Rosacea (rosacea) is an inflammatory, chronic condition of the facial skin that runs in bouts. It starts with skin redness. Later, vascular dilations, blisters, nodules and tissue neoplasm may be added. Those affected suffer from itching and pain, stressful is also the cosmetic impairment. Find out everything important about rosacea here – symptoms, causes, diagnostics, treatment and prognosis.

Quick Overview
- What is Rosacea? Chronic inflammatory skin disease that progresses in spurts and varying degrees of severity. Affected is usually the face, rarely other parts of the body.
- symptoms: At first volatile skin redness (erythema), later often vasodilatation, inflammatory blisters and nodules as well as tissue formation (phymen). In addition, burning, itchy skin and piercing pain. The special form Ophthalmorosazea affects the eye and can lead untreated to severe vision problems.
- Triggers and risk factors:strong, long-lasting UV radiation (sunbathing, solarium), heat, hot baths and showers, certain cosmetics, alkaline lotion (> 7), special medicines, coffee and tea, alcohol and nicotine, stress.
- Treatment:Medications (ointments, creams, lotions, antibiotics), laser treatment, sclerotherapy, photodynamic therapy, surgery; Avoid typical triggers such as UV radiation, heat, spicy food, alcohol as well as certain toiletries and cosmetics
- Causes:Still unclear. A genetic predisposition in interaction with various immunological, microbacterial and neurological factors is suspected.
- Forecast:Chronic course, not completely curable. With proper treatment, care and appropriate lifestyle, the symptoms can be well controlled and reduce the relapses. Sometimes the disease comes to a sudden halt.
Rosacea: symptoms
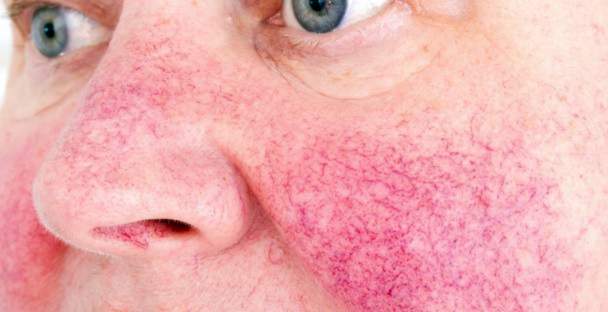
The Rosacea (rosacea, “copper rose”) is a skin disorder (dermatosis). It affects the classic way face and rarely other parts of the body.
The rosacea runs in spurts and varying degrees of severity, which accompany typical symptoms. In addition, the symptoms may vary from patient to patient, so that they can not always be clearly assigned to a severity.
Pre-stage: rosacea diathesis
Typical of the beginning of a rosacea are sudden, fleeting reddening of the skin (Erythema). They mainly affect the cheeks, nose, chin and middle forehead area. Rarely, rosacea is also found on other parts of the body, such as the eyes, scalp, chest or neck.
Severity I: Rosacea erythematosus teleangiectatica
Come to the skin redness vasodilatation (Telangiectasia) in the facial skin. The skin is dry and desquamates occasionally easy. In addition, those affected suffer from itching as well burning, stinging pain.
Severity II: Rosacea papulopustulosa
At this stage form additionally inflammatory reddened occur Bubbles (pustules) and Nodules (papules) as rosacea symptoms. They usually disappear after several weeks. Sometimes they also develop lymphedema (Fluid retention) in facial tissue.
Because acne-like inflammatory skin lesions develop in rosacea, the disease was previously mistakenly called “acne rosacea”.
Severity III: Glandular hyperplastic rosacea
This is the heaviest form of rosacea. Connective tissue and sebaceous glands enlarge, causing bulbous Growths (Phymas) arise, for example, a bulbous nose or potato nose (rhinophym). For cosmetic reasons, sufferers usually suffer greatly from these skin changes.
Unlike acne, blackheads do not form on rosacea. If you experience typical rosacea symptoms and blackheads, you are probably suffering from a mixed form.
Special forms of rosacea
In addition to the classic rosacea, there are some special forms that occur relatively rarely.
The Ocular is observed in about every fifth person affected. It affects the eye, either in addition to the classic skin disease rosacea or isolated. Typical symptoms are enlarged blood vessels in the eyes as well as inflammations of eyelids (Lidrandentzündung = Blepharitis) and conjunctiva (conjunctivitis = conjunctivitis). The eyes are usually dry and often burn. The Ophtalmorosacea should be monitored very closely. If left untreated, it can cause keratitis, which in extreme cases leads to blindness.
In the Rosacea fulminans The typical symptoms are particularly pronounced within a few days or weeks. Mostly young women are affected, while men are almost never affected. Once the rosacea fulminans has been overcome, it usually does not reappear.
To a gram-negative rosacea It comes when the disease has already been treated for several weeks without sustained success with antibiotics. Then only certain pathogens were destroyed. Others, so-called gram-negative bacteria, have survived. They multiply and subsequently cause further skin reactions.
If the rosacea is treated with glucocorticoids (steroid hormones such as cortisone), after the medication has stopped Steroidrosacea develop. This often goes much harder than the rosacea that you really wanted to treat. For this reason, rosacea is treated only in exceptional cases with these drugs.

Rosacea: treatment
With special medicines and the right cosmetic care, rosacea symptoms can often be alleviated significantly. When left untreated, rosacea usually gets worse in batches.
In addition or as an alternative to drug treatment, further therapy methods can be used. These include sclerotherapy, photodynamic therapy and surgical procedures. In addition, people with rosacea should keep an eye on the diet and avoid typical triggers of the symptoms as much as possible.
Some patients use homeopathy in the treatment of rosacea (often in addition to conventional medical therapy). An effectiveness of the alternative healing method has not yet been scientifically proven. Nevertheless, some patients report an improvement in symptoms.
Rosacea treatment with drugs
Drug treatment is the most important component of rosacea therapy. One distinguishes between local and systemic therapy. Experience has shown that the combination of local and systemic rosacea therapy is particularly effective.
Local (topical) rosacea treatment
Here, the drug is applied as an ointment, gel or lotion directly on the affected skin. Which dosage form is most effective and best tolerated depends on the individual case. The external treatment of rosacea is usually carried out over a very long period of time (as topical maintenance therapy). The two most important active ingredients used are:
- metronidazole (an antibiotic)
- azelaic acid
Both agents are said to have an anti-inflammatory effect on rosacea. They may also slow down the typically overreacting immune system in rosacea. Azelaic acid also ensures that certain skin cells (keratocytes) do not grow too much.
In addition, other substances can be used for local rosacea therapy:
- permethrin: Properly dosed, the actual poison has a positive effect on the rosacea.
- clindamycin: The antibiotic is also used locally in exceptional cases.
- retinoids: Like permethrin, they are also used in acne.
- Calcineurin inhibitors: They help especially with a steroid rosacea.
The substances mentioned primarily fight the nodules and blisters. However, they usually do not help against the typical flushing of the face. In contrast, in the US, a special gel with the active ingredient brimonidine developed. Since 2014, it has also been authorized in the EU. The drug causes the blood vessels in the facial skin to contract. As a result, the redness fades.
Systemic rosacea treatment
Some milder forms of rosacea will require local treatment. In more severe cases, however, additional systemic rosacea treatment is necessary. The drug is used internally, for example in the form of tablets. Thus, the active ingredient passes through the blood in the entire body. This makes systemic rosacea therapy more effective than the local one. On the other hand, it often comes to stronger side effects.
Most are for systemic rosacea therapy antibiotics used, in particular two groups:
- tetracyclines: Doxycycline and minocycline are the most commonly used drugs in this group of drugs. They are the first choice in antibiotic treatment of rosacea because they are better tolerated by the stomach and intestines than macrolides.
- macrolides: This group of drugs includes, for example, erythromycin and clarithromycin. Macrolides are used when patients can not tolerate tetracyclines.
Antibiotics are actually used to fight bacteria. In rosacea treatment, however, a different mechanism of action of these substances is exploited: At low doses, the antibiotics have a predominantly anti-inflammatory and dampening effect on the overreacting immune system – similar to metronidazole and azelaic acid in local rosacea treatment.
In addition to antibiotics, systemic rosacea treatment sometimes also uses active ingredients that are normally used for topical treatment – such as tablets metronidazole.
Also retinoids such as isotretinoin can relieve the symptoms of rosacea when administered internally, as studies show. However, isotretinoin is only approved in Germany for the treatment of severe acne. Therefore, it is only used in exceptional cases outside the official approval (“off label”) for severe rosacea. Great care should be taken because taking isotretinoin capsules can have many side effects, including severe ones, such as irritation to the skin and mucous membranes. In addition, isotretinoin must not be taken by women who might become pregnant (risk of childhood malformations!).
Unlike many other skin diseases, rosacea is only rarely treated with glucocorticoids (“cortiosis”), as these agents usually worsen the condition. Even after an initial recovery, the symptoms usually return even more after discontinuing the cortisone preparation.
Laser treatment and sclerosing
With a laser treatment, the persistent redness and vascular dilation (telangiectasia) can usually be well removed. For this purpose, the affected skin is treated with bundled, high-energy rays of light. This way you can also remove phy- men.
Vascular dilatations can also become acidic using electric current.
Photodynamic Therapy (PDT)
In photodynamic therapy, rosacea patients first receive a substance that makes the skin more sensitive to light. This so-called photosensitizer is deposited on the affected areas of the skin. Then these areas are irradiated with light of a certain wavelength. This changes the structure of the photosensitizer. As a result, the substance destroys defective skin structures.
Surgical therapy
The rosacea can also be treated surgically, such as with a dermabrasion or a Dermashaving. These methods are mainly used in phymen. They are therefore described in more detail in the article “Rosacea: Rhinophyma”.
Change diet & avoid triggers
It is also very helpful if people with rosacea change the diet. There is no special rosacea diet. But as experience shows hot spices, very hot food and drinks such as alcohol If you have a facial enlargement, you should refrain from doing so as a patient. Care for one healthy, balanced diet, In particular, reduce yours Fat and sugar consumption in favor of a lot of fruits and vegetables. This will help prevent the pores from clogging the facial skin. This, in turn, has a positive effect on the skin’s appearance.
In addition, you should test how your rosacea reacts to various foods. Again and again, consciously do without individual foods and observe whether and how the rosacea symptoms change as a result.
It is also important that you have the typical trigger avoid a rosacea boost:
- strong, long-lasting UV radiation (sunbathing, solarium)
- Heat, hot baths and showers, sauna visits
- Wash lotions and soaps with alkaline pH (> 7)
- certain cosmetics
- certain medications
- coffee and tea
- alcohol
- nicotine
- stress
Also, hormonal changes, such as in pregnancy, can trigger a disease boost. Talk to your doctor about it.
Rosacea patients respond differently to the different possible triggers. Therefore, observe exactly which stimuli your skin reacts to and adapt your lifestyle accordingly.
Rosacea: care
The rosacea skin should be properly cared for. This may help with medication and / or other therapy methods. Because certain ingredients and improper use of care products can irritate the skin and thus increase the symptoms.
Proper skin care
Take care of the following tips during skin care:
- Clean facial skin only with lukewarm water. Extreme water temperatures and rapidly changing temperatures can lead to sudden flushing (flushing).
- Do not use facial peels, as they irritate the rosacea skin additionally.
- Use only care and washing products without menthol, camphor, sodium lauryl sulfate and astringents.
- Avoid water with a high degree of hardness.
- After washing, gently dab the facial skin with a towel rather than rubbing with the towel.
- Use soaps and washing lotions with a slightly acidic pH (<7).
As far as facial cleansing is concerned, so-called washing syndets are well suited for rosacea patients. These are relatively low pH (4.5-5.5) artificial wash-active substances that are much gentler on the skin than traditional soaps.
Attention, sun!
UV rays are an important risk factor for rosacea sufferers. Therefore you should protect your skin conscientiously against (strong) UV radiation:
- Avoid direct sunlight between spring and autumn.
- Do not go to solarium visits.
- Use sun protection products with a high sun protection factor (50+) and apply them several times a day. Prefer physical sunblockers with titanium dioxide or zinc oxide (pharmacy). In rosacea these are considered to be better tolerated by the skin than chemical sunscreens.
Rosacea: cream, ointment or lotion?
The products differ in terms of water and fat content. An ointment contains no water, only fat. In contrast, a cream has a certain amount of water. A lotion contains even more water than fat. It is therefore also referred to as an oil-in-water emulsion.
For rosacea patients, products with high water content are ideal, ie creams and lotions. Because they do not form a pore-blocking film of fat on the skin, but allow the skin to breathe without drying it out. The same applies to preparations based on glycerine or silicone oil (cyclomethicone, dimethicone).
You should completely dispense with products with fragrance or dye additives, as these irritate the skin unnecessarily.
Tip: Get detailed advice in the pharmacy before buying your care products.
Make-up at Rosacea
Basically, you can also use rosacea makeup. However, you should make sure that the products are free of irritating ingredients such as menthol, camphor, sodium lauryl sulfate and astringents. In addition, the cosmetics should not clog the sebaceous glands, so be non-comedogenic.
Do without very strong covering make-up. Because this is difficult to remove, which in turn can trigger skin irritation. On the other hand, it makes sense to use a special rosacea make-up which covers the redness of the face well and is easy to remove.
Rosacea sufferers can respond very individually to cosmetics. If you notice that you can not tolerate a product, you should immediately stop the application and try an alternative.
Rosacea: Rhinophyma
The rhinophyma is a symptom of rosacea, which can develop in a severe course of the disease. It is a proliferation of connective tissue and sebaceous glands (phyme). Rhinophyme usually occur on the nose. This so-called tuber nose or potato nose is observed especially in older men.
Phyme are treated by medication or surgery. Especially in the surgical field can be achieved today good optical treatment success. However, there is the possibility that later forms a new bulbous nose.
More about “rhinophyma” in rosacea read in the article Rosacea: Rhinophyma.
Rosacea: causes and risk factors
Depending on which study is used, between 2 and 20 percent of the population in Germany suffer from rosacea. People over the age of 30 are most often affected. But even children can contract a rosacea in exceptional cases. Serious differences between the sexes can not be observed – in women rosacea occurs only slightly more often. In addition, light skin types are affected more often than dark ones.
The typical symptoms of rosacea are a permanent dilation of the blood vessels as well as a chronic inflammation of the skin. The causes are not yet fully understood. A genetic predisposition is suspected. In combination with various factors, it could lead to the development of a rosacea, experts believe.
How is a rosacea created?
Among other things, probably plays the body’s immune system a role. It produces certain antimicrobial substances in the skin, which are to fight entering pathogens. Some of these substances trigger inflammation and also cause new vessels to form (angionegenesis). This is normal and useful to destroy invading pathogens. In the blood of rosacea patients, however, significantly increased concentrations of these antimicrobials were detected. This could explain the pathological dermatitis and tissue regeneration.
As a trigger of the immune reaction are certain microorganisms In the suspicion. Thus, the skin of rosacea sufferers is often above average with so-called demodex (Demodex folliculorum) populated. The microscopic little animals are indeed on the skin of every human being. In rosacea patients, however, they appear to be more prevalent and trigger the inflammatory immune response described above.
In addition, there is evidence that in a rosacea receptors of the immune system not working properly. These receptors recognize foreign bodies and produce certain substances to fight them. In case of a dysregulation However, the receptors overreact and trigger so persistent skin inflammation.
Last but not least, too inflamed nerves to play a role in the face during rosacea formation. The nerves control the blood vessels by placing them in heat and contracting in cold weather. In rosacea patients, communication between nerves and blood vessels on the face does not work properly because the nerves are inflamed. This leads to dysregulations – even with weak stimuli such as spicy food, the blood vessels widen, without subsequently completely contracting again.
Rosacea: examinations and diagnosis
In most cases, the dermatologist can recognize the rosacea based on the typical symptoms (skin redness, dilated vessels, etc.). Special examinations are therefore usually not necessary.
Sometimes, the doctor withdraws from suspected rosacea skin sample (Biopsy). It is examined more closely under the microscope. Thus optically similar skin diseases can be excluded, such as the rarer butterfly lichen or stewardesses disease (cosmetic acne). In addition, the study helps to assess the severity of rosacea.
Rosacea: disease course and prognosis
The rosacea is usually chronic and intermittent – phases with stronger symptoms alternate with periods in which the symptoms disappear or at least improve. Although the disease is not completely curable, but can be well controlled with the right treatment, skin care and lifestyle. Sometimes that comes rosacea even to a halt without further development.
Additional information
Books:
- Rosazea: A guide, Volker Nölle, Volker Sayn, WiKu publishing house publishing house for science and culture, 2003
guidelines:
- Guideline “Rosacea” of the German Dermatological Society (2013)
Self-help:
- German rosacea help e.V.