Tooth root inflammation is usually caused by caries damage to the tooth root, especially the root canal and the nerves running inside. In severe cases, a tooth can die from the inflammation. The doctor makes the diagnosis by examining the tooth and using the typical X-ray image. Read all about symptoms, diagnostics and therapy of tooth root inflammation.
Tooth root inflammation: description
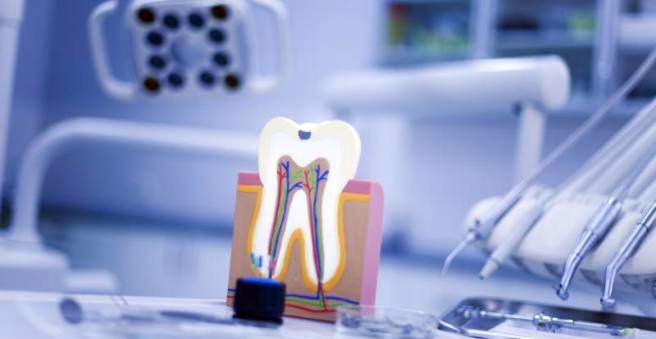
Tooth root inflammation is a deep inflammation of the tooth. The most common cause is tooth decay. The inflammation penetrates through the various layers of the tooth down to the pulp and the root tip (apical periodontitis), which anchors the tooth in the jawbone. First, the damage to the pulp is often reversible, but not in the further course. It threatens nerve damage and death of the tooth, so you should contact his dentist early.
Tooth root inflammation: symptoms
Typical tooth root inflammation symptoms include pain and pressure around the inflamed tooth. These symptoms should be taken seriously and quickly turned to your dentist to avoid serious dental damage.
First, the bacteria spread unnoticed on and in the tooth. When the inflammation approaches the root area, mild to severe toothache often develops. First, the pain only occurs in provocation, such as biting (biting pain) or tapping the inflamed area (percussion pain). If the pulp is severely attacked (pulpitis), there is a throbbing, persistent pain. The tooth root inflammation symptoms can also radiate to other teeth and facial areas.
Damage to the gums
Tooth root inflammation also affects the gums. When brushing your teeth, the gums may begin to bleed. In addition, the gums retract and remain exposed necks. The periodontal pockets sometimes secrete secretions or pus. This results in partly unpleasant bad breath. In addition, unfortunately, the maintenance of teeth under the damaged gums.
Sudden stop of pain is a dangerous signal
If the tooth root inflammation symptoms suddenly stop, the tooth nerve is usually so severely damaged that the pain perception is interrupted – the tooth is “dead”.
With already advanced nerve damage, the root inflammation can also be completely painless. The tooth can then die off, the inflammation become chronic and spread unhindered (abscess and fistula formation). Chin and cheek swell (“thick cheek”) and the pain radiates into other areas of the head. A swelling jawbone is a sign of an advanced inflammatory process.
Tooth root inflammation: causes and risk factors
In most cases, changes caused by tooth decay are the cause of tooth root inflammation. The human mouth provides good growth conditions for over 700 bacterial species. Some of these metabolize sugars in particular. The resulting waste products also attack the teeth. An untreated tooth decay leads to permanent tooth damage. Through the resulting holes, the bacteria can also penetrate into the interior of the tooth and there call the immune system on the plan, an inflammation arises. If the inflammation spreads to the area around the tooth root, this is also called periradicular periodontitis. The tooth nerve can also be attacked and die off in the worst case. In addition, if the caries bacteria reach the root tip, they can also damage the jawbone rooting.
In very rare cases, a dental root disease can be triggered by an injury that was years ago. An example is a blow to the jawbone, through which the tooth nerve slowly dies. Even a fall in which the hard tooth tissue breaks off and the tooth nerve suddenly exposed unprotected, can trigger a tooth root inflammation.
Other triggers for tooth root inflammation may be wisdom teeth, which grow obliquely and offset below the bone surface and irritate the tooth roots of the neighboring teeth.
risk factors
Malnutrition and also certain illnesses (diabetes mellitus, tumor diseases etc.) favor the emergence and the progression of caries. A genetic susceptibility is also discussed. Known wound healing disorders, a close proximity to neighboring teeth, root malformations and severe courses can make healing difficult. Signs of a difficult course are acute signs of infection and advanced damage to the tooth.
Tooth root inflammation: examinations and diagnosis
At least once a year, preferably every six months, you should go to the check-up at the dentist. Then an incipient caries or a dental root inflammation is detected early and treated as effectively as possible.
At best, early treatment prevents caries bacteria from passing through the enamel and dentin to the nerve of the tooth. Apart from the check-ups, you should contact his dentist immediately in case of complaints, so that he can examine the aching teeth. For the doctor, it is important to first hear:
- What complaints do you have?
- How intense is the pain?
- How long are the complaints?
- Have already been known or treated diseases of the teeth?
Examination of the tooth
For the dentist, the description and localization is an important indication of tooth root inflammation. When inspecting and probing the teeth, he checks the vitality of the tooth. In addition, the doctor pays attention to discoloration, cracks and fractures on the tooth. When tapping the inflamed area, this is particularly sensitive. If the pain is permanent, the dental pulp is probably irreversibly damaged. In the case of pain caused only by tapping or biting, there is the hope that the pulpal damage can still regress.
Test for sensitivity to cold
With a cold stimulus, the doctor tests whether the nerve is still reacting. Irritation and inflammation make the nerve sensitive. A cold-sensitive tooth is a good sign. Then this is still vital. However, if the nerve is already severely damaged, the cold stimulus remains unresponsive. As a cold stimulus can be used, inter alia, carbonic acid snow, Dichloridfluormethan or ethylene chloride.
If there is any uncertainty regarding the status of the teeth, the doctor performs a small trial drilling (trial reworking). If the affected person does not feel any pain while drilling, the tooth is probably dead.
X-ray photograph
With an X-ray, the bony structures of the oral cavity and the teeth can be viewed in detail. Important for the evaluation of the tooth root inflammation is the comparison with previous photographs. Also recordings in different levels, a computed tomography (CT) or a 3-D volume tomography (DVT) can be made.
A small shadow on the affected tooth in the X-ray indicates a tooth root inflammation. Typical is the shadow around the root (periradicular radiolucency) and an extension of the gap between the root and the tooth compartment in the jawbone (periodontal cleft).
It may still be necessary to have a laboratory control of the inflammatory parameters or coagulation parameters.
Tooth root inflammation: treatment
The treatment of tooth root inflammation depends on the type and severity. Objectives of the therapy are the removal of the inflammation and a bacteria-proof root canal occlusion. The health insurance does not always cover the costs of the treatment. Therefore, inform yourself in advance about the conditions and the costs of the therapy.
Caries removal and cleaning
First, the surface should be smoothed and cleaned in a tooth root inflammation. This can be done with different techniques (ultrasound, curettes or scalers). This is to remove concrements, plaques and tartar. The mouth is additionally rinsed with antibacterial solutions. This is important to prevent germ spreading when opening the tooth.
root canal treatment
Often a root canal treatment can provide a remedy. After eliminating caries, the pulp is opened and (completely) removed. Then the root canal entrances are exposed (prepared) and rinsed to completely remove the tooth root inflammation. The root canal is then prepared and possibly expanded to introduce a root filling. The dense and complete filling is important to protect the tooth from invading bacteria. The root can only be filled if it is symptom-free, dry and odorless. If necessary, the definitive filling is therefore introduced in a second session. As a check, X-rays are taken during the procedure.
Wurzelspitzenresektion
The so-called root tip resection is an operation in which the tooth root tip is shortened. This procedure may be necessary, for example, for inflammation of the tip of the tooth root (apical osteitis). First, the gum and the periosteum are severed so that the bone is exposed. Then the jawbone is drilled out (osteotomy). Through the bone window, the root tip is shortened, the root canal expanded and filled as in a root canal treatment.
In severe cases, the tooth must be removed. In the case of recurrent tooth root inflammation, the existing root filling must be renewed and examined. If surgery is not possible, at least antibiotic treatment should be started.
What should be considered after treatment?
As long as the effect of the local anesthetic stops, one should not eat any food. Smoking, coffee and black tea should be avoided for around 24 hours. Also physical effort should be avoided at first. To avoid swelling and pain, it is advisable to cool the treated area.
Especially important is the adherence to a strict oral hygiene according to the instructions of the treating dentist. If a suture has been made, it can be removed after seven to ten days.
If you experience particularly severe pain, swelling, fever or other signs of inflammation after surgery, you should immediately contact the treating dentist or a dental emergency room. Very important is the follow-up of a dental root infection by the treating dentist.
complications
As with any surgery, wound healing disorders or infection can occur. For each intervention on the teeth should therefore be checked whether an antibiotic treatment is necessary as a prophylaxis. Also, injury to surrounding structures, such as nerves, or the tooth structures themselves (e.g., root breakage) are possible.
How can I prevent tooth root inflammation?
The basis for the prevention of tooth damage is good oral and dental hygiene. At least twice a day, preferably in the morning and in the evening, it means: brush your teeth. You should leave enough time and rest as well as observe the advice of the dentist. Especially the back teeth and the inner tooth surfaces are often omitted. The interdental spaces are also cleaned with floss or interdental brushes at least once a day.
Tooth root inflammation: disease course and prognosis
An early diagnosis and treatment for tooth root inflammation is crucial for the preservation of the tooth. Without treatment, the dental root inflammation progresses unchecked and can spread more and more. Then the tooth loss threatens. Periodontal disease, including root inflammation, is the main reason for tooth loss in adulthood.
After a treated Root inflammation You should regularly ask for follow-up care at your dentist and maintain a good oral hygiene. That’s how your teeth stay healthy.