The most important diabetic values for diagnosis and review of treatment success are fasting blood glucose and HbA1c. The oral glucose tolerance test (oGTT) can also detect a precursor to diabetes (“prediabetes”). Since elevated blood sugar levels permanently harm the entire organism permanently, the values should be checked regularly. Here you read everything important about diabetes values.

When does one speak of diabetes?
The blood sugar is Germany usually in milligrams per deciliter (mg / dl). Internationally distributed (especially in the USA), however, the figure in millimoles per liter (mmol / l). At your doctor or on the Internet you can convert the diabetes values with the help of a diabetes calculator.
The most important values are the Fasting blood sugar and the HbA1c, The latter is also known as “blood sugar long-term memory”. In addition, conspicuous values in the oral glucose tolerance test (oGTT) indicate a precursor to diabetes (“prediabetes”) or diabetes. Also, a detection of sugar in the urine is used for diagnosis.
Diabetes values: Table
The limits for each blood sugar parameter can be found in the following diabetes chart. There you will find the most important blood glucose parameters that are used for diagnosis or for follow-up. Further explanations of the individual tests can be found below the table.
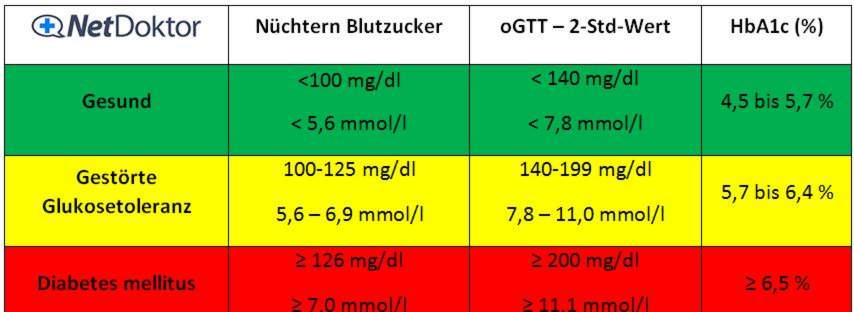
Fasting blood sugar
Fasting blood glucose is the most important of the diabetes blood tests for diabetes diagnostics. In healthy people it is between 60 and 99 mg / dl or 3.3 and 5.6 mmol / l. If the fasting blood glucose is between 100 and 125 mg / dl, one already speaks of an abnormal fasting glucose (IFG = impaired fasting glucose). At levels above 125 mg / dl, the presence of diabetes mellitus is already very likely. However, the value should first be determined a second time to rule out incorrect measurements.
Also note: After eating a meal, the blood sugar in healthy people increases to levels up to 140 mg / dl. The blood sugar should therefore be determined only after eight hours of abstinence from eating (food delay).
Diabetes – HbA1c (long-term blood glucose)
In both the healthy and the diabetic, sugar molecules attach themselves to some of the red blood pigment (hemoglobin). The sugar loaded hemoglobin is called glycohemoglobin A (also HbA1c). Normally, however, no more than 5.7 percent of hemoglobin has a sugar molecule attached to it.
Due to the permanently increased blood sugar levels, a higher proportion of hemoglobin in the diabetic is loaded with a sugar molecule. Since the red blood cells live on average for about 120 days, the HbA1c value is suitable as a long-term diabetes value and thus provides information on the blood glucose control of the last eight to twelve weeks. Daily individual fluctuations do not affect the HbA1c value. The determination of HbA1c takes place mainly to control the treatment success.
Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (oGTT)
If diabetes mellitus or a precursor to diabetes is suspected, the oral glucose tolerance test (oGTT) can be used. The patient is taken for fasting (after eight hours of abstinence) blood and determined the fasting blood glucose level. Subsequently, the patient should drink a glucose solution with 50 or 75 grams of glucose. The sugar solution tastes like sweet grape juice and is well tolerated by most patients.
After 120 minutes, another blood collection takes place for blood sugar determination. This two-hour value provides an indication of how much of the glucose absorbed in the blood was absorbed into the cells with the help of insulin. At two-hour values above 200 mg / dl, diabetes mellitus is very likely. If diabetes is known, the oGTT should not be used to prevent blood sugar derailment.
Desirable levels of diabetes in the course of treatment
The desired blood glucose levels should always be discussed individually with the attending physician. Because they differ depending on the constitution and the age of the patient. However, the diabetes standard values recommended by the German Diabetes Society can apply to most patients. They differ only slightly in type 1 diabetics and type 2 diabetics.
Diabetes type 1 values
With diabetes type 1, the insulin supply (insulin syringe, pump) should keep the blood sugar constant within a range of 100 mg / dl. The HbA1c value should be below 7.5 percent. Although the sugar levels should be adjusted as precisely as possible, without risking hypoglycaemia.
Diabetes type 2 values
In type 2 diabetes, treatment control is based on fasting blood glucose and HbA1c. In a type 2 diabetic, the fasting blood glucose level before a meal should be between 80 and 120 mg / dL. If he is higher, the medication must be adjusted.
If concomitant diseases such as high blood pressure (hypertension), kidney damage (nephropathy) or a lipid metabolism disorder (hyperlipidemia) are present, they must be treated as high blood sugar levels make these diseases worse. The German Diabetes Society (DDG) recommends a HbA1c value between 6.5 and 7.5 percent. However, the individual needs of patients should also be taken into account. For example, in elderly patients, an HbA1c value of 8.0 may still be tolerable.
Check diabetes values regularly!
The above values, especially the HbA1c value, should be checked regularly. If you measure your fasting blood sugar level on a daily basis, take a log for self-assessment. See your doctor as soon as you realize that you can no longer adjust the blood sugar level correctly.
A good blood sugar control is crucial to prevent or at least delay the serious diabetic sequelae on the kidney, the retina of the eye and the blood vessels. An annual ophthalmological examination is recommended in addition to regular blood glucose monitoring. In case of doubt, your doctor will inform you about the desired Diabetes values.