An anal fissure is a painful, elongated tear in the anal mucosa. It is often caused by excessive pressure in hard chair. Typical signs of anal fissure are sharp pains during bowel movements. In most cases, it is an acute anal fissure that can be treated with ointments and chair-regulating measures. If the condition is chronic, surgery may be necessary. Learn here what causes an anal fissure, how to treat it and what an effective prevention looks like.

Quick Overview
- What is an anal fissure? Painful tear in the mucous membrane of the anal canal
- symptoms: Pain during stool and afterwards, cramps of the anal sphincter, itching, bleeding, oozing or mucous secretion of the wound, possibly thickening of the skin
- Causes: often severe pressure during bowel movements or hard feces, possibly also anal sexual practices, hemorrhoids, diarrhea, inflammatory bowel disease (Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis)
- Diagnosis: Conversation, physical examination, if necessary rectal examination
- Treatment: conservative with ointments, creams, baths; in chronic course surgery
- Doctor treating: Proctologist, gastroenterologist
- Forecast: An anal fissure is easy to treat, but can persist again and again if the feces are persistent or other risk factors.
Anal fissure: symptoms
The anal fissure (Latin fissura, “tear”) is a longitudinal tear of the fine skin or the mucous membrane at the mouth of the anal canal (anoderm). There are very many sensitive nerve endings. Correspondingly painful is an injury in this area.
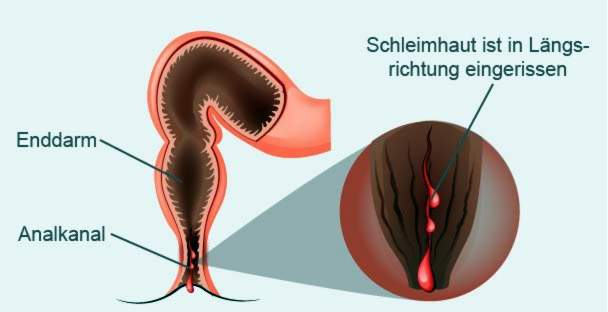
A acute anal fissure There is a maximum of four to six weeks. It makes itself felt by a sharp pain on the anus, which arises when the skin tears. As a result, stool can only be excreted in pain (painful defecation), To avoid this pain, many sufferers hold the chair back (stool behavior). A vicious circle, because the retained feces continue to thicken and become even harder. Ultimately, the toilets become even more painful. Typically, the symptoms remain after the visit to the toilet in the form of a burning persistent pain consist.
Problematic: Through the pain of the Cramp the sphincter so muchthat the symptoms continue to increase. The tissue may not be well supplied with blood, so that the anal fissure heals worse. There is a risk that from the acute crack one chronic anal fissure developed.
In addition, spasm of the sphincter may cause further mucosal tears, Because of such muscle cramps you have to press harder during bowel movements.
If the tear reaches the depth of the inner sphincter, the strong cramping can increase the connective tissue around the muscle and harden with time (fibrosis). Such thickening of the skin may develop in a chronic anal fissure. she will outpost fold called.
Other possible symptoms of anal fissure are:
- Pain-related chronic constipation (constipation), when those affected hold back the chair for fear of pain
- Itching on the anus
- the wound can wet or secrete mucus (mucus secretion)
- bright red blood deposits on the chair and blood remains on the toilet paper
Blood in the stool should always be clarified by a doctor. In addition to an anal fissure, a serious cause (such as cancer) can be behind it.
Anal fissure: causes and risk factors
Why an anal fissure arises can often not be clarified clearly. It is clear that she can occur at any age. However, she does so much between the ages of 30 and 40 years. Mostly an anal fissure develops in the direction of the rump.
The most common cause of anal fissure is Too much pressure during bowel movements, paired with too hard chair, Both stretch the mucous membrane and it can easily rupture. For example, hard feces are caused by chronic constipation. This in turn can be caused by lack of fluid intake, low fiber diet, lack of exercise and a “sluggish bowel”.
In some cases anal sexual practicesin which the mucous membrane is injured, the cause of an anal fissure. Also hemorrhoids, one Inflammation in the region of the rectum (Cryptitis) as well as long-lasting diarrhea come as a trigger in question. Patients with inflammatory bowel disease such as Crohn’s disease or Ulcerative colitis also tend to anal fissures.
An anal fissure that occurs as a result of another condition (such as Crohn’s disease) is called a secondary anal fissure. In contrast, a primary anal fissure is a disease in its own right (for example, as a result of excessive pressure during bowel movements).
Anal fissure: examinations and diagnosis
If an anal fissure does not heal itself within a few days, you should always see a doctor. The right contact person is a specialist in diseases of the rectum (proctologist) or a specialist in diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (gastroenterologist). But you can also go first to your family doctor, who will then refer you further.
Most sufferers are embarrassed by their problem. They shy away from going to the doctor and try to control the complaints with home remedies. Often, they seek help only when the suffering from constant itching, burning, pain and blood leakage becomes too great.
In the case of a wound in the area of the anus (such as an anal fissure), the risk of infection is very high. There are many germs here. If one waits too long with the doctor’s visit, one risks an infection with possibly serious complications.
patient consultation
The doctor first inquires about the medical history (anamnesis). He interviews the patient in detail about his complaints. Possible questions are:
- In which situations does the pain occur? Only during bowel movements?
- Do you feel an itch on the anus?
- Do you suffer from constipation?
- Have you noticed mucus or fresh blood on the toilet paper?
- Does the wound on the anus wet?
Physical examination
Then the doctor inspects the anal area and gently scans it. In most cases, the characteristic high-grade mucosal injuries are found at the expected sites. A rectal examination is in many cases only possible after local anesthesia. This allows the doctor to assess whether it may be due to hemorrhoids or other diseases of the anus.
endoscopy of the rectum
If there is an anal fissure, the doctor may do an endoscopy (proctoscopy). He can look at the inside of the rectum and take mucosal samples. For proctoscopy, the patient usually receives a local anesthetic (local anesthesia) – in an anal fissure, the examination may indeed be quite painful.
Further investigations
If the doctor detects signs of a malignant disease (eg, anal carcinoma = anal cancer), further investigation may be needed. These can be, for example, blood tests, colonoscopy, computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Anal fissure: treatment
The treatment of an anal fissure depends on whether it is an acute or a chronic anus tear. The two forms differ not only in duration (acute: maximum of 4-6 weeks, chronic: longer), but also in the extent of tissue change:
- In acute anal fissure the mucous membrane is rather superficially injured. This can be treated well with conservative (non-operative) means. These include soothing ointments, creams or sitz baths.
- A chronic anal fissure develops when a deep ulcer (ulcer) develops from the acute mucosal injury and the wound margins change scarred. Sometimes a coarse skin fold (outpost fold) is formed. If conservative treatments do not work, the chronic anal fissure must be operated on.
An anal fissure is only operated when absolutely necessary. There is a risk that the intervention of the anal sphincter muscle is injured. Then the patient may not be able to control the stool outlet (fecal incontinence).
Anal fissure: Conservative treatment
An acute anal fissure can with special creams treated to relax the sphincter. They contain as active ingredients calcium antagonists or nitrates, Helpful are also agents that soften the stool and promote defecation, for example solutions with Macrogol. use laxative but only in consultation with the doctor!
In addition, you can with a Analfissur Ointments for local anesthesia of the skin (anesthetic ointments). Also analgesic and anti-inflammatory ointments and suppositories are often used.
Wash your hands before applying an ointment. This prevents wound infections.
Also temperature rising sitz baths can relieve the anal fissure symptoms. They promote blood circulation in the area of the anus. This strengthens the local defense and strengthens the afterrage better. How the sitz bath works: Sit upright in the bathtub with your feet on a stool outside the tub. Add chamomile extract to the tub and start letting in lukewarm water first. Then raise the water temperature to 36 to 40 degrees for ten to fifteen minutes. Then take a short shower and lie down for as long as possible (bed rest). If you feel cold during the bath, you can wear socks and a pullover.
Also advisable with an anal fissure is the right one anal hygiene: It is best to wash the anal region after lavatory with lukewarm water. Do not use soap or shower gel! Both can destroy the skin’s natural anti-acid greasy film and dry out the skin. That makes them more susceptible to bacteria. Intimate wash lotions and intimate sprays are also discouraged.
Do not use wet toilet paper. The additives contained therein can lead to allergic reactions of the skin. Use normal toilet paper that is as soft as possible.
Watch out for an anal fissure on one high-fiber dietTake at least 30 grams of fiber per day. These stimulate intestinal movements and bind water in the faeces. This will make the feces softer overall. For example, many fibers are found in whole grains, vegetables and fruits. Also wheat bran is very valuable. But you must make sure that you drink enough liquid. Only then can the fiber swell well and act accordingly.
Tip: If you suddenly consume large amounts of fiber, it can cause flatulence. Therefore, you should only increase the fiber content of your diet slowly. That’s how your digestive system can adjust.
With a chronic anal fissure it can be helpful to treat the anus several times a day with a special one anal dilator Carefully to widen. This can slightly reduce spasm of the sphincter. The blood circulation of the skin / mucous membrane improves and hardening is counteracted.
Anal fissure: surgery
If conservative measures in anal fissure therapy do not help enough, surgery is the last resort. In general, anal fissure surgery is just a minor procedure performed under short-term anesthesia or spinal cord anesthesia. The surgeon will remove the surrounding scar tissue as completely as possible. Rarely also a part of the anal sphincter must be removed. The procedure is usually performed on an outpatient basis in younger patients. Older patients are hospitalized for a short time in the hospital for the operation.
Like any surgical procedure, anal fissure surgery carries its risks: Especially in operations in the area of the anal sphincter, which forms a ring around the anus, nerves can be damaged. The possible consequence is that in future the patient will no longer be able to control the discharge of faeces (fecal incontinence).
The healing process after the operation takes a long time (usually four to six weeks). He can still extend, if it comes to a wound infection. This is not uncommon for surgery on the anus, because this body region is heavily populated with germs.
Anal fissure: Botox
A new but expensive treatment option for chronic anal fissure are Botox injections in the anal sphincter. Botox (botulinum toxin) is a neurotoxin that paralyzes the sphincter for several weeks. Thus, the ulcer can heal in peace.
Anal fissure: Disease course and prognosis
An acute anal fissure usually heals after a few weeks without problems, if it is treated with conservative measures. If left untreated, there is a risk that it will become chronic. In addition, then anal fistulas or abscesses (pus accumulations) arise.
A chronic anal fissure can be successfully treated by surgery in most cases.
Acute or chronic – after successful treatment, anal fissure may recur if the causes and risk factors (such as hard stools, heavy pressure) are not resolved. Therefore, ensure a high-fiber diet, adequate hydration and plenty of exercise. This keeps the stool soft and supports the bowel movement so it can (again) anal fissure prevent.