A hernia (inguinal hernia, inguinal hernia) occurs when layers of the abdominal wall break through the inguinal canal. A typical symptom is a palpable swelling, similar to a bump that can often be pushed inwards. Also pain can occur, which increase under stress. In most cases, the patients are male. A hernia in women or girls is less common. The therapy usually consists of surgery. Read more here: What is a hernia exactly? How can one recognize a hernia? How is he diagnosed and treated?
Inguinal hernia: short overview
- Important symptoms: visible and palpable swelling in the groin, pulling and possibly pain, which become stronger under stress
- Reason: Weakness in the abdominal wall (innate or acquired)
- Risk factors: severe pressure load (sneezing, coughing, pressing with defecation, lifting of heavy loads etc.), tissue weakness, diabetes mellitus, asthma, COPD, cystic fibrosis (cystic fibrosis)
- complications: entrapment
- Treatment: usually surgery. In men with a hernia that shows no symptoms and does not increase, it is also possible to wait and see the hernia.
Inguinal hernia: symptoms
Even if the term suggests otherwise: In a hernia (inguinal hernia) no bone is broken, but it is pierced tissue in the groin – the so-called inguinal canal. This tubular connection between the abdominal cavity and the outer pubic region draws obliquely from back to front. In this channel run blood and lymph vessels and the spermatic cord in the man and one of the mother tapes in the woman.
If this inguinal canal is punctured by a hernia, this can be recognized by a visible and / or palpable swelling in the grointhat can often be pushed inwards. Sometimes the genital region is also affected by inguinal hernia: In the case of a woman, the swelling can then occur in the area of the labia, in the man on the scrotum.
In most cases, the inguinal hernia symptoms (woman & man) are on the right side.
Inguinal hernia: pain
In many cases, the inguinal hernia causes no pain. Those affected report more of an indefinite feeling of pressure or a pulling, sometimes of abdominal pain or a foreign body sensation in the groin.
If inguinal hernias occur, they can drag into the testicles or labia. Increases the abdominal pressure, for example, when coughing or lifting loads, the complaints increase. At rest and while lying on the inguinal hernia symptoms. So if someone is more in pain lying down / at night, it is usually not a hernia. Instead, for example, a hip joint or muscle disease behind it.
Both pain and swelling increase during exercise. In the case of particularly intense inguinal hernia signs, tissue may already be trapped. Then you should immediately go to the doctor!
Inguinal hernia symptoms in children
Recognizing a hernia in children is not always easy. Often, parents accidentally discover visible swelling in the groin or genital area as they bathe, dress or undress their child. When pushing on the child reacts sensitively. Other signs of a hernia in children may be:
- Tearfulness or seemingly groundless crying (especially by baby and toddler)
- Refusal to eat
- great restlessness
Pinched hernia: warning symptoms!
In rare cases, inguinal hernias (such as bowel loops) are trapped in a hernia. These are then no longer sufficiently supplied with blood and can die off. The symptoms of a hernia with entrapment are much more intense, for example:
- strong pain
- Redness of the site
- Nausea and vomiting
If someone shows such symptoms, one must immediately alert a doctor. It threatens a bowel obstruction and a life-threatening peritonitis!
Severe pain in a hernia is a symptom of there are (dangerous) complications. Go to the doctor immediately!
Inguinal hernia: causes and risk factors
The abdomen is largely closed and lined with a fine skin, the peritoneum. It houses organs such as the stomach, liver and intestine. Gravity pulls the organs down. The abdominal wall holds her in position. But especially in the lower abdominal area there is still a certain pressure.
This pressure is also felt by the inguinal canal. Especially when lifting heavy loads, sneezing, coughing or pressing (such as when defecating), the abdominal organs press on the inguinal canal. Normally, he can withstand the strain – thanks to the powerful muscles, ligaments and tight connective tissue surrounding him.
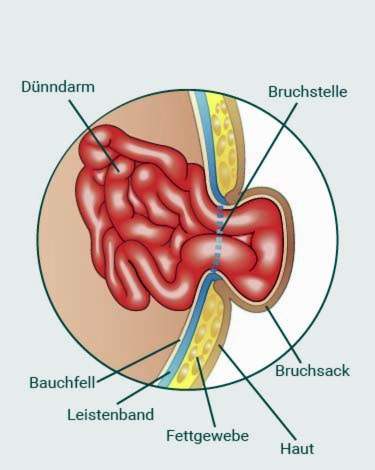
But if the pressure becomes too great, a gap in the inguinal tissue (hernial): The peritoneum bulges at this point baggy outward. That is why one speaks of one sac, Sometimes also entrails occur (usually parts of the intestine) – enclosed by the fracture sac- through the gap and out of the abdomen (breaking content).
Indirect and direct inguinal hernia
Most patients have one indirect inguinal hernia: Here, the hernia sac occurs laterally through the inguinal canal and can penetrate to the scrotum or labia.
The indirect inguinal hernia is innate in most cases: it is then based on an incompletely closed inguinal canal. Normally, the inguinal canal is lined by the peritoneum until it returns to birth and usually closes completely until the end of the first year of life. If this does not happen, often a congenital indirect inguinal hernia arises. Babies, children and young people are the most affected, boys more often than girls.
Rarely, an indirect hernia develops later in life (acquired indirect inguinal hernia).
In contrast, the direct inguinal hernia always purchased. It arises from a weak spot in the wall of the inguinal canal. The fractured bag pushes directly through the abdominal wall, so it does not reach the genital region. Various factors can favor this wall weakness and thus the direct inguinal hernia (such as surgery or various diseases: see below). Mostly, adults develop this form of inguinal hernia. Women are relatively rarely affected. As a rule, the patients are older men.
risk factors
There are several factors that favor inguinal hernia, such as those associated with tissue weakness (such as Marfan syndrome) or increased abdominal pressure (such as constipation or constant coughing in heavy smokers or COPD). These risk factors for inguinal hernia include:
- Diverticulosis (protuberance of the intestinal wall)
- Varicose veins
- Marfan syndrome (genetic connective tissue disease)
- Diabetes (diabetes mellitus)
- asthma
- COPD
- cystic fibrosis (cystic fibrosis)
- overweight
- Smoke
- Malformations of the urinary tract and genitals
In children it can be through umbilical hernia (Omphalocele) or one prolapse (Gastroschisis) come to an increased pressure in the abdomen. The possible consequence of this is a hernia. In the pregnancy weight bearing in the groin can cause a hernia. Children who as premature birth were also more susceptible to inguinal hernia.
In addition, the hernia occurs frequently in some families. This suggests that the Gene to play a role.
Inguinal hernia: examinations and diagnosis
If a hernia is suspected, go quickly to the doctor. The first point of contact can be the family doctor or pediatrician. However, a inguinal hernia is usually treated by specialized surgeons.
First, the doctor will raise the medical history in the so-called anamnesis interview. For example, he can ask the following questions:
- What complaints do you have?
- Where exactly do you feel pain?
- Will the symptoms get worse under stress?
- Has anyone in your family ever had a hernia?
- Have you ever been operated on the abdomen or in the groin area?
Physical examination
In the physical exam, the doctor first asks the patient to stand straight. He then scans the groin region of the patient to detect any swelling. He may also instruct the patient to cough or contract the abdominal muscles, increasing abdominal pressure. This usually increases swelling in a hernia. The palpation examination can be repeated by the doctor while the patient is lying down.
It also checks whether the contents of the inguinal hernia can be pushed back into the abdomen with the fingers. If that works, there is a so-called repulsive inguinal hernia in front. If the doctor can push back the fracture contents but not the correct position, the hernia is broken irreducible.
To clarify a suspected inguinal hernia, a rectal examination may be necessary. The doctor scans the last piece of the rectum with a finger.
The typical swelling in the inguinal region is often enough for the doctor to diagnose the inguinal hernia.
ultrasound
If the physical examination is not sufficient to diagnose a hernia clearly, the doctor can examine the groin by means of ultrasound (lying and standing). So you can also judge how pronounced the inguinal hernia is and how urgent it must be treated. Especially in patients with severe overweight (obesity), an ultrasound examination or even magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may be necessary.
Exclusion of other diseases
Sometimes other illnesses can be behind a supposed inguinal hernia. These so-called differential diagnoses include, for example enlarged lymph nodes: They can cause swelling similar to that of a hernia.
Especially in athletes, a suspected inguinal hernia often turns out to be so-called soft bar (Sportsman or footballer bar). As in the case of a hernia, those affected have groin pain, which often intensifies when coughing, sneezing or squeezing. The sporting activity (sprinting, shooting balls and the inside of the foot, etc.) can overload the muscles and tendons in the groin and the inguinal canal and lead to small injuries – a soft groin arises.
Also at one hydrocele (Hydrocele) creates a bump. However, it is a bulge-elastic bulge in the course of the spermatic cord, which can not be moved. In ultrasound, the water break is usually clearly recognizable as a kind of sphere.
Sometimes, a suspected inguinal hernia in the male (boy) actually turns out to be testicles in the groin (Undescended testicles).
When is a hernia an emergency?
A inguinal hernia is an emergency, though severe pain with nausea and vomiting occur. Toddlers scream in this situation seemingly without reason, refuse the food and are very restless. Only later does the abdomen look distended, tender and bulging. In this case, you must immediately inform a doctor!
General information on inguinal hernia treatment
One Inguinal hernia in children must be treated medically, because the inguinal hernia does not heal by itself. In addition, there is always the danger that stomach tissue is trapped.
One Inguinal hernia in the woman should always be operated on, according to the guideline of the European Hernia Society (EHS), even if it does not cause any complaints. In fact, there could also be a femoral hernia (femoral hernia, femoral hernia) – in addition to or instead of inguinal hernia. A femoral hernia can also cause pain and possibly swelling in the groin, but is often difficult to identify clearly. The danger with her is that she leads in up to 30 percent of cases to entrapment. As women suffer leg fracture much more frequently than men, a (supposed) inguinal hernia is always operated on.
a Inguinal hernia in the man, which shows no symptoms and does not progress (that is, does not enlarge), you have also always operated on. The reason was the risk of entrapment. However, this risk is low according to a new study. That is why experts now recommend watchful waiting for such patients (wait and see).
Some people who have ever had an inguinal hernia Op, later get a new inguinal hernia (Rezidivleistenhernie). Doctors then decide on a case by case basis and type of reoperation.
In all inguinal hernia patients – if viscera are trapped, must be operated on immediately!
Hernia surgery
Inguinal hernia surgery is one of the routine procedures. Various Op techniques are used. One differentiates between:
- open procedures: Here the doctor sets a larger incision and shifts the fracture content back into the abdomen. Usually either a synthetic net is used or connective tissue and muscles are used to prevent a relapse.
- minimally invasive procedures: These surgical techniques come with several small cuts. Mostly a network for stabilization is inserted. The relapse rates are higher here, but the pain is often not as persistent as after open surgery.
Which method is most suitable in a particular case, the doctor will decide from case to case.
Read more about the course of an inguinal hernia operation and the possible complications in the article inguinal hernia – OP.
Inguinal hernia: disease course and prognosis
Most inguinal hernias are harmless. It can be trapped at any time gut tissue. Doctors are talking about incarceration here. The patient must then be operated on within a few hours, because a pinched loop threatens intestinal obstruction. The intestinal wall can also break open so that the contents (faeces) escape. Then a life-threatening peritonitis (peritonitis) may develop.
Depending on the location of the inguinal hernia can also interrupt the blood supply to the testicles or ovaries. Without treatment, the reproductive organs are damaged.
The inguinal hernia operations are without complications in most patients. Sometimes it comes later to a relapse (recurrence), that is: It forms a new one hernia.
Additional information:
guidelines:
- S1 guideline “inguinal hernia, hydrocele” of the German Society of Pediatric Surgery (as of 2014, validity extended until 29.09.2019)