Bursitis (bursitis) usually develops after excessive exercise. Characteristic are sudden onset, severe pain, which usually occur the first night after the overload. Sometimes the bursitis is based instead on a bacterial infection or other disease. Also, wear and chronic overload can cause bursitis. Read more about the forms, causes, treatment, diagnosis and course of bursitis.
Quick Overview
- Description: Painful, acute or chronic inflammation of a bursa. Bursae are fluid-filled tissue bags that protect joints, muscles, tendons and ligaments from movement-induced friction and pressure. The inflammation often affects the bursae of large joints such as shoulder, elbow, knee and hip.
- Causes: mostly overload due to unfamiliar, power-intensive, repetitive movements. Other possible causes: age-related wear, underlying diseases such as rheumatism or gout, bacterial infection. Certain professional groups such as tilers, musicians and athletes are particularly often affected by bursitis.
- Diagnosis: Doctor-patient interview to collect the medical history (anamnesis), physical examination, possibly blood test, tissue sample, imaging (ultrasound, X-ray, magnetic resonance imaging = MRI).
- Treatment: Immobilization of the affected joint, analgesics, cortisone, if necessary, shock wave therapy, aspiration for suction of excess fluid, physiotherapy. For bacterial bursitis: often surgical removal of the bursa, antibiotics. In case of bursitis due to an underlying disease: targeted treatment of the underlying disease.
- Forecast: Mostly fast recovery, when the affected joint is immobilized. On further overload danger of chronicity with persistent, recurring complaints.
Bursitis: Description
Bursitis (Bursitis) is an acute or chronic inflammation of a bursa. There are about 160 bursae in the human body. The several centimeters long, filled with fluid tissue cushions are found mainly in the joints. But bursae are also located where skin, muscles, tendons or ligaments lie directly over a bone protrusion – for example, in the area of the large rolling hill (bony prominence on the outside of the thighbone). Like a cushion between muscles, bones, tendons, and ligaments, bursae cushion the friction and pressure on these elements that arise when they move.
Normally, bursae are rather shallow and not completely filled with fluid. Ignite, however, swell and squeeze painfully on the surrounding body structures.
A acute bursitis is usually the result of overloading. If you do not treat them properly or eliminate the cause, they can become chronic. A chronic bursitis can also be the result of an underlying condition such as rheumatism. Then intermediate walls of connective tissue can develop in the bursa (Schleimbeutelhygrom). Besides, it can lime to deposit in it.
Frequent forms of bursitis
Theoretically, every bursa can catch fire. In practice, however, the most common forms of bursitis are observed:
- Bursitis in the shoulder joint: subacromial bursitis and subdeltoid bursitis
- Bursitis in the elbow joint: Bursitis olecrani
- Bursitis on the hip: bursitis trochanterica
- Bursitis on the knee: Bursitis preppatellaris and infrapatellar bursitis
- Bursitis in the ankle joint: subacute bursitis
Symptoms of bursitis
Bursitis is always painful, In addition, the affected area is swollen, often reddened and warmed and is very sensitive to touch. In a bursitis near the joint, the affected joint is only limited mobility.
Bacteritis caused by bacteria is often accompanied by fever and general malaise.
So that the bacterial infection does not spread, it should be treated immediately.
Bursitis: causes
A bursitis usually arises through overload involved structures (joint, muscles, tendons, ligaments). This may be the case with unfamiliar, recurring movements. Sometimes bursitis also develops age-related wear or one underlying disease like rheumatism. Rarely is one bacterial infection the cause of bursitis. Of these, men are slightly more affected than women.
Bursitis caused by overuse
Bursae act as a buffer between joints, muscles, tendons and ligaments, protecting them from pressure and allowing a smooth movement. If this function is overstressed by unfamiliar, vigorous and repetitive movements, the bursa may react with inflammation.
For example, hobby runners often contract bursitis on the heel, knee or hip. Typical is about the Bursitis subachillea, the inflammation of a bursa on the Achilles tendon. This can later extend to the Achilles tendon and become one in the long term Achilles tendon injury to lead. The affected foot is then not fully loaded for a long time. The regeneration can take months or even years.
Also on the arms, especially on the upper arms, overloading often leads to bursitis.
Bursitis due to an underlying disease
Bursitis can also cause common diseases rheumatism or gout accompany. Especially with recurrent bursitis, this should be taken into account.
Infectious bursitis (septic bursitis)
Sometimes bursitis is infectious (septic bursitis). Bacteria like “Staphylococcus aureus“Can penetrate into the body after skin injuries or broken bones, for example, and cause bursitis.
Risk factors for bursitis
Obesity and age are considered risk factors for bursitis. Certain professional groups such as tilers, musicians and athletes are also more susceptible to bursitis because, due to their occupation, they burden certain parts of the body with one-sided, recurring movements.
Important: Anyone who suffers from chronic bursitis for professional reasons may be able to recognize this as an occupational disease.
Bursitis: treatment
If a congestion-induced bursitis is detected early enough, it is usually enough to have the joint for a few days to calm down, Additionally help analgesic and anti-inflammatory drugs such as ibuprofen or diclofenac (as an ointment). Also cold can ease the symptoms: It is recommended, for example, to cool the affected area with a Coolpad.
If the symptoms despite sedation and anti-inflammatory analgesics do not subside and there is no bacterial infection, the doctor cortisone inject into the inflamed bursa. It has a stronger anti-inflammatory effect than NSAIDs.
Some experts recommend a bursitis to one Shock Wave Therapy, The inflamed region is treated with pressure waves. This should alleviate the pain and eliminate any lime deposits.
With a aspiration of the bursa, excess fluid can be aspirated. This can speed healing.
Also recommended are Physiotherapeutic measures, They help to make the affected joint movable again.
Sometimes, however, the described measures do not help permanently and the affected bursa inflames again and again (chronic bursitis). Then it may be advisable to Operatively remove bursa, Even with bacterial bursitis, the bursa usually needs to be removed. In addition, one is antibiotic necessary so that the bacteria do not spread in the body.
If another underlying disease is behind the bursitis, it must be treated accordingly.
Bursitis: shoulder
Bursitis on the buttocks is one of the most common forms of bursitis. She is often accompanied by very strong, stabbing pain. Depending on which of the four bursae is inflamed in the shoulder area, the following bursitis forms are distinguished:
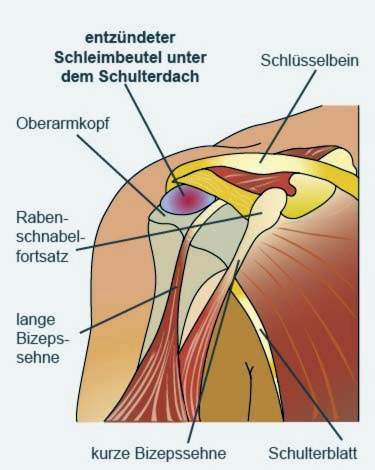
Subacromial bursitis and subdeltoid bursitis
The two bursa Bursa subacromialis and Bursa subdeltoidea inflame mostly with chronic overload:
- The bursa over the shoulder joint roof (Bursa subacromialis) prevents the humerus bumping against the bony roof of the shoulder when lifting the arm. In the shoulder area, he is most often affected by inflammation (Subacromial bursitis).
- The bursa Bursa subdeltoid located between the deltoid muscle of the shoulder and the shoulder joint. An inflammation of this bursa becomes Subdeltoid bursitis called.
Particularly susceptible to these two forms of bursitis are people who work a lot with their arms above their heads. These include, for example, painters and forestry workers. Also sports such as badminton or climbing favor inflammation of Bursa subacromialis or Bursa subdeltoidea.
Subcoracoid bursitis and subscapular bursitis subtendinea musculature
The subcutaneous bursa Bursa subcoracoid and Bursa subtendinea musculum subscapularis become inflamed mostly as a result of natural age-related wear, Overloading plays no role in these forms of bursitis. Wear and tear narrow the space above the shoulder joint, which can lead to tendons and muscle tears. In addition, calcification in the tendons and bursae can cause inflammatory prostateurosis and cause long-lasting discomfort.
Most inflammatory pain occurs slowly. The sufferers then gradually take a restraint, the medium term further complaints on the shoulder to attract.
Some shoulder bursae are linked together. If a bursa inflamed, this can therefore be transferred to the others. Since some bursae are also connected to the joint, inflammation can also extend there.
treatment
If the shoulder is not moved for a longer time due to pain, it can permanently stiffen. Doctors refer to this phenomenon as “frozen shoulder syndrome“To avoid this, one is efficient pain therapy Very important with anti-inflammatory drugs such as ibuprofen. If that is not enough, the gift of cortisone help.
In the case of wear-related as well as chronic bursitis, the pain therapy is often insufficient. Then the inflamed Bursae removed surgically become.
Naturopathic experts also recommend homeopathic remedies such as Silica or Sticta for the treatment of shoulder bursitis. However, the effect of homeopathic remedies has not yet been scientifically proven.
Bursitis: elbow
The bursitis on the elbow is considered by medical professionals Bursitis olecrani designated. It manifests itself through a reddened, visibly swollen elbow tip. Pressure pain may be added (in case of acute inflammation).
This type of bursitis often affects people who spend a lot of time at their desks, and who do not Support the elbow, The applied pressure triggers the inflammatory reaction. But it can also bacteria or other underlying diseases cause the bursitis olecrani.
Nonbacterial bursitis on the elbow is treated with cold compresses, elbow relief, anti-inflammatory analgesics or cortisone. In infectious bursitis olecrani, the bursa must usually be removed. In addition, an antibiotic is given.
Read more about the development, symptoms and treatment of the disease in the article Bursitis – Elbow.
Bursitis: Knee
Bursitis on the knee is one of the most common forms of bursitis. In the knee area, there are several bursae that can catch fire. Particularly susceptible to this are people who have to work a lot on their knees, such as floor layers.
A bursitis in the knee area is noticeable by a painful swelling and redness on the knee. Depending on which bursa is inflamed, the symptoms may occur above or below the kneecap or below the knee in the direction of the tibia.
Everything important about causes, symptoms and treatment of this form of bursitis read in the article Bursitis – Knee.
Bursitis: hip
Bursitis around the hip can also affect various bursae. Most commonly, the bursa inflame on the outside of the hip – more specifically, on the large hillock (bursitis trochanterica) – as well as in the groin (bursitis iliopectinea). Women are slightly more affected than men.
Bursitis in the hips is usually the result of excessive stress. It is associated with pain that usually gets worse with movements in the hip.
Treatment generally consists of sparing and using analgesic anti-inflammatory drugs. Cortisone injections and / or shockwave therapy may be added. For frequently recurring inflammations, the affected bursa is often removed.
Learn more about the causes, symptoms and treatment of bursitis in the hip area in the article bursitis – hip.
Bursitis: examinations and diagnosis
If a bursitis is suspected, the doctor will first ask you about your bursitis medical history (Anamnesis): He describes the symptoms exactly, asks about recent physical stress and possible underlying diseases.
Then follows one physical examination: The doctor looks at the affected body region exactly. He can recognize a bursitis on the basis of the reddened skin as well as the swollen, immovable joint.
If the doctor suspects a bacterial infection as the cause of bursitis, he will become yours Measure body temperature and you take a blood sample, The inflammatory values (number of white blood cells, CRP, etc.) are determined in the laboratory. If there is actually a bacterial infection, the bursa becomes one tissue sample taken (biopsy) to find out the nature of the pathogen. So the doctor can tailor the treatment individually to the triggering bacterium (selection of a suitable antibiotic).
In unclear cases further investigations are necessary. Thus, the inflamed structures by means of Ultrasonic or Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) in order to be able to judge them more accurately. A X-ray photograph can show if lime has already deposited in the bursa.
As part of the investigations, the doctor must exclude diseases with symptoms similar to bursitis. These so-called differential diagnoses include rheumatism, tuberculosis, lipomas (benign adipose tissue tumors) and liposarcomas (malignant adipose tissue tumors).
Bursitis: history and prognosis
How long a bursitis lasts and how severe the symptoms are depends in particular on the cause of the inflammation. If the bursitis is treated effectively and the joint is immobilized, the symptoms usually improve after a few days.
However, if the inflammation is ignored and the joint is not sufficiently relieved, the inflammation can become chronic (chronic) and cause discomfort for months or even years. Such chronic bursitis is much more difficult to treat than an acute one. Therefore: one Housemaid’s knee You should take it seriously at an early age.