Sinusitis (sinusitis) is an inflammation of the mucosa in the sinuses. These are the air-filled cavities in the skull, which are connected via narrow openings with the nose. Depending on the course one differentiates between acute and chronic sinusitis. The former usually treats the doctor with decongestant and / or expectorant medication. Chronic sinusitis may require surgery. Read here all important information on the topic: What is the diagnosis of sinusitis? What to do about the complaints? How to prevent sinusitis?

Quick Overview
- What is sinusitis? Inflammation of the mucosa of the sinuses; acute and chronic course possible
- Causes: mostly viruses, sometimes bacteria, fungi or allergies; favoring factors: anatomical bottlenecks in the nose, diseases of the immune system, allergic mucosal swelling or respiratory diseases
- symptoms: Headache, feeling of pressure in the head, reduced sense of smell, production of secretions, if necessary fever, general exhaustion
- Treatment: An acute sinusitis often heals on its own; supportive are decongestants and expectorants. In case of chronic course, surgery if necessary
- Doctor treating: ENT doctor
- Forecast: good in acute course; rarely does the inflammation spread to neighboring structures (bone, eye socket, brain, etc.).
- Prevent: Keep nasal mucosa moist, healthy lifestyle (no smoking, lots of exercise in the open air, adequate sleep, etc.);
Sinusitis: treatment
Depending on the duration, there are two types of sinusitis. They are treated differently:
Acute sinusitis
Acute sinusitis often resolves on its own within two to four weeks. The healing process can be supported with medicines: These include Agents that allow the mucous membrane to swell, With their help, the paranasal sinuses are released again, and the sinuses are ventilated again.
antibiotics sometimes the doctor prescribes bacterial sinusitis.
Medications for mucus solution liquefy the secretions in the sinuses. It can be better. The same effect can be achieved Nasal sprays and inhalations with 0.9% salt water.
The previously often performed jaw irrigation is rarely needed.
Chronic sinusitis
The treatment for chronic sinusitis depends on the cause of the disease. stick Allergies or tooth inflammation behind it, they need to be targeted. If anatomical changes The Sinusitis favor, they should be remedied as far as possible: For example, can be a straightened nasal septum operatively straighten, narrow excretory ducts of the sinuses can be expanded and remove large nasal polyps.
Nasal rinses and inhalations with salt water In chronic sinusitis, they can help to loosen the stuck mucus.
Sinusitis: home remedies
In sinusitis therapy, it does not always have to be (just) a drug. With home remedies you can even relieve the symptoms of acute inflammation and support the healing process. For example, this is helpful essential oil of myrtle with its anti-inflammatory effect. It is obtained in capsule form in the pharmacy.
On the other hand it works Tea from primrose root (Cowslip root) secretolytic. Recommended for sinusitis is also a steam bath with decongestant and soothing essences (lavender, chamomile, thyme etc.) or Inhalation of warm water vapors.
Find out more about home remedies and complementary healing methods for sinusitis, their use and any risks in the article sinusitis: home remedies.
Sinusitis: symptoms
Along with allergic and viral diseases of the upper respiratory tract (flu, cold) is the sinusitis one of the most common diseases of the respiratory tract acute sinusitis Affected have it after a maximum of twelve weeks survived. Within this period, the sinusitis symptoms completely disappear. The chronic sinusitis is more persistent. it lasts for more than twelve weeks, and the symptoms never completely disappear in the meantime. Also, if the symptoms recur more than four times a year, it is called chronic sinusitis.
Acute sinusitis: symptoms
An acute sinusitis is usually preceded by a cold (rhinitis), ie a pure inflammation of the nasal mucosa. This usually continues even when the inflammation spreads to the paranasal sinuses. This simultaneous mucosal inflammation of the nose and paranasal sinuses is called rhinosinusitis designated.
The most important signs of acute sinusitis (or rhinosinusitis) are:
- Headache or pressure in the head: In severe cases, the pain throbs over the forehead, in the cheek area, behind the eyes or more rarely in the area of the back of the head. The pain intensifies as soon as one tilts the upper body forward (for example when stooping) or firmly with the foot occurs. If you exert slight pressure on the affected areas from the outside or knock against it, the pain also intensifies.
- Sniff: often with purulent nasal discharge; Often the nose is completely blocked.
Severe sinusitis can cause symptoms like Fever, fatigue and blurred visionto be added. Sometimes, then develops one painful, externally visible swelling.
Chronic sinusitis: symptoms
Chronic sinusitis is often present much weaker complaints associated with acute sinusitis. Those affected do not even have to be in pain. However, the nasal breathing is hampered for more than twelve weeks and is usually accompanied by mucous and purulent nasal discharge. Sometimes chronic sinusitis also occurs acute episodes of infection with greater pain on.
Also typical for chronic sinusitis is a impaired smell and taste: Those affected smell much less or even smell no more and also taste less than normal.
Forms of sinusitis
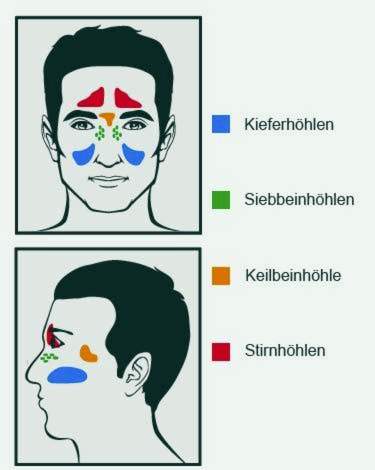
The paranasal sinuses include:
- the two sinuses: in the middle directly above the nose above the eyebrows,
- the two maxillary sinuses: right next to the nose; the largest paranasal sinuses,
- the ethmoid sinuses (Ethmoid sinus or ethmoid labyrinth): between the nose and the inner corner of the eye,
- the two Sphenoidal sinuses: above the back end of the nasal cavity.
If sinusitis involves several sinuses, doctors call it sinus Polysinusitis, If all sinuses are affected, there is one pansinusitis in front.
Sometimes the inflammation extends only to single sinuses: The most common forms of sinusitis are Antritis (Maxillary sinusitis) and Siebbeinzellenentzündung (Ethmoid sinusitis). Rarer is the Sinusitis (Sinusitis frontalis), most rarely the Sphenoid sinus inflammation (Sphenoidal sinusitis).
Antritis
The maxillary sinuses are located right next to the nose and resemble inverted pyramids. If they are inflamed, they are usually caused by fungi, bacteria, viruses or allergies. But also injuries of the maxillary sinus mucosa can trigger an inflammation of the maxillary sinus. This can be when pulling a tooth in the upper jaw or when a bone fracture in the area of the middle facial skull. Rarely a root infection in the region of the maxillary teeth is the trigger of this form of sinusitis. Toothache can do this odontgene or Dentogenous sinusitis accompany.
An antritis manifests itself in dull to throbbing pain and a feeling of pressure in the cheek area. These complaints increase when bending or hopping. Toothache, headache and purulent nasal secretions may also indicate a disease.
Find out more about the symptoms, causes and treatment of this sinusitis form in the article Anorexia.
Sinusitis
For example, sinusitis can occur if the ventilation of these sinuses is permanently compromised. That’s about the case if someone has a severely curved nasal septum or large nasal polyp. Nasal infections and allergies are among the possible causes of this sinusitis form.
In acute sinusitis develop within a few hours strong, stinging and pulsating pain on the affected front as well as around the eye. Other possible complaints are a slimy-purulent cold, a reduced sense of smell and conjunctivitis.
If the inflammation is chronic, sufferers report headaches. In addition, odors are reduced or misperceived. Slimy-purulent nasal secretions may also form.
For all important information about this form of sinusitis, see Sinusitis.
Sinusitis: Causes & Risk Factors
The paranasal sinuses are air-filled cavities in the facial bones, which open into the nose. They reduce the weight of the head and serve as a resonance chamber for speaking and singing. Usually they are well ventilated and are cleansed by the body itself: they are lined with the same mucous membrane as the nose. This mucous membrane produces one secretion, It is made by means of fine cilia transported on the mucosal surface from the paranasal sinuses into the nasopharynx – an effective cleaning mechanism. Is this way, however congested, the secretion jams in the cave. This favors the growth of Bacteria and other pathogens – the mucous membrane becomes inflamed and causes sinusitis.
Main cause for one acute sinusitis are viral or bacterial infections of the nose, Even with a simple cold, the sinuses are usually affected (rhinosinusitis). The bacterial sinusitis is usually the result of viral rhinosinusitis: the virus infection causes the mucous membrane to swell up. On top of this bacteria can easily colonize and multiply. Then a nasal sinus vascular development develops.
Less common pathogens in the water, while swimming or bathing, can cause sinusitis. Then doctors speak of one swimming sinusitis.
If germs are the cause, sinusitis is contagious.
In contrast, the so-called Barosinusitis caused by strong fluctuations in pressure, such as occur during diving or flying.
A Antritis can also be caused by a root inflammation: The roots of the upper molars are namely in close spatial relationship to the maxillary sinuses.
The chronic sinusitis is often based on anatomical bottlenecks in the nose, which hinder the ventilation of the sinuses. These include, for example, curvatures of the nasal septum or large nasal polyps.
Other causes of sinusitis can be allergic mucosal swelling, Cystic Fibrosis or Immune system disorders be. In people with respiratory diseases like COPD or asthma There are frequent (chronic) sinus infections. Particularly affected are people with asthma in combination with nasal polyps and incompatibility of ASA (acetylsalicylic acid). This trio is also called Samter’s triad designated.
Sinusitis: Examinations & Diagnosis
Although a sinusitis heals untreated in many cases. If you suspect sinusitis, you should still go to the (ENT) doctor. He can clarify the exact cause of the complaint, prescribe necessary medications and detect possible complications early on.
The doctor first raises im conversation with you your medical history (anamnesis): He asks about the nature, duration and extent of the symptoms and whether you have had such symptoms before. He also inquires about possible pre-existing conditions (such as allergies).
Subsequently, the doctor uses your nose Nose Mirroring (Rhinoscopy) from the inside: He introduces a thin, usually rigid tube (endoscope) into the nose, which has a light source and a small camera at the front end. This allows the excretory ducts of the paranasal sinuses to be inspected.
Purulent rhinitis indicates a bacterial infection. The doctor then takes one smearto have him examined in the laboratory for the causative bacteria. Among the bacteria that often participate in sinusitis include Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus influenzae.
A X-ray photograph shows if fluid has accumulated in the sinuses. However, X-rays are no longer routinely recommended for the diagnosis of sinusitis. The examination exposes patients to a certain level of radiation exposure. Instead, the doctor can do one ultrasound make: This does not provide as accurate images of the sinuses, but is more gentle. Especially in pregnancy and in children the ultrasound is used. Also for the follow-up of a sinusitis the investigation is suitable.
Further imaging studies are Computed tomography (CT) and Magnetic resonance imaging (magnetic resonance imaging, MRI), However, they are only performed in certain cases, such as complications, planning surgery and chronic sinusitis. Also, the suspicion of a rare tumor as the cause of the discomfort can bring a CT or MRI clarity.
If the cause of sinusitis is (presumably) an allergic reaction, is one allergy test meaningful. This usually helps to find out which allergen is responsible for the excess immune response. As an allergy test, for example, the prick test or a provocation test in question.
Paranasal Sinus Inflammation: Course & Prognosis
Acute sinusitis usually resolves after a short time – 60 to 80 percent within two weeks, and 90 percent of cases of acute sinusitis within six weeks. On the other hand, the duration of chronic sinusitis can extend over years. Some patients even suffer from it for life. The decisive factor here is whether it is possible to eliminate the cause of chronic inflammation (such as narrowness in the nose).
complications Sinusitis is rare – with early and correct treatment. For example, persistent purulent sinusitis may spread untreated to the adjacent periosteum as well as to the bony and soft tissues. Serious problems threaten when, for example, the eye socket, the meninges or the brain itself (encephalitis) become infected. Such dangerous complications of sinusitis usually require treatment in the hospital.
Sinusitis in children
Sinusitis can also occur in children. The possible causes are the same as in adults. Which part of the sinus area is affected, varies depending on the age of the child, because the paranasal sinuses develop only fully in the course of childhood: In infants, only ethmoidal cells and maxillary sinuses are already so far developed that here can develop a sinusitis. However, sphenoid sinus and frontal sinusitis are often observed only from the school age.
Sinusitis in children: symptoms
The symptoms of sinusitis in children are similar to those in adults. However, they are the less obvious the younger a child is. Most common in children is acute, virus-induced sinusitis, which is accompanied by general symptoms such as coughing, sore throat, runny nose and possibly fever.
Sinusitis in children: treatment
The treatment of sinusitis in children is similar to that in adults: The doctor prescribed as needed Decongestant drugs and (in purulent sinusitis) antibiotics, The anti-inflammatory and analgesic drug acetylsalicylic acid (ASA) is not suitable for children under twelve years. He can – in conjunction with a viral infection – the rare, but potentially life-threatening Reye’s syndrome trigger.
Infrared treatments have proven to be successful in the treatment of sinusitis Red light lamp, Such a heat treatment improves blood circulation and thus supports the body’s immune response in the inflamed tissue. Have the same effect inhalationswith chamomile or saline. They open the airways and promote drainage of stuck secretions.
Essential oils should only be used on children in consultation with a doctor. They may even cause allergies or (with menthol-containing or strong-smelling oils) even respiratory arrest.
A chronic sinusitis In children (and adults) treatment is successful only if the cause is eliminated. For example, in a surgical procedure, bottlenecks between sinuses and nasal cavity, nasal polyps or enlarged tonsils are removed.
Sinusitis in children: prognosis
Acute sinusitis in children generally heals easily. If it has developed into a chronic inflammation, the prognosis depends on how well the treatment of the cause succeeds.
Without (sufficient) treatment, sinusitis can cause similar complications as in adults (for example, spread of inflammation to bone, eye socket or meninges). But that rarely happens.
Prevent sinusitis
Healthy mucous membranes help to prevent sinusitis. That’s why you should do not smokebecause it chronically irritates the mucous membranes. In winter, you should avoid overheated rooms and ensure sufficiently humid room air (for example by regular airing). Dry mucous membranes are more susceptible to germs.
You can also cleanse the mucous membrane with a pure Salt-water solution (in the form of a nasal spray or a nasal douche). This also helps to rid them of dust particles and dirt.
Generally it can also be with a targeted strengthening of the immune system prevent sinusitis. This is possible, for example, with visits to the sauna, changing showers and lots of exercise in the fresh air. A vitamin-rich diet strengthens the immune system and can thus prevent sinusitis. Avoid stress, lack of sleep and regular alcohol consumption – all factors that weaken the immune system.
If you have one sniff When you are blowing your nose, you should hold a nostril and not snort too hard. Or you pull up the nasal secretions – according to many experts, this is gentler for the sinuses than the whining. Drink enough to keep the nasal secretion fluid. In case of severe cold symptoms, mucous decongestant nasal sprays are also helpful. They facilitate secretion drainage. However, use such nasal sprays for a maximum of five to seven days. Otherwise, the mucosa may get used to the agent and swell even more. There are also herbal supplements that help liquefy the mucus.
If you have recurrent sinusitis due to anatomical narrowness in the nose, you should talk to your doctor. Then an operation can be useful. For example, the straightening of a curved nasal septum may become one in the future Sinusitis prevent.
Additional information
guidelines:
- Guideline “Rhinosinusitis” of the German Society of Otolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery e.V. (2017)