In case of tonsillitis (tonsillitis, tonsillitis) the palatine tonsils are inflamed. This is usually noticeable with sore throat and difficulty swallowing. Often you can treat an tonsillitis medication. Only if the almonds ignite very often, they are removed. Read all about symptoms, treatment and home remedies for tonsillitis!

Quick Overview
- Common symptoms: Sore throat, difficulty swallowing, red and tufts of palate, reddened pharyngeal wall, swollen lymph nodes
- Treatment: Home remedies (neck wrap, gargling, lozenges, etc.), antibiotics if necessary, surgery
- Special form: Chronic tonsillitis (recurrent tonsillitis)
- Contagion: high in the first few days, about droplet infection
- complications: Middle ear and sinusitis, earache, peritonsillar abscess, rheumatic fever, sepsis
Symptoms: This is how tonsillitis manifests
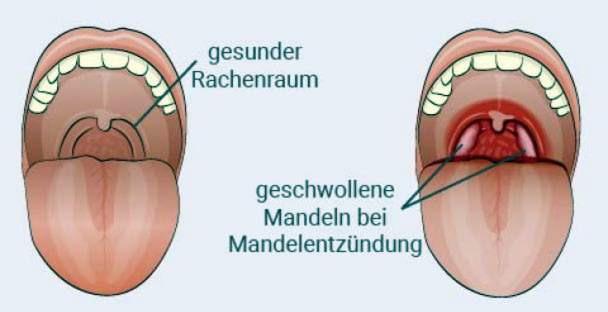
Symptoms of tonsillitis include sore throat and difficulty swallowing. Mostly they develop within a few hours. The palatine tonsils on both sides of the uvula are clearly reddened, swollen and whitish.
The pharyngeal wall is also red and the lymph nodes in the jaw angle are often palpably enlarged. This is accompanied by an unpleasant bad breath as another typical sign of tonsillitis. Often the patients feel weak and dull, often accompanied by a high fever. Almond inflammation without fever is also possible.
Differences between viral and bacterial tonsillitis
Mostly it is bacteria, especially streptococci, that cause tonsillitis. Pus on the tonsils – recognizable by white dots – is a typical sign of a bacterial infection. Coughing or runny nose, on the other hand, are not symptoms of bacterial tonsillitis, but rather indicate a rarer viral infection (usually caused by rhinoviruses, coronaviruses or adenoviruses).
For patients 15 years of age and older, a special criteria system (Centor Score) helps the doctor estimate the likelihood of streptococcal infection (more specifically, group A streptococci):
- Fever over 38 degrees
- no coughing
- swollen cervical lymph nodes
- proven palatine tonsils
When all four symptoms of tonsillitis occur, the disease was caused by streptococci in 50-60% of cases.
This score can only indicate a tendency, but can not make a diagnosis. Safety is just the analysis of an almond smear.
Tonsillitis as a symptom of other diseases
An tonsillitis is not just a disease. It can also be a symptom that accompanies other illnesses. Examples are:
- Pfeiffer’s glandular fever
- diphtheria
- Scarlet fever
- Herpangina
- Angina Plaut-Vincent
- Syphilis and gonorrhea
- Kawasaki disease
Tonsillitis in glandular fever: In about six percent of cases, tonsillitis occurs as a symptom of this viral disease. The tonsils are patchy and dirty occupied and the lymph nodes in the jaw angle, in the neck, neck and the groin area are often swollen.
Tonsillitis symptoms in diphtheria: Diphtheria is a dangerous bacterial infection, often accompanied by laryngitis or tonsillitis. The almonds are covered by a greyish-white coating. If you try to remove the pads, it usually bleeds. Those affected often have a sweetish bad breath.
Tonsillitis symptoms in scarlet fever: An tonsillitis in scarlet fever is expressed in deep red palate tonsils, which are covered with purulent specks. The pharyngeal wall is usually reddish. Small, whitish deposits may appear on the oral mucosa of the cheeks.
Tonsillitis symptoms in Herpangina: In tonsillitis caused by Coxsackie A virus (Herpangina), the tonsils are only slightly swollen. Small blisters (aphthae) on the palate and buccal mucosa form, which leave flat, painful defects after bursting. Fever, dysphagia and a distinct malaise are other symptoms.
Tonsillitis symptoms in Angina Plaut-Vincent: Angina Plaut-Vincent is a rare form of tonsillitis. Mostly only the almond is inflamed on one side, plus a bad breath. Patients with this condition usually have no fever and usually feel relatively healthy.
Tonsillitis symptoms in syphilis and gonorrhea: Syphilis (syphilis) is a sexually transmitted disease that occurs in multiple stages. In the second stage, tonsillitis sometimes develops. Symptoms of this so-called angina specifica are swollen, reddened tonsils with veil-like, gray-white coverings. Fever does not occur.
Also with the gonorrhea (Gonorrhea) – another sexually transmitted disease – it can among other things come to an almond inflammation.
Tonsillitis Symptoms of Kawasaki Syndrome: Kawasaki syndrome is an inflammatory vascular disease in children that can cause very different symptoms. One of them is tonsillitis.
Tonsillitis: treatment
Depending on the severity and frequency of the disease, different treatment strategies may be appropriate. Home remedies often help against mild sore throat. Conventional antibiotics are used in bacterial tonsillitis. Chronic or recurrent tonsillitis may require surgery.
If complications occur, such as a peritonsillar abscess (encapsulated inflammatory focus in the pharyngeal area), inpatient treatment in a hospital may be necessary.
Self-help with tonsillitis: What to do at home?
Not every throat infection needs to be treated by a doctor. Often mild tonsillitis develops as part of a cold. By resting and using home remedies, you can also do something about your tonsillitis yourself. For example, it can reduce the impact on the person
- neck wrap
- Salt solution for gargling
- damp room air
- adequate drinking (no acidic drinks, eg juice)
- preferably eat soft, cool, spicy foods
- Also, various herbal remedies can help with tonsillitis.
What else you can do at home and where the limits of home remedies for tonsillitis lie, read in the article Tonsillitis: home remedies.
Tonsillitis: When do you need to see a doctor?
Pain is the most annoying symptom of tonsillitis especially in the first few days. First, you can try to cure the pain with measures such as neck wraps or lozenges, special lozenges, sprays, and antiseptic and local anesthetic gargle solutions from the pharmacy.
If these measures are insufficient, the painkillers can paracetamol or ibuprofen relieve the symptoms. Both have pain-relieving (analgesic) and fever-reducing (antipyretic), ibuprofen also exerts an anti-inflammatory (anti-inflammatory) effect. You may only use these substances if you have no allergies to the active ingredients.
Painkillers only relieve the symptoms, they do not fight the pathogens.
If, despite calm and “gentle support”, the immune system does not succeed in eliminating the disease-causing viruses or bacteria, or if the tonsillitis is very severe, you should consult a doctor. He examines throat, mouth and usually also nose and ears with special devices. He can also do a quick test for streptococci.
For this the doctor uses a cotton swab to take a smear from various places in the throat, the result is available within a few minutes.
In some cases, the doctor will perform an ultrasound scan, for example, to rule out an abscess.
Medical treatment for bacterial tonsillitis
If the doctor is able to detect streptococcal tonsillitis or is very likely to do so, the doctor usually prescribes antibiotics, often of the type penicillin V.
Those who can not tolerate this drug will get other antibiotics (erythromycin, 1st generation cephalosporins) that also work well against streptococci. So-called reserve antibiotics (eg clindamycin) are only used when the pathogenic bacteria have become insensitive (resistant) to the standard active substances or the patient can not take the latter.
Each antibiotic therapy can produce resistant bacterial strains. Therefore, antibiotics should not be used prophylactically for tonsillitis, but only if actually bacteria are the trigger of inflammation.
Medical treatment for viral tonsillitis
Antibiotics only work against bacteria, so they are not used in viral infections. They are only required for viral tonsillitis if it has come on the diseased mucous membranes in addition to a bacterial infection (superinfection).
Caution should be exercised in the case of Pfeiffer’s glandular fever (caused by Epstein-Barr virus). Antibiotics amoxicillin and ampicillin can cause a skin rash and should not be used
The treatment of viral tonsillitis is therefore limited to the treatment of symptoms such as fever and pain. In addition to the painkillers mentioned above, home remedies and physical protection can accelerate the recovery process.
Especially with the Pfeiffer’s glandular fever, it is important to protect oneself physically. In this disease, namely, the internal organs can swell and there is a risk of a splenic rupture. This complication is life threatening and requires inpatient treatment in a hospital.
You should also seek medical help with tonsillitis in the following situations:
- morbid breath sounds
- difficult breath
- severe unilateral pain, especially if you chew, swallow or open your mouth
- Disease duration of more than a week without improvement
- acute rheumatic fever in the family
- severe general conditions
- high fever that can not be reduced with medication
Chronic tonsillitis: what to do?
Some patients get chronic tonsillitis. Unlike acute tonsillitis, almond tissue is repeatedly inflamed in chronic tonsillitis.
It can arise when germs “hide” or encapsulate in the hollows (crypts) of almonds. They can then not be combated by the immune system. Doctors refer to this form of recurrent tonsillitis as recurrent tonsillitis.
If the bacteria are spread over the bloodstream in the rest of the body, they can also cause or increase other diseases. Then an operative removal of the tonsils makes sense.
Read more about the symptoms and treatment of chronic tonsillitis in the article Chronic tonsillitis.
Tonsillitis: When to have surgery
If tonsillitis often occurs, the tonsils are usually completely removed. This so-called tonsillectomy is in this country one of the most commonly performed procedures.
Children benefit most from the procedure. For example, it has been proven that after almond removal, they are less likely to be missed in the classroom due to illness. Nevertheless, a throat infection can still occur after a tonsillectomy.
How a toillectomy is performed, which risks it holds and when it can be useful, you will learn in the article tonsillectomy.
Tonsillitis: treatment with homeopathy
With the question “What helps with tonsillitis?” Many patients turn to a naturopath. Alternative healing methods can also contribute to the symptoms of tonsillitis. Homeopathy is especially popular here. But it is not a substitute for a necessary conventional medical treatment.
Depending on the symptoms, for example, homeopathic remedies may become acute tonsillitis aconite, Belladonna, Apis or Pyrogenium recommended. Patients should seek advice from an experienced therapist or pharmacist.
Tonsillitis: where it comes from
Tonsillitis (tonsillitis) is an inflammation of the palatine tonsils, which sit right and left in the throat. It happens frequently. In total, over one million people in Germany suffer from it every year. Tonsillitis is especially common in children between the ages of six and twelve.
Often, those affected previously had a flu infection. This weakens the immune system, which bacteria or viruses can exploit – they attack the pharyngeal mucosa. Mostly bacteria of the type streptococci are the pathogens. The stabs or yellow-whitish deposits on the inflamed tonsils, which are typical for a bacterial tonsillitis, consist of dead bacteria and dead cells of the immune system. Mostly there is a one-sided tonsillitis. Bilateral tonsillitis is rarer.
In the so-called Angina Plaut-Vincenti several different bacteria are responsible for the inflammation. This form of tonsillitis occurs only in adulthood. It forms an ulcer on a pharyngeal site. The palatine tonsils are covered with a foul-smelling green-gray mucus. The palatine tonsils of the other side are often completely unremarkable.
The inflammation of the tonsils usually heals by itself. Sometimes drugs, especially antibiotics, have to be given to accelerate the healing process.
Tonsillitis: causes and risk factors
An tonsillitis can be triggered by various pathogens. These can easily settle on the ragged surface of the palatine tonsils. In principle, this is even good:
As part of the immune system, it is one of the tasks of the palatine tonsils to catch pathogens that have entered the pharynx and to prevent them from infecting the respiratory tract. The cells in the palatine tonsils produce very specific antibodies, which settle on the surface of the invading pathogens and thus make them harmless.
However, if the immune system has been unable to fend off a germ effectively, for example because it has been weakened by a flu infection, tonsillitis can develop.
Is tonsillitis contagious?
Since the pathogens are also found in saliva, the purulent tonsillitis is contagious. When the patients cough or sneeze, other people can become infected with germs via germ-containing droplets. Doctors speak of droplet infection.
Since the risk of infection with tonsillitis is particularly high in the first few days, you should avoid as possible contact with other people in this time.
If you take an antibiotic, the risk of infection can greatly reduce after just one day. If none is prescribed, for example in the case of viral tonsillitis, the infection is contagious for one to two weeks.
Unlike, for example, with chickenpox, one is not immune to a re-infection after tonsillitis.
Tonsillitis: examinations and diagnosis
Strong sore throat and dysphagia, fatigue and fever lead those affected often to the doctor. This will first ask a few questions about the course of the disease:
- Since when do you suffer from the complaints?
- Do you have fever?
- Do you have a rash?
- Do you suffer from shortness of breath?
- Do you experience pain when you chew, swallow or open your mouth?
- Has the tonsillitis re-emerged (acute tonsillitis) or suffer from recurrent tonsillitis (chronic tonsillitis)?
- Do you have abdominal pain?
Physical examination: Subsequently, the doctor checks whether the throat and palate tonsils redness, swelling or white plaque can be seen. He also feels the lymph nodes on the neck and back of the head. You may be swollen with tonsillitis.
The examination and the described complaints are usually enough for the doctor to diagnose “tonsillitis”.
Throat swab: If it is suspected that tonsillitis is caused by certain bacteria (group A beta-hemolytic streptococci, GABHS for short), the doctor will make a throat swab. For this purpose, he strokes with a cotton swab along the back wall of the pharynx to take a sample of the saliva there. With a rapid test or in the laboratory, any existing streptococci in saliva can be detected.
Blood test: Like the throat swab, a blood test is not routine in clarifying a tonsillitis, but only in individual cases necessary. For example, it is examined whether and which inflammatory levels in the blood are increased.
Tonsillitis: disease course and prognosis
The course of tonsillitis depends on many factors. These include the type of pathogen, the physical condition and resistance and climatic factors. Taking an antibiotic shortens the duration of the disease.
Tonsillitis: duration
Unless complications occur, symptoms usually resolve significantly within three to five days. After one to two weeks almost all patients are symptom free.
Complications of tonsillitis
Sports should be avoided in case of tonsillitis, since the immune system already requires a lot of energy for the fight against germs. Otherwise, tonsillitis may become chronic or cause complications. Because physical exertion also increases the risk that bacteria will be carried over the bloodstream to other organs.
In addition, complications often arise when antibiotic therapy has not been performed for a sufficient period of time.
Middle ear and sinusitis: Otitis and sinusitis are among the purulent complications of tonsillitis. They arise when the ventilation of the so-called Eustachian tube (connection of the throat to the middle ear) or the paranasal sinuses is prevented by the mucosal swelling.
Earache or pressure pain over the jaw and frontal sinus are typical symptoms.
peritonsillar: In tonsillitis with peritonsillar abscess, an inflammatory focus in the pharyngeal area encapsulates. Mostly, the pharyngeal wall then bulges inward on the affected side. Often sufferers also have severe sore throat and can only open the mouth minimally (jaw clamp). People who smoke during tonsillitis are more likely to develop an abscess.
Rheumatic fever: The rheumatic fever usually occurs three weeks after streptococcal tonsillitis. It is a type of autoimmune reaction triggered by cell components of streptococci. Mostly those affected get a fever again. In addition, a circular, reddish rash and painful arthritis may occur. The latter can last for many years if unfavorable.
In addition, in the course of rheumatic fever, a heart attack may develop. Affected is either the inner layer of the heart (endocarditis), the heart muscle (myocarditis) or the pericardium (pericarditis). These inflammations can cause the heart to stop beating evenly.
The acute rheumatic fever can also affect the nervous system and manifest as a so-called chorea minor. This disease appears several weeks to months after the onset of tonsillitis. Symptoms are instantaneous movements of the arms, pharynx and pharynx. These jerks occur suddenly and can not be controlled.
Renal cell inflammation (glomerulonephritis): This acute inflammation of the kidneys sometimes develops six to twelve days after the onset of tonsillitis. Signs is blood in the urine. Sometimes, however, these are only very small amounts of blood that are hardly visible to the naked eye, but can only be safely detected in the laboratory.
Sepsis: Sometimes bacteria get directly into the bloodstream. One speaks then of a blood poisoning or sepsis. Sepsis is a serious condition in which many body organs lose their ability to function.
Complications in children
Common complications of tonsillitis in childhood include otitis media (otitis media) and sinusitis (sinusitis). Sometimes, one to four weeks after streptococcal tonsillitis, rheumatic fever develops with joint inflammation, inflammation of the heart valves, the pericardium, or the heart muscle.
Streptococci can also cause kidney inflammation in children. In severe cases, the kidney may even fail completely. Most of the time, however, the children recover within a few days.
Complications in pregnancy
Pregnant women have a higher risk of tonsillitis. Pregnant women also have a greater risk of developing complications. Therefore pregnant women should be with one tonsillitis always consult a doctor. Responsible is an ENT doctor.
Additional information:
guidelines:
- Inflammatory diseases of the palatine tonsils / tonsillitis, therapy, valid until 31.12.2019