In a torn muscle, one or more fibers break in a muscle. Reason is a strong muscle load, such as football or tennis. The torn muscle fibers are noticeable with a sudden, stabbing pain. The affected muscle can no longer be loaded to the maximum. Read more about this topic here: How does a torn muscle fiber develop? Which symptoms occur? What to do with hamstring?

Quick Overview
- symptoms: sudden, stinging pain, possible bruise; Loss of power of the affected muscle, restriction of movement
- Causes: extreme stress, z. B. by jerky movements, abrupt stopping. Often happens in sports like tennis or football. Risk factors include lack of fitness, bad shoes, muscular inequalities, infections.
- Diagnosis: Patient interview (anamnesis), physical examination, possibly ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging (magnetic resonance imaging, MRI)
- Treatment: Acute measures include pausing, cooling, pressure bandage and high-altitude positioning of the injured body part. The doctor can prescribe painkillers and physiotherapy. In severe cases, surgery if necessary.
- Forecast: A hamstring usually heals without consequences. But that takes several weeks.
Muscular rupture: symptoms
A torn muscle with a sudden, knife-like pain associated. The affected muscle is in his Function restricted and can not be loaded more than maximum. The patient can not continue the sports activity that led to the injury. The natural movement is disturbed. Mostly sufferers take one relief attitude at. When trying to hook the injured muscle against resistance, kick Pain on. There are also pressure and stretch pain.
Immediately after the injury, there may be a visible and palpable dent in the affected area – especially if not only muscle fibers are torn, but the entire muscle has been severed (muscle tear). But as the tissue usually swells, the dent is soon no longer felt.
Sometimes a visible one is formed at the site of the torn muscle bruise (Hematoma).
The symptoms described are all the more pronounced, the more severe the muscle injury is – so if more than one fiber, a fiber bundle or even the whole muscle is torn.
Muscular rupture: causes and risk factors
A torn muscle fiber destroys the smallest structural units of the muscle: the muscle fibers. These are long, cylindrical cells with many cell nuclei. Depending on muscle and strain, they can be up to 30 centimeters long and between 10 and 100 microns thick. Each ten to twenty muscle fibers form a muscle fiber bundle, which is surrounded by connective tissue. A skeletal muscle consists of several such muscle fiber bundles.
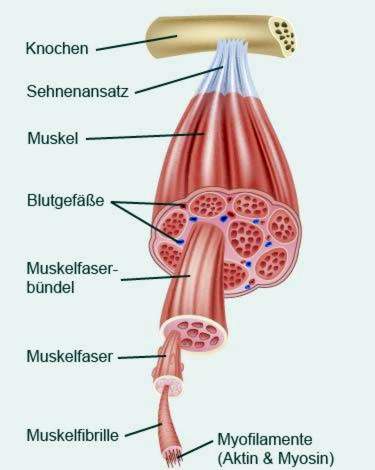
Muscle fibers can rupture as a result of a sudden overload of the muscle. Overloading means that a force is applied to the muscle that is greater than the strength of the muscle itself. Therefore, the muscle can not withstand this excessive force – tissue tears. This can happen, for example, with several long sprints, sudden stopping, quick changes of direction when the muscles are tired or untrained or extremely stressed. Depending on the extent of the resulting muscle damage one speaks of:
- Hamstring: One or (mostly) several fibers of a muscle tear. This often causes a hemorrhage (bruise) in the tissue. Particularly often a hamstring concerns femoral (quadriceps femoris muscle) and calf muscle (gastrocnemic muscle).
- Muscle bundles plan: In this form of muscle damage whole fiber bundles are injured.
- Muscle tear: The most serious consequence of muscle overload. In muscle rupture, the entire muscle is completely severed. He is then no longer functional.
If the acting force overloads the muscle only slightly, it is only stretched, but does not break. It creates a (also painful) muscle strain.
Injuries like a hamstring happen especially in sports – In fact, the hamstring is one of the most common sports injuries. Especially risky are sports that require sudden, rapid acceleration and stops. These include football, handball, tennis, squash and short-distance sprints. Even a direct trauma (such as a kick against the calf) can cause a torn muscle. Mostly, however, it arises without violence from the outside.
Risk factors for hamstring & Co.
Various factors favor a torn muscle, torn muscle, torn muscles or a simple strain. These include, for example:
- Tired or insufficiently warmed-up or distensible muscles
- disturbed coordination of movement
- muscular imbalance in extremities or spine
- Lack of training condition / lack of fitness
- unhealed previous injuries
- unfamiliar soil conditions
- cold weather
- wrong shoes
- Lack of fluids, vitamins, minerals and trace elements
- Infections (such as glandular fever)
- Intake of preparations for rapid muscle growth (anabolic steroids)
Muscular rupture: treatment
If a hamstring or a heavier muscle damage (muscle tear, muscle tear) should be as fast as possible First aid measures according to the PECH scheme be initiated:
- P like break: Stop physical activity, immobilize the injured limb.
- E like ice: Cool the injured area for ten to twenty minutes with an ice pack or a cold envelope.
- C likeCompression: Create a compression / compression bandage.
- H as high-altitude storage: The torn muscle often affects the upper arm, thigh or calf. The injured limb should be stored high, so that less blood flows into the injured tissue.
These measures are designed to stop bleeding into tissues, reduce pain and swelling, and prevent further damage. The tissue should be as possible do not warm and should not be massaged, Both can cause the hemorrhage to increase.
Muscular rupture: Therapy at the doctor
The doctor may have a torn muscle non-steroidal, anti-inflammatory analgesics (NSAIDs) like prescribe ibuprofen or diclofenac. A dosed physical therapy (Lymphatic drainage, cold therapy, etc.) can promote the regeneration of the injured muscle. Once the complaints go back, you should go with it physiotherapy kick off. Recommended are exercises that increasingly stress the affected muscle. Sometimes the therapist lays a special one Taping at the injured site.
Exercises to treat a hamstring should not cause pain!
One big bruise in the tissue may need to be punctured. The doctor introduces a hollow needle into the bruise so that the blood can either drain off by itself or be aspirated (drainage).
In a pronounced hamstring or in a muscle tear or a complete muscle tear may be surgery to be necessary. The torn muscle parts are sewn. The surgeon uses sutures that dissolve over time and are absorbed by the body.
Muscular rupture: examinations and diagnosis
If you suspect a torn muscle, you should go to the family doctor or a sports physician. He will first inquire about the complaints and the injury mechanism (Survey of the medical history = Anamnesis). Possible questions are:
- Where did the injury happen?
- How long ago was that?
- Where exactly do the complaints occur?
Then follows physical examination, The doctor examines the injured area for a possible muscle cell or swelling. He examines whether stretching and straining the muscle causes pain and whether the muscle has lost strength.
through Ultrasonic (Sonography) and if necessary magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI, Magnetic Resonance Imaging) supports the diagnosis of muscle fiber rupture. In addition, the doctor can detect possible bleeding into the tissue with the help of imaging techniques. If there is a suspicion that an additional bone has been injured, this can be checked by means of an x-ray examination.
Muscular rupture: course and prognosis
In a hamstring, there are generally no complications. The injury usually heals without consequences. However, the cure for a torn muscle fiber lasts: Depending on the severity of the injury you should no sports for two to six weeks do. In case of a muscle tear, a break of four to eight weeks is recommended. If you strain the muscle before the hamstring (muscle bundle rupture, muscle rupture) has healed, it easily causes a renewed injury (retraumatization).
Torn muscle: Prevention
You can reduce the risk of muscle injury from over-stressing by warming up before exercising and doing regular balance exercises / muscular exercises. If necessary, endangered muscles can be helped with a bandage or a tape bandage – this can possibly be one Hamstring prevent.