A bruise is a blunt, closed injury caused, for example, by impact, impact, falling objects, fall or fall. In doing so, the tissue (skin, fatty tissue, muscles, etc.) is squeezed. Read all important information on the topic: What is a bruise? What symptoms causes them? How can you treat bruises? How long does a bruise take?
Contusion: Description
As a bruise doctors refer to a direct injury caused by compression. It is closed – so there is no visible skin injury and no bone fracture. The tissue at the bruised site (ie, skin, adipose tissue, fascia, muscle, tendons, tissue capsule, etc.) is squeezed.
Depending on the nature and localization of the bruise one speaks for example of bone bruise, muscle bruise, eyeball bruise, lung bruise, brain contusion, thigh bruise (“horse kiss”), rib contusion, knee bruising or shoulder bruising.
Rippenprellung
Find out more about the cause, symptoms and treatment of bruised ribs in the article “Rib Contusion”.
bruised knee
Find out more about the cause, symptoms and treatment of a bruised knee in the article Knieprellung.
shoulder contusion
Learn more about the cause, symptoms and treatment of a bruised shoulder in the article shoulder bruising.
Contusion and contusion
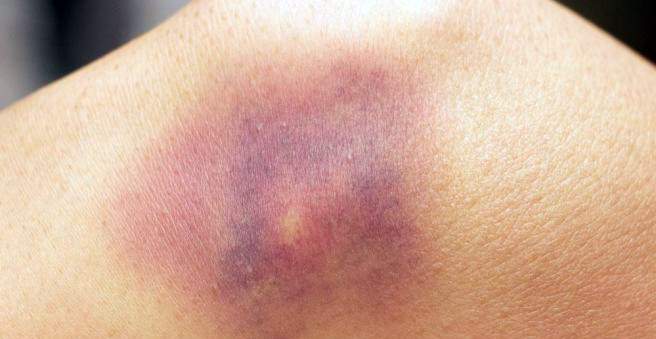
The medical term for bruise is contusion (contusion). In practice, however, a distinction is often made between the two terms: a bruise is a banal and pain-related tissue damage without long-term significance.
A contusion, however, is a strong contusion, which is also associated with a swelling and bleeding (bruise). If additional tissue has been destroyed, physicians speak of a bruise.
Contusion: Symptoms
A bruise is painful, especially during exercise or strain on the injured area. But there is no bleeding and no significant swelling. Such symptoms only occur with a strong bruise (contusion).
Often, a bruise is also associated with a restriction of movement, such as a muscle bruise around the thigh (thigh bruise).
Depending on the location, additional symptoms may occur. Thus, a strong contusion of the eyeball can not only lead to swelling and bleeding of the eyelids and conjunctiva, but also limit vision and move the lens from the optical axis. In case of brain contusion (contusio cerebri), unconsciousness and neurological symptoms (such as epileptic seizures, olfactory loss = anosmia, speech and vision disorders, etc.) occur.
If the contusion affects a joint, an effusion may form, that is, more fluid is secreted into the joint cavity. If blood vessels have been destroyed, blood collects in the joint cavity (bruise).
Contusion: causes and risk factors
A bruise is caused by direct blunt external trauma. This may be, for example, a shock, fall, impact, impact falling objects or entrapment.
Very often bruises occur during sports, especially in contact sports such as football or ice hockey. But even in sports where you have no direct contact with players, you can get such an injury, such as when a tennis ball flies in the eye (eyebrow bruise).
Special protective clothing can reduce the risk of bruising or other, more severe (sports) injuries. For example, you should wear a helmet during cycling, skiing and inline skating, and in hockey and soccer shinguards. Back protectors are recommended for snowboarders and mountain bikers.
Contusion: examinations and diagnosis
A simple bruise generally does not require a doctor’s visit. In severe or persistent complaints or to exclude further injuries (such as bone fracture), but the walk to the doctor is necessary. In case of cranial bruises one should generally seek medical advice.
The doctor will first inquire about the symptoms and their development. Possible questions are:
- How did the injury come about? For example, did you fall or did you get a blow?
- Where exactly are you in pain?
- Do you have any further complaints?
Then follows the physical examination. The doctor examines the injured area and carefully scans it. He pays attention, for example, to swelling, tenderness and restricted mobility.
Imaging procedures
A bone bruise occurs especially in body parts, where a bone is covered only by a thin layer of skin. This is the case, for example, on the head, on the ribs and on the tibia. However, a painful, blunt injury at such sites can be not just a bruise but also a bone fracture. This can not be differentiated solely on the basis of pain intensity. For this an X-ray examination is necessary.
For a more detailed diagnosis (such as the exclusion of ligament injuries or brain contusion), the doctor can order a computed tomography (CT) or a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Contusion: treatment
First aid measures for a bruise are based on the PECH rule:
- Break (interrupt sports training)
- Ice (place ice cubes wrapped in a cloth or a cold washcloth to cool)
- Compression (in case of bruise on extremities create elastic pressure bandage)
- Elevating the injured limb
Herbal supplements, such as an ointment or arnica-based gel, can help against the pain and swelling. In severe pain, the doctor may prescribe painkillers (such as acetaminophen).
In general, the treatment also depends on the type and extent of the bruise. For example, in the case of eyeball contusion, it may be necessary to administer medication that reduces the increased intraocular pressure. If the bruise has led to retinal detachment, surgery is required. A brain bruise usually has to be treated in the hospital.
Contusion: Disease course and prognosis
A bruise generally heals by itself and without consequences. The same is usually true for a strong bruise (contusion). Only in exceptional cases can scarred changes in the area of the hemorrhage occur in the latter.
If the symptoms start to get worse when the bruise starts to seem trivial, you should definitely go to the doctor.
Contusion: duration
The healing time in a banal bruise is usually two to three weeks, in mild cases, only a few days. In a contusion associated with scarring, healing may take four weeks or more.