Gout is a metabolic disorder that primarily causes painful inflammation in the joints. Cause is too much uric acid in the blood, which deposits in crystal form in the artificial skin. Through a consistent change in diet and other lifestyle factors but the uric acid level can be controlled. Read here what you can do if you suffer from gout, and learn all about gout.

Gout: Short overview
- Causes: Mostly innate, sometimes also acquired predisposition to increased uric acid levels. In combination with an unfavorable lifestyle gout attacks occur.
- Adapt diet: Reduce purine-rich foods (meat, offal, certain types of fish), high-fructose drinks, alcohol, especially beer, severely restrict
- Typical symptoms: Painful, sometimes swollen, reddened joints. The big toe is especially often affected by gout. Later also movement restrictions deformations.
- Tests / diagnosis: increased uric acid level, in later stages joint damage, kidney damage
- Therapy: Lifestyle changes, uric acid lowering drugs, physiotherapy, removal of nodular uric acid deposits, correction of deformed joints
This is how gout develops
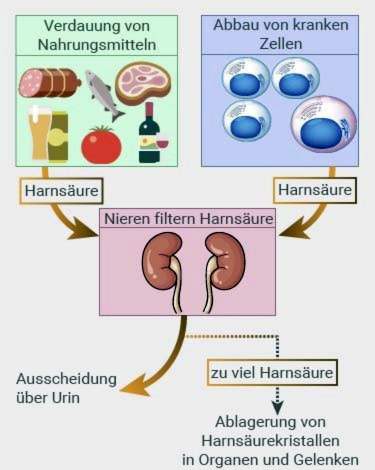
In gout, the uric acid level in the blood is too high. Either because too much of it is produced or because the kidneys are not getting enough out of it. It form tiny uric acid crystals, which are deposited in particular in the joints. At particularly high levels an acute gout attack with pain, redness and swelling threatens.
The uric acid is formed during the breakdown of purines. Purines are breakdown products that form when the body breaks down diseased cells. But they are also taken with food, especially meat and offal, but also some vegetables.
Primary gout – congenital disorder
Most gout patients suffer from a congenital metabolic disorder. Physicians then speak of a “primary hyperuricemia” or “primary gout”. In most cases, the kidneys do not excrete enough uric acid.
In rare cases, the body produces so much uric acid that the kidneys are overwhelmed. The cause is a genetic defect, the so-called Lesch-Nyhan syndrome. It occurs mostly in boys.
Secondary gout-acquired disorder
In a so-called secondary gout other diseases cause the excess of uric acid. In leukemia, for example, endogenous cells are destroyed in large numbers. It releases large amounts of purines that accumulate in the blood.
Other diseases that cause increased production of uric acid
- some tumors
- Anemia
- certain medications (cytostatics)
- Radiation in the context of cancer therapy
Conversely, the uric acid level also increases if not enough uric acid is excreted. This is the case with kidney disease or with an untreated or insufficiently adjusted diabetes.
Prosperity Gout
Gout is considered a disease of affluence. It is more widespread in developed countries than in poorer countries. The factors that favor gout include obesity, a diet rich in meat, fructose and alcohol as well as a lack of exercise.
Trigger for an acute gout attack
An acute attack of gout occurs when the uric acid level exceeds a certain level. The main triggers are:
- excessive consumption purine-rich foods like meat and offal.
- excessive enjoyment fructose-rich foods like sweetened fruit juices.
- too much alcoholAlcohol also increases uric acid levels. This is particularly true for beer, which is also particularly rich in purine
- strict diets: In order to gain energy, the body breaks down muscles during strict diets. It is released ample purines.
- physical overexertion: This causes lactic acid in the body, which is excreted by the kidneys and thus blocks the uric acid degradation.
- diuretic or laxativeThey thicken the blood when used excessively or for a long time. This increases the uric acid concentration.
How long does a gout attack last?
Duration of gout attack can last for days or even weeks. Then the symptoms slowly fade away. Fast, targeted treatment significantly reduces the duration of gout attacks.
Gout: treatment
A gout treatment should reduce the excess of uric acid in the blood to a healthy level. Physicians recommend 5.5 to 6.4 milligrams per 100 milliliters of blood as upper limits.
Gout: What you can do yourself
Much can be achieved through a changed lifestyle, especially through an adapted diet. If this is not enough for gout therapy, medications can additionally lower the uric acid level.
Diet in gout
To reduce the uric acid level, sufferers can contribute a lot themselves. Here, the conversion of nutrition plays a crucial role:
Purine-rich foods only in small portions: Purines are among other things contained in the genetic material of all living cells. When it breaks down, it produces uric acid. This applies to the obsolete own cells as well as to the food. The purin-rich foods include meat (especially offal), sausage, seafood and certain fish species. Luscious food can lead to an acute gout attack if it is predisposed to gout.
As little alcohol as possible: Excessive consumption of alcohol is particularly problematic in gout. Its breakdown products are excreted by the kidneys and thereby make the uric acid competition. For example, alcohol slows down the breakdown of uric acid and raises its level. Even if you exceptionally consume alcohol once again, it can provoke a gout attack. Particularly critical is beer. In addition to alcohol, it also contains a lot of purine.
Caution with fructose: Fructose is not just in fruits. It is also used to sweeten juices of yogurt or other foods. The breakdown of fructose in the body enhances purine formation. At the same time, sugar, like alcohol, inhibits the excretion of uric acid via the kidneys.
Save fat: Also too much fat inhibits the excretion of uric acid. Gout patients should therefore eat as little as possible high-fat foods. If possible, you should not cover more than 30 percent of your daily calorie intake with fat. This limit is reached quickly, because fat has the highest energy density of all nutrients.
Pay particular attention to hidden food fats, for example in sausages or finished products.
If you want to know more about how you should eat the best with gout, read here the text gout – nutrition.
What you can do yourself
Reduce overweight: Body mass index over 25 should decrease body weight. If you weigh less, your uric acid level will drop automatically. But watch out: The weight loss should be slow and controlled. Severe fasting can trigger an acute gout attack!
Do you drink much: Nutritionists recommend drinking at least two liters a day, preferably bottled water or unsweetened tea. The fluid in the body helps keep the uric acid concentration low and supports the kidney’s filtering function. In addition, uric acid is flushed out and the uric acid level is lowered.
Move, but do not exaggerate: Exercise has a positive effect on the gout joints. The function improves and inflammatory symptoms sound faster. However, you should not overdo it with gout – the resulting lactic acid slows down the breakdown of uric acid via the kidneys.
However, gout can not be cured with medication. Once the medications are discontinued, their influence on the uric acid level is lost and this increases again.
Recommended is the Intake of uric acid for example in the following cases:
- at uric acid levels above nine milligrams per deciliter of blood serum
- with a family history of gout and elevated uric acid levels
- in joint gout
- in the presence of kidney stones
- in chronic gout
Drugs for uric acid reduction
Uric acid can be reduced in two ways: either by excreting it more or by reducing its production. At the beginning of a gout treatment usually both classes of uric acid suppressants are prescribed. For the long-term treatment of gout, agents are used that block production.
Uricosuric – increased uric acid excretion
Uricosuric drugs cause more uric acid is excreted. For example, benzbromaron belongs to this group. The gout treatment with uricosuric begins in small doses, as larger doses could provoke a gout attack. It is important that patients drink more than two liters a day.
Uricostatic drugs – reduced formation of uric acid
Uricostatic agents contain the active substance allopurinol. It inhibits an enzyme that is necessary for the last step of uric acid formation. As a result, the precursors of uric acid are increasingly present in the blood. However, these are more soluble in water and are therefore excreted more easily than the uric acid itself. Treatment with uricostatic agents can even dissolve already formed deposits of uric acid crystals. So-called gout tophi and kidney stones are ideally formed.
What to do with a gout attack?
Long-term gout therapy is unsuitable for acute attacks of gout. This is mainly about alleviating complaints such as pain as quickly as possible. Particularly effective help with gout provide anti-inflammatory analgesics.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are the first drug of choice in acute gout treatment. They do not contain cortisone. Gouty patients are mainly prescribed indomethacin and diclofenac. As a rule, the symptoms improve within a few hours.
Cortisone therapy: If NSAIDs are not enough, cortisol-containing glucocorticoids are used, for example prednisolone. If larger joints such as the knee are affected by gout, the doctor can inject cortisone directly. For smaller joints, cortisone is given in tablet form. The cortisone preparations should not be taken for more than a few days.
Renal impairment is immediately treated with cortisone. A gout attack therapy with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs is then not possible.
colchicine: In the past, gout was often treated with colchicine. Today it is hardly prescribed because of its side effects such as diarrhea, nausea and vomiting. It must not be taken during pregnancy. Even men who want to father a child in the near future should refrain from doing so.
No self-treatment with painkillers!
Self-treatment with over-the-counter painkillers is risky. For example, acetylsalicylic acid can increase uric acid levels significantly. Even with a symptom-free gouty patient, she can trigger an acute seizure. A gout treatment should never be done by yourself, but always in consultation with a doctor.
Therapy even with no complaints
In order to avoid secondary diseases, a consistent therapy for gout is crucial. The German Society of Rheumatology recommends a uric acid-lowering therapy for at least five years. If tophi have already formed, then five years after their dissolution should be treated further.
Surgery for gout
If some joints are already severely damaged, they have the option of replacing them with artificial joints. Such an intervention is stationary. After the operation a stay of a few days in the hospital is necessary.
This is followed by exercise and occupational therapy to help patients learn to handle the new joint. A new joint can cause severe pain at the beginning. As a rule, however, this procedure is more painless than continuing to live with the broken joint.
Gitttophi can also be surgically removed. The small nodular thickenings of the skin form above all above the joints and at the ear cartilage. Although they are harmless, patients often find them a cosmetic problem. For surgical removal only local anesthesia is necessary. In isolated cases, small scars may be formed at the sites where the tophi were removed. As a rule, they can be removed completely.
Physical gout treatment
A physical gout therapy aims to reduce existing discomfort and reduce pain. In addition, they should prevent joint damage and misalignments in the case of a long-standing gout.
- Heat and cold treatments can reduce gout pain in the joints.
- Procedures for muscle relaxation reduce pain.
- Physiotherapy strengthens the muscles and relieves the joints.
- Physiotherapy and occupational therapy prevent or restrict the movement restrictions and deformities of the joints.
Gout: homeopathy
Many sufferers swear by the question “What helps against gout?” On homeopathic remedies. However, the efficacy of homeopathic medicines has not been proven. But if you are convinced of it, you can use it for therapy. However, you should not renounce a lifestyle change or conventional medicine if necessary. Homeopathic gout remedies are:
- Bryonia: recommended especially for acute pain and general relaxation of the mental state.
- Colchicum: used for nausea and general malaise.
- Ledum: is used when cooling applications improve the pain.
- Lycopodium: is also used in acute pain and a restless general condition.
- Belladonna: is said to be effective against severe pain and fever.
Gout: home remedies
In case of a gout attack, the following home remedies can be a useful supplement:
Protect joints: Keep the affected joint steady. Do not stress it until you have no complaints. You may even need bed rest.
Cool joints: In addition, pain in the affected joints can be relieved with cooling envelopes. This is enough even a towel that has been soaked in cold water. Alternatively, you can cool aching joints with quark wrap. Quark keeps the cold longer than a wet cloth.
Ice packs, on the other hand, are too cold and can quickly cause skin damage. Cooling should not take longer than ten minutes at a time, but several times a day.
Warm joints: Conversely, heat can also relieve the pain, for example, by baths in warm water. This relaxes muscles and joints and reduces pain. As a bath additive hay flowers or chamomile flowers are recommended as gout attack home remedies.
To drink tea: Good against gout is drinking tea. He washes the uric acid out of his body. Often, special teas such as linseed tea, birch leaves or infusion with a clove of garlic are recommended. The basis of the effect of tea, however, is that it is diuretic.
Gout: symptoms
The most common symptoms of gout are severe pain in the joints. They first appear like an attack. If a gout remains untreated, the symptoms gradually worsen and the gout becomes chronic.
Gout symptoms after stages
Over the course of years or even decades, the first symptoms appear. How they become noticeable depends on the stage of the disease.
Stage I gout symptoms: hyperuricemia
In the first stage, only the uric acid level is increased. In a healthy person, it is three to six milligrams per 100 milliliters of blood serum. From a value of 6.5 milligrams per 100 milliliters of blood serum, doctors speak of a hyperuricemia.
A slightly elevated uric acid level can be present for several years without causing discomfort. First signs of gout are then kidney semolina, kidney stones or an acute gout attack (stage II). The risk of a gout attack is greater, the higher the uric acid level rises.
Stage II gout symptoms: Acute gout
If the uric acid level exceeds a certain level, an acute attack of gout occurs. Symptoms are severe pain in individual joints.
Most commonly, the metatarsophalangeal joint of the big toe is affected, as well as other joints of the legs and feet. Less often it hits hands and arms. If left untreated, a gout attack takes a few hours to a few days. Thereafter, the symptoms slowly fade away.
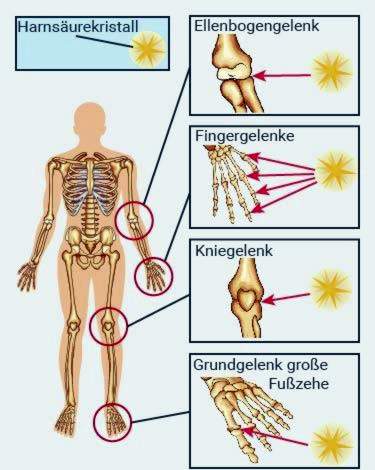
In more severe cases, additional inflammatory symptoms occur. The affected joints are then reddened, swollen and warmer than usual. In addition, they are usually extremely sensitive to touch. The skin over the joint may itch or peel. Doctors call this arthritis urica.
Other possible symptoms in stage II:
- fever
- a headache
- heartbeat
- Nausea and vomiting
- Weakness and limited efficiency
The first gout attack usually comes at night. If left untreated, the seizure may last for several days and up to two weeks. Then the gout symptoms slowly fade away. Treated in time, the gout attack duration can be shortened.
Repeated gout attacks make the mobility of affected joints increasingly worse. Walking and grasping are harder for the patient.
Stage III Gout Symptoms: Intercritical Phase
As an intercritical phase, doctors refer to the period between two gout attacks. If left untreated, the symptoms of gout occur again and again at irregular intervals. During the intercritical phase, the patients are initially symptom-free, but their uric acid levels are still elevated.
Stage IV gout symptoms: Chronic gout
If the gout continues to progress, symptoms such as pain and restricted mobility also occur between attacks: the gout becomes chronic.
Joint-gout: In a chronic course, more and more uric acid crystals are deposited in the joints. They are then permanently reddened and swollen and hurt even in peace. Finally, joint changes occur that deform the joint and restrict its mobility. Such changes can not be reversed with medication.
Soft-gout: The uric acid crystals are also deposited in other body tissues. Under the skin, for example, on the ear cartilage, or above the affected joints, sometimes small hard Gewebeknötchen with white spots, so-called Gelenktophi form. Especially often the soft tissue gout affects fingers and feet. The internal organs are also affected, especially the kidneys.
Renal gout: Uric acid crystals also accumulate in the kidneys. They first form tiny stones called kidney semolina. Clumps this together, resulting in larger kidney stones. They can severely impair kidney function. Clog the drainage system of the kidney, jams the urine back into the kidney. The organ can then ignite and eventually fail. In 40 percent of cases, the kidney is even affected by gout before the first seizure occurs.
Gout: examinations and diagnosis
If gout is suspected, the family doctor or a doctor for internal medicine, ie an internist, is the right contact person. In an anamnesis interview, he records your medical history and asks you about your complaints. Afterwards he will ask several questions, for example:
- Have you ever had similar complaints in the past?
- Do you have relatives with similar complaints?
- What does your diet look like?
- Do you drink alcohol?
- Do the symptoms occur permanently or seizure-wise?
Physical examination
After the anamnesis, a physical examination takes place. The doctor scans the joints, the abdomen and the lower abdominal organs in order to localize pressure sensitivities or pain. Under certain circumstances, he discovers nodular tissue changes over the joints (so-called gouty typhus), which are typical for gout.
With exercise tests, the doctor can determine movement restrictions of the joints. In particular, an attack of gout in the foot must also be differentiated from other injuries such as sports injuries or kinking.
uric acid levels
With a blood test, among other things, an elevated uric acid level can be determined. In a healthy human, the uric acid levels are between three and six milligrams per 100 milliliters of blood serum. Values above 6.5 milligrams per 100 milliliters of blood serum are called hyperuricemia.
After an acute attack of gout, the concentration of uric acid drops back to normal. Therefore, gout can not be safely excluded, even if the values are normal.
Inflammation marker in the blood
Certain inflammatory markers in the blood provide further evidence of gout. This includes
- increased value of the C-reactive protein (CRP value)
- increased white blood cells (leucocytes)
- increased blood cell lowering rate (ESR)
To ensure the diagnosis of gout, a sample of synovial fluid is also examined. If it is possible to detect uric acid crystals, it is most likely gout.
X-ray and ultrasound examinations
Using X-rays, the doctor can determine what damage caused the gout at the joints. In addition, an ultrasound is sometimes performed. An X-ray examination with contrast agents can clarify whether the kidneys were damaged by the disease.
Kidney function test
With a kidney function test can be determined whether and if so how much the performance of the kidneys is impaired.
Gout: Disease course and prognosis
Most cases of gout occur for the first time between the age of 40 and 60. About two percent of the adult population in industrialized countries suffer from gout. Men are affected much more frequently than women.
The predisposition for elevated uric acid levels is usually innate and therefore not curable. Through consistent therapy, however, the uric acid level can often be lowered permanently. The danger of an acute gout attack is not banned, but significantly reduced.
Prognosis in acute gout attack
If the uric acid level exceeds a certain level, an acute attack of gout occurs. If left untreated, it will last for several hours to a few days. Thereafter, the symptoms slowly fade away. After a gout attack, some time (even months to years) may pass before the next gout attack occurs. Duration of gout attacks as well as the periods in between vary individually strongly.
Gout: long-term prognosis
The course of the disease and the prognosis depend on how pronounced a high uric acid level is and how consistently a patient takes his uric acid-lowering medication or how well he implements a urate-lowering lifestyle. This includes above all a purine, fructose and low-alcohol diet.
No break from therapy
Between two attacks of gout, there may be long periods of time during which patients have no symptoms. Even in these “intercritical phases”, it is important to continue the therapy. If it is interrupted, the symptom-free sections shorten. Increasingly, symptoms such as pain and restricted mobility occur during the periods between two attacks of gout.
Permanent joint changes
Once incurred damage to the joints do not form back. They can cause permanent pain or loss of exercise. In severe cases, the joints can also deform. Pronounced joint damage caused by gout is called arthritis urica.
Kidney damage and kidney stones
A long time untreated gout can also cause various sequelae, especially the kidney. Common complications of gout are kidney stones. They close the drainage channels of the kidney and the urine builds up. This is usually followed by an inflammatory reaction. As a result, and by the progressive accumulation of uric acids, the kidneys may eventually fail. Doctors speak of a gout kidney. In order to prevent such damage, the treatment of gout should be consistent as early as possible and also in the long term.
Chronic gout
Chronic gout develops relatively rarely today. Patients suffer permanent pain. Unlike an acute attack of gout, they do not sound anymore. Chronic gout develops primarily when there is hyperuricaemia for a long time which is not treated. As a rule, chronic gout is more likely to affect older than younger people.
Additional information
Books
Sven-David Müller: Gout Traffic Light, Trias, April 27, 2016
Edeltraut Hund-Wissner: Delicious food at Gicht: Over 130 recipes: Finally low uric acid levels Trias, October 21, 2015
guidelines
DGRh Guideline: Long version of the S2e guideline Gouty arthritis (specialist), Evidence-based guideline of the German Society of Rheumatology (DGRh), 08/2016
DEGAM guideline: Frequent gout attacks and chronic gout in primary care, 09/2013
society
German Gout League e.V.