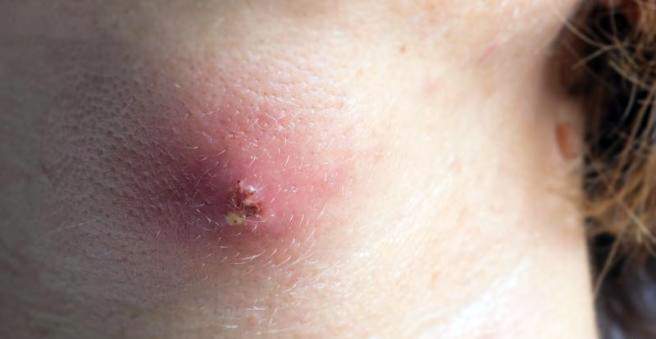
A boil occurs when a hair follicle becomes inflamed. It usually starts with a small, red “pimple” and then develops into an often painful puddle with pus. Boils often heal on their own. But sometimes a doctor has to cut her up or prescribe antibiotics. Read here why you should never express a boil yourself, what role the immune system plays and what promotes the appearance of pustules.
Quick Overview
- What is a boil? A deep, purulent inflammation of a hair follicle (hair follicle). It can occur at any hairy body site. Boils are often found on the buttocks, on the face or neck, in the armpits, in the genital area or on the inner thighs.
- symptoms: typical symptoms of inflammation (pain, redness, etc.), visible elevation of skin with pus cores
- Causes: Bacteria, usually staphylococci. Risk factors include, for example, a weakened immune system, poor hygiene and too tight clothing.
- Occurrence: Boils are common worldwide. Above all, the humid-hot climate in the tropics and subtropics can promote skin infections as in boils. Overall, men are more affected by boils than women.
- Treatment: Often waiting and disinfecting are sufficient. In severe cases treatment by the doctor (eg slicing, train ointment, antibiotics)
- Forecast: A boil usually heals easily. In rare cases, there are complications such as lymph node inflammation, blood poisoning, meningitis.
Boils: treatment
The best you can do for yourself is to let the fingers from the boil, Even if it is still so tempting – if you press around on the pus knot or even cut it open, the bacteria can spread with the pus exiting.
Those who want to remove or puncture boils with their own hands risk serious complications such as sepsis!
It makes sense, however, the keep the affected body region calm, This prevents the germs from being carried off. In the case of a boil on the face, the game is often moved automatically as little as possible. For example, if a whisker follicle is painfully inflamed, speaking and chewing can be quite uncomfortable.
With a Red light application you can support the healing process: The heat accelerates the maturing of the boils.
home remedies may also be useful, for example, a marigold tincture: Applied externally, it can help against inflammation and suppuration.
At the beginning of the disease, it is also advisable to moist and warm envelopes with antiseptic agents like Povidone iodine to lay on the boil.
Always watch out adequate hygiene, Disinfect the boil and wash your hands thoroughly after touching the pus knot. This will prevent you from spreading the bacteria to other parts of the body where they may cause another infection.
Furuncle treatment at the doctor
If the boil is very painful, treatment by the doctor may be useful. The same is true if someone has several boils or the pus ulcers always return. Then there is often one underlying disease such as diabetes (diabetes mellitus), chronic infections, blood cancer (leukemia) or possibly also HIV / Aids. The consistent therapy of the underlying disease also supports the boilermaker treatment.
If there is no opening in a boil, the doctor may Zugsalbe Instruct. Such ointments with the active ingredient ammonium bituminosulfonate have an anti-inflammatory effect and reduce sebum production in the sebaceous glands. They are generally used in inflammatory skin conditions such as boils.
In severe cases, boils are associated with antibiotics treated. This is mainly a spread of infection via the bloodstream (or blood poisoning sepsis) as well as other complications like Meningitis (Meningitis).
Important is the antibiotic treatment especially with a boil on the face. Patients with extensive facial darkening are often hospitalized in hospital. There, the antibiotics are administered directly into a vein. In addition, patients should not talk and chew (liquid foods only) and should observe bed rest.
Boils: Symptoms
A boil can grow anywhere the skin is hairy. However, it often forms on the face (like boils on the ear), on the neck and in the armpits. Also, boils in the pubic area and on the thighs and boils on the butt are very common.
The small pus knots express themselves with the typical signs of inflammation at the point in question:
- pain
- reddening
- overheat
- swelling
The patients first notice an inflammation of the skin. It starts as painful, taut knot, After some time, it empties pus from the boil. Thereafter, the complaints usually resolve.
Sometimes boils patients feel altogether weakened and beaten off, Others, on the other hand, have no such general symptoms.
If several boils coexist and flow together, it is called carbuncle, If boils repeatedly occur on different parts of the body, it is one furunculosis.
Boils: causes and risk factors
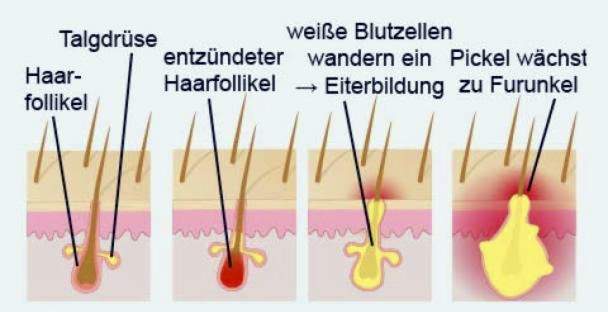
Boils are bacterial infections of hair follicles and surrounding tissue. As a hair follicle (hair follicles) refers to the tissue that surrounds the hair root and the hair, so to speak, anchored in the skin.
Triggers of deep hair follicle inflammation Bacteria, usually Staphylococcus aureus, These generally live on the skin and mucous membranes, often without manifesting themselves in any way. However, if they get into deeper tissue layers or the immune system is weakened, they can trigger various infectious diseases, including boils.
Concretely, one first arises folliculitis, This is a superficial hair follicle inflammation. In the further course, the infection can spread to the skin layers around the hair follicle. The tissue dies, the result is a purulent meltdown (necrolysis) – a boil has developed. At first, this deep-seated inflammation often makes itself felt in a pimple-like red elevation on the skin. Later, a plug of yellow pus is formed.
Own or smear infection
The bacteria that cause a boil usually live naturally on the skin of the patient. If these “own” bacteria infect a hair follicle, it is a self-infection.
But it can also happen that the boils trigger over one contact infection The bacteria thus reach the skin of a healthy person via direct skin contact with patients or via contaminated objects. Over tiny injuries to the sweat glands or along the hair follicle, you can invade the body and cause an infection.
Boils: risk factors
Certain factors favor the formation of boils. These include:
- Closure of the hair follicle due to secretion in the sebaceous glands
- smallest injuries (microtrauma)
- Tendency to allergic diseases (atopy)
- tight, scathing clothes
- insufficient disinfection after shaving or depilation
- lack of personal hygiene
- weakened immune system, either as a result of underlying disease (such as poorly controlled diabetes mellitus, chronic infections, leukemia, HIV / AIDS) or by the use of drugs that suppress the immune system (immunosuppressants such as cortisone)
Boils: examinations and diagnosis
Mostly it just takes a bit of patience with a boil. As soon as the pus has leaked, the inflammation usually stops by itself. But if the boil is very painful or sits on your face, you should better yours family doctor attention. Depending on the situation, the risk of facial blemishes increases, as the bacteria enter the brain and cause complications (such as an abscess).
A doctor’s visit is also advisable if several boils occur at the same time or the pus knots recurrent.
conversation
The doctor first asks you in detail about your medical history (anamnesis). He can ask you the following questions:
- Since when is your skin inflamed?
- How strong is the pain?
- Are other skin areas affected?
- Have you had such an inflammation before?
- Do you have fever?
- Do you suffer from any diseases (diabetes, atopic dermatitis, chronic infections etc.)?
Physical examination
This is followed by a physical examination. The doctor examines especially the affected skin site. He is looking specifically for pus and crusting. Then he looks at the rest of the skin to detect further possible inflammation. He also scans your lymph nodes to detect any swelling.
The information from the anamnesis interview and the physical examination are usually sufficient to make the diagnosis boils.
Further investigations
Especially in severe cases, as well as frequently occurring or recurring boils, further investigations may be useful. The patient may be suffering from a previously undiscovered underlying disease, such as diabetes, chronic infections, leukemia or HIV. Thus, for example, the suspicion of a diabetes with a Determination of blood sugar clarify.
Sometimes it makes sense to have one Smear of inflammation close. In the laboratory, the pathogens that are in the boil can be identified. The doctor can then select antibiotics that are specifically effective against this germ.
Boils: course and prognosis
As a rule, a boil heals without complications. But it usually remains a small, retracted scar back.
In rare cases, the inflammation may spread, especially in a severely weakened immune system. As a result, can be about one lymph node inflammation (Lymphadenitis) or Lymphbahnenentzündung (Lymphangitis) arise.
Especially a lip or nose burn can trigger a dangerous sepsis (blood poisoning). In addition, you can boil Inflammation of the eye socket (orbitaphlegmone), meningitis (meningitis) or a vascular occlusion in the brain through a blood clot (sinus cavernosus thrombosis) in the face.