommends the vaccination against chickenpox for all children from 11 months. Adolescents who did not have chickenpox and who have not been vaccinated against it should do the vaccination. The same applies to adults if they belong to one of the following risk groups:
- Women with children who do not have antibodies to chickenpox in their blood
- Patients prior to initiating therapy that weakens the immune system (for example, prior to organ transplantation) when antibodies to chickenpox are not detectable in the blood
- Occupational groups at increased risk of infection (such as medical staff and preschool teachers) who have never had chickenpox and are not vaccinated against it or who have no chickenpox antibodies in their blood
- People with severe atopic dermatitis if they have never had chickenpox and are not vaccinated against it or no chickenpox antibodies are detectable in the blood
Read more about the protective vaccination against varicella in the article Chickenpox – Vaccination.
Chickenpox: symptoms
Chickenpox only shows in the first two days general symptoms such as feeling sick, light fever and fatigue. Of the typical rash develops later, from the third to fifth day of illness:
There are small red spots forming within a few hours bubbles filled with clear liquid develop. she itch strong, After one to two days, they dry up to become crusted. New vesicles can form over a period of three to five days. This creates a complexion with vesicles in various stages of development, which you can starry sky is called.
The number of blisters varies from patient to patient. It is usually between 250 and 500. Small children usually show fewer vesicles than adults.
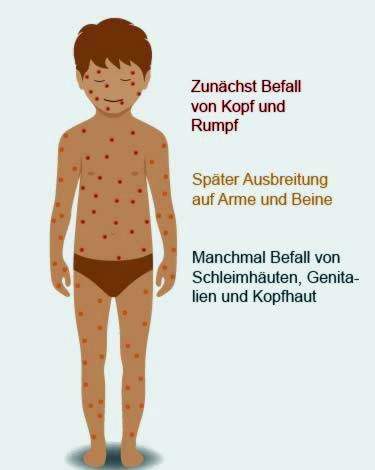
The rash begins on the trunk and face, then spreads to the arms and legs, later on the scalp, oral mucosa and genitals. Often the rash of up to 39 degrees high fever accompanied.
The typical chickenpox symptoms (skin blisters) can be after overcoming illness permanent scars recall. These arise when the bubbles have additionally been infected with bacteria and then inflamed (bacterial superinfection). Scarring the itchy blisters can also leave scars.
The varicella pathogens remain in the body following the healing of the chickenpox, in an inactive state. They can still “wake up” years later. Then a shingles (zoster) develops. This can only occur in people who had chickenpox at some point.
Chickenpox: examinations and diagnosis
If chickenpox is suspected, the doctor first raises the medical history (Anamnesis): For example, he asks for the exact complaints udn since when they exist. Then one follows physical examination, The characteristic rash makes the doctor usually recognize at first glance a chickenpox infection.
Only in special cases, if suspected chickenpox special investigations are necessary. This is true for example in patients with weakened immune systems, because the disease is often atypical for them. Also in people with central nervous system diseases or pneumonia as well as in pregnant women and newborns further investigations are recommended. They serve to detect the chickenpox directly or indirectly:
- In the case of direct detection, one looks for the genetic material of the viruses in the vesicular fluid, the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), the pulmonary secretion or the patient’s blood. In order to directly detect chicken pox in the unborn child, a sample of the placenta (chorionic villus biopsy), the amniotic fluid (amniocentesis) or the child’s blood (umbilical cord puncture) is examined for varicella genomes.
- In indirect detection, antibodies to varicella in the blood or cerebrospinal fluid of the patient are sought.
The indirect varicella detection (antibody test) is also useful to determine if someone already had the chickenpox or the vaccine was effective against it.
Chickenpox: treatment
If the chickenpox develops without complications, only the symptoms are treated, in particular the itching. So you can prevent the bubbles ignite by scratching. The following methods have proven to be useful:
- Stay in a cool environment, as heat and sweat increase the itching
- Cut fingernails to avoid scratching the bubbles
- daily bathing
- antipruritics for local application on the skin (lotions, gels, powders, usually with active ingredients such as tannins, zinc or polidocanol)
From anti-pruritus drugs for use (antihistamines) advise experts. Their effectiveness in chickenpox has not been adequately studied.
For fever and body aches may be needed Fever and pain medication such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen.
Acetylsalicylic acid (ASA) also helps against fever and pain, but should not be used in children and adolescents (or at the express advice of the physician). The drug can trigger with them the rare but life-threatening Reye syndrome!
In severe cases, the windpox pathogens can be treated directly with special drugs that inhibit the multiplication of viruses. To this Antivirals (antivirals) For example, the active ingredient is acyclovir. You can shorten the duration of chickenpox disease. These remedies have proven to be particularly effective in patients with weakened immune systems.
Chickenpox: Disease course and prognosis
In otherwise healthy patients, the disease is usually uncomplicated and heals without scars. However, in very rare cases, chickenpox can cause complications:
- additional bacterial inflammation of the blisters (bacterial superinfection)
- Pneumonia caused by varicella virus (varicella pneumonia)
- Complications in the area of the central nervous system, such as balance disorders, encephalitis (encephalitis) or meningitis (meningitis)
- Complications of the heart, kidneys, joints or cornea such as myocarditis, nephritis, arthritis, corneal damage
Chickenpox: pregnancy and childbirth
If a pregnant woman receives chickenpox within the first six months of pregnancy, the child may also become ill. Doctors then speak of fetal varicella syndrome: The unborn child may develop skin lesions (such as ulcers, scars) and eye damage. In addition, skeletal malformations and diseases and malformations of the nervous system threaten. For example, a loss of brain tissue (brain atrophy), paralysis and seizures are possible consequences of prenatal infection with chickenpox. Babies in the womb can even die from the disease.
A neonatal chickenpox infection occurs in newborns whose mother has varicella between five days before and two days after birth. It is very difficult, because the immune system of the little ones is not yet mature. Up to 30 percent of all affected babies die.
Chickenpox in adults
Even adults can get chickenpox if they are not vaccinated and have not had the disease yet. At this age children’s disease is often more severe than at a young age. In addition, adults more often develop complications in the disease process.
A very serious and dreaded complication is pneumonia caused by chickenpox (varicella pneumonia). Up to 20 percent of all adult patients get it. Here, pregnant women are at particular risk. The pneumonia usually begins three to five days after the onset of chickenpox infection.
Unprotected adults with an increased risk of serious illness and complications should therefore oppose chickenpox vaccinate. These risk factors include, for example, women who want to have children who do not have antibodies against varicella.
Read more about the course and prevention of adult varicella infection in the article Chickenpox in Adults.
Additional information
guidelines:
- RKI guidebook “Chickenpox, herpes zoster (shingles)” of the Robert Koch Institute (2017)