Skin fungus (dermatomycosis) is a fungal infection of the skin or its appendages (hair, nails). Which symptoms occur at which body site depends on the particular pathogen. Skin fungus is usually treated with so-called antimycotics (antifungals). Home remedies such as vinegar or essential oils can support this drug therapy. Read all important information about the causes, symptoms, treatment and prognosis of skin fungus.

Quick Overview
- What is skin fungus? Fungal infection of the skin and / or its appendages. Common forms include athlete’s foot (tinea pedis), ringworm (tinea corporis), nail fungus (onychomycosis or tinea unguium), head mushroom (tinea capitis), hand fungus (tinea manuum), cutaneous candidiasis and bran fungus lichen (pityriasis versicolor).
- Causes and risk factors: Dermatophytes (filamentous fungi), yeasts (yeast fungi) or molds. Contagion from person to person, from animal to human or touching contaminated objects possible. Particularly susceptible are people with circulatory disorders (such as diabetes, weakened immune system or overweight).
- symptoms: Depending on pathogen and affected part of the body, e.g. reddened, itchy skin on the torso and extremities in ringworm (tinea corporis) or grayish white, swollen skin with small tears in the toe gaps in athlete’s foot (T. pedis) or round, sharply defined skin changes on the head with broken or failed hair in head mushroom (T. capitis).
- treatment: Antifungals (antimycotics) for external (and possibly also internal) use. Supporting home remedies such as vinegar and essential oils. Careful hygiene. Regular changing of socks and shoes, washing the clothes at least 60 degrees Celsius. Fungus treatment of infested pets (may transmit certain skin fungi).
- Forecast: With consistent treatment usually complete healing without permanent skin damage. Complications in people with weak immune systems and children: Fungal infection of internal organs possible.
Skin fungus: symptoms
The skin fungus symptoms depend on which pathogen causes the infection, which body site is affected and how extensive the infection is. Filamentous fungi (dermatophytes) are among the most common pathogens. They can infect skin, hair and nails. Other common pathogens are yeast and mold. In addition to the skin, they can also affect the mucous membranes and internal organs. Here are some typical symptoms of important types of skin fungus:
Symptoms of Athlete’s Foot (Tinea pedis)
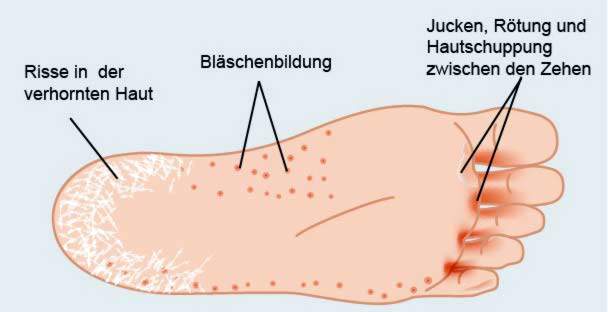
Athlete’s foot is one of the most common infectious diseases and is triggered by filamentous fungi. The mushrooms settle especially in the Toe webs To: The affected skin looks greyish white and swollen off and shows little fisssures, These tiny skin lesions can easily infiltrate bacteria and cause additional infection (superinfection).
Also the soles can be affected by athlete’s foot. Sign is one dry, white flaking of the skin, Sometimes a more inflammatory infection develops Blisters and itching, The symptoms can also spread to the side edges of the feet. The back of the foot usually remains asymptomatic.
Ringworm symptoms (tinea corporis)
Tinea corporis (ringworm) is also a skin fungus infection caused by filamentous fungi. It affects the trunk and extremities. The affected skin areas show round, scaly redness, mostly with clear itching are connected.
Along with hair, this superficial fungal infection can occur in deep skin layers expand. The result is an increased inflammatory response associated with the formation painful, fluid-filled knot accompanied. Neighboring lymph nodes swell. In addition, patients can general disease symptoms how to develop fever and fatigue.
Learn more about the ringworm in the article Tinea corporis.
Symptoms of head mushroom (tinea capitis)
Filamentous fungi can also affect the hairy scalp. The resulting skin fungus symptoms are very diverse. In some patients, the mushroom infection is almost without symptoms (no signs of inflammation). Many others are developing circular, sharply defined hairless districts different size. The scalp shows at these points greyish flaking, In other cases, the affected scalp areas remind of one stubblefield – By the fungal attack, the hair is broken at about the same height.
A special form of tinea capitis is the rare one Favus (Erbgrind), This form of fungal infection of the scalp is now only found in countries such as Nigeria, China and India. Typical are scar-like changes on the scalp that lead to hair loss.
Symptoms of facial fungus (tinea faciei)
A filamentous fungus infection in the face is in the form of scaly, itchy skin, The symptoms usually worsen when exposed to the facial skin strong light exposure. The tinea faciei can also occur together with a tinea corporis. If the symptoms are very severe, it may be a sign of a weakened immune system.
Symptoms of hand fungus (tinea manuum)
Symptoms of skin fungus on the hands can also be attributed to infection with filamentous fungi. Usually only one hand is affected at first. Later, the fungal infection can spread to the other hand. Many patients with tinea manuum also suffer from athlete’s foot.
Doctors differentiate two forms from hand mushroom:
- hyperkeratotic-squamous form: Most widely used. Typical symptoms are quickly drying skin blisters, from which develop round, flaky foci of infection. Sometimes the whole palm of the hand along the skin lines “floury dusty” covered with fine scales. Later, thick scales may form and spread all over the palm. In addition, numerous fine, painful skin cracks can arise. The hair follicles on the back of the hand can also affect the fungus. Then develop round, inflammatory foci of infection, which are partially covered by pustules.
- dyshidrosiformer hand fungus: Occurs less often. Typical skin fungus symptoms here are itchy blisters in the palm, at the edges of the hands and / or on the sides of the fingers.
A special form of tinea manuum is that “One hand / two feet” syndrome, It is also called Tinea palmoplantaris known: The skin fungus symptoms show up on one palm and two soles. Diabetics are often affected because they are particularly susceptible to infections.
Symptoms of Nail Fungus (Tinea unguium)
The nail fungus (tinea unguium or onychomycosis) is usually caused by filamentous fungi. Rarer stuck behind mold or yeast fungus. The most common are the toenails. But it can also hit the fingernails. Sometimes the pathogens penetrate below the nail at the end of the nail. In other cases, they attack the nail surface. Typical symptoms are in both cases lackluster nails and a thickened nail plate, In addition, the discolored Nail edge white or yellowish, In addition arise whitish, yellow or grayish-brown spots in the nail, At an advanced stage can also Pain occur.
Symptoms of inguinal fungus (tinea inguinalis)
Fungal infections in the inguinal region often cause men who sweat profusely. Typical symptoms are itching, sharp redness with accented edge and partial dandruff, The infection usually begins at the skin between thighs and scrotum. Later, it often spreads to the anus and buttocks. The scrotum itself is rarely directly involved.
Symptoms of cutaneous candidiasis
Cutaneous candidiasis is a skin fungus infection caused by yeast fungi of the genus Candida (especially C. albicans). It develops preferentially in moist warm body regions. Most of the so-called intertriginous regions are affected. These are parts of the body where adjacent, sometimes directly opposite skin areas often touch. Examples include armpit, groin, buttock, genital region, toe and finger spaces, and the skin area below the female breast.
Cutaneous candidiasis shows up initially nodular vesicles (Papulopustules). That’s what happens quickly large red, partly oozing plaques with scaly edgesthat of small pustules to be accompanied.
In general, a yeast infection (candidiasis) can affect not only the skin but also the mucous membranes. If the fungal infection affects the genital region, it is called genital candidiasis, It manifests itself in women as vaginal fungus. Typical symptoms include severe itching, blotchy redness, wipe-off white deposits on the mucosa, and an odorless, friable white discharge. Men are less affected by a genital yeast infection. If it does, it manifests itself as acornitis (penile fungus).
Bile fungus symptoms (Pityriasis versicolor)
Bile fungus is a skin fungus infection with yeast fungi of the genus Malassezia. It develops predominantly on the chest, back, shoulders and neck. Sometimes, however, the infection also spreads to the arms and middle trunk.
This form of dermal fungus starts with sharply defined, roundish spotsthat are as big as lentils or pennies and hardly itch, The spots connect with time larger, herd-shaped herds with a smooth surface, If you stroke it with a spatula, the skin will flake. The dander Remember the eponymous bran.
The skin patches are discolored against healthy skin. This shows up Color difference depending on the skin color: In dark or tanned patients the spots look bright. Responsible for this is the dense mushroom carpet on the skin, which prevents UV rays. Thus, the skin underneath can no longer form a color pigment (melanin). The result is white spots on darker skin. This appearance of the bran mushroom bears the name Pityriasis versicolor alba.
In fair-skinned patients, on the other hand, reddish-brownish spots are produced by pigments produced by the fungus itself. Doctors speak of this Pityriasis versicolor rubra.
Symptoms in microspore
This skin fungus disease is caused by filamentous fungi of the genus Microsporum (like M. canis). These fungi often infest pets such as dogs and cats. Through contact with such infected animals, a human can become infected with the fungus. This happens especially to children. They develop inflammatory, disc-shaped skin changes on the trunk and on the scalp, If the scalp is affected, the hair may break off at the affected areas.
Skin fungus: treatment
Skin fungus infections are associated with antifungals treated. These are medicines that specifically target fungi. With general tips and home remedies patients can support the drug treatment.
Skin fungus treatment: medicines
Antifungals can either inhibit the growth and proliferation of fungi (fungistatic action) or kill the fungi (fungicidal action). They are almost always externally (topically) in the form of Ointments, creams, powders, sprays, tinctures or shampoos applied. Only very rarely, in severe cases, is a treatment with tablets necessary.
Many antimycotics are freely available. Before you treat your own skin fungus yourself, you should go to the dermatologist. He can tell you which antifungal drug is best for you. A role is played by the type of skin fungus and individual factors such as the age of the patient or a possibly existing pregnancy.
Antifungals applied topically include, for example, nystatin, clotrimazole, miconazole, isoconazole and amorolfine. For internal use, amphotericin B, itraconazole ketoconazole, terbinafine and flucytosine are used.
In case of severe itching or skin burning in addition to the antimycotics anti-inflammatory glucocorticoids (“Cortisone”) in cream or ointment form on the appropriate skin.
Skin fungus treatment: General tips
As a patient, you can support drug therapy by avoiding typical causes and risk factors of a fungal infection. In the case of the widely used athlete’s foot, this means, for example:
- Avoid athlete’s foot for less breathable shoes.
- Socks, stockings and underwear should be changed daily and washed at a minimum of 60 degrees Celsius.
- During and immediately after an athlete’s foot treatment it helps to disinfect stockings, socks and shoes with an antifungal agent.
- Dry the toe gaps after showering or bathing always well (use a separate towel!), As mushrooms love it moist and warm.
- In places with a high risk of infection with fungal infections (such as swimming pools, saunas, etc.), it is best to pay special attention to hygiene and do not walk barefoot.
Basically, it is important to keep endangered or already affected body parts such as underarms, genital area and feet always dry. To dry off, you should always use a separate towel. This will prevent the fungal infection from spreading to other parts of the body or other people.
Another valuable tip: Support your immune system in the fight against the fungus by sleeping sufficiently, eat healthy, avoid stress and regain fresh air regularly.
Skin fungus: home remedies
As with many other diseases, a wide range of home remedies are also recommended for skin fungus. How effective these are in the individual case can not be predicted. It is best to discuss with your doctor or pharmacist which home remedies for skin fungus are suitable for you. The expert can also point out possible side effects and interactions.
Extensive fungal attack always requires a drug treatment. You should only use home remedies as an adjunct here. An insufficiently treated skin fungus can namely become chronic and sometimes even spread to internal organs. This can potentially lead to life-threatening complications!
Skin fungus treatment with vinegar
Apple cider vinegar is an old home remedy for dermal fungus. For athlete’s foot, for example, vinegar socks should help: To do so, one stirs six tablespoons of apple cider vinegar in 200 milliliters of water, dipped cotton socks and pulls them before going to bed. You should wear some dry woolen socks over it. If you do this several nights in a row, it should heal the athlete’s foot.
Skin fungus treatment with essential oils
Various essential oils can kill fungi. In addition, they have a regenerating effect on the skin and anti-inflammatory. The most important essential oil for the fungal treatment is tea tree oil. Since this oil dries out the skin, you should treat it with a nourishing oil or shea butter at the same time.
Skin fungus: causes and risk factors
Different types of fungi can trigger skin fungus:
filamentous fungi
In most cases, skin fungus infections are caused by filamentous fungi (dermatophytes). Experts then speak of dermatophytosis. The most common trigger in Central Europe is filamentous fungus Trichophyton rubrum, He is mainly responsible for ringworm and nail fungus. More filamentous fungi, which often cause fungus, are Trichophyton mentagrophytes, Microsporum canis (Trigger of the microsporie) and Trichophyton verrucosum (especially in rural areas).
A fungal infection with Trichophyton species is also called trichophytia.
yeast
Skin and mucous membranes can also be attacked by yeast fungus. The most famous yeast fungus is Candida albicans, It belongs to the natural flora of the mucous membranes. Under certain circumstances (such as immune deficiency) it can proliferate and trigger an infection, for example in the vaginal region (vaginal fungus). Another known yeast infection of the skin is the Branched mushroom lichen (Pityriasis versicolor).
molds
Mold fungi play only a minor role as pathogens of skin fungus. But they can – as well as yeasts – also infect internal organs and so a serious Systemmykose trigger. This is a fungal infection that affects several organ systems or virtually the whole body.
Skin fungus: transmission and infection
When asked “is skin fungus contagious?” The clear answer is yes. Skin fungi can be transmitted directly from person to person, but also from animal to human. You can also indirectly contaminate contaminated items, such as bath mats, clothing and shoes. Since mushrooms love it wet and warm, the danger of infection in swimming pools, saunas, tanning salons and public toilets is particularly high.
Skin fungus: risk factors
Various individual risk factors favor a skin fungus. These include, for example Diabetes mellitus and overweight, In the latter, perspiration is increasingly formed in the skin folds, which provides fungi with optimal living conditions.
Skin and mucous membranes of people with Circulatory disorders are also prone to a fungal infection.
Another risk factor is one weakened immune system, This deficiency can be caused by a serious illness (such as HIV) or medications that suppress the immune system. Such immunosuppressants are prescribed, for example, after organ transplants and in autoimmune diseases.
Skin fungus: examinations and diagnosis
Is there a suspicion of skin fungus, is the family doctor or a Dermatologists (Dermatologist) the right contact person. For skin fungus in the genital area you can also visit a gynecologist or urologist.
The attending physician collects the first in a detailed conversation medical history (Anamnesis): He interviews the patient exactly to type and duration of the complaints. He also asks if there are any underlying conditions (diabetes etc.) and if the patient recently had contact with people with skin rash.
After that follows one physical examination, The doctor examines exactly the skin changes. Usually he already knows with the naked eye whether it is actually a skin fungus or not.
To secure the diagnosis, the doctor takes one smear from an affected skin area and thus puts it in a special nutrient medium fungal culture at. In this way, fungi can be grown and identified under optimal growing conditions. This can take up to four weeks. Proof of the type of pathogen is important for choosing the right treatment.
Certain types of fungus can be additionally directly on the skin microscopic or under special UV light (Wood light) detect. This light has a wavelength of approximately 365 nanometers and is an important tool in the diagnosis of various skin diseases. For example, in case of a bran fungus (pityriasis versicolor), the affected skin areas under wood light show an orange color. Some dermatophytes, on the other hand, fluoresce yellow-green under the Wood light.
In some cases, it may be useful to have one tissue sample for a closer examination.
Skin fungus: disease course and prognosis
Skin fungus does not heal itself, but must be treated. Patience is required because fungal infections are usually persistent. It is particularly important to use the antifungal drugs (antifungals) as long as the doctor has prescribed. Canceling the therapy prematurely, the skin fungus can return. However, when treated correctly, pizinfection almost always completely heals. The complexion normalizes, possibly fancy hair grows after.
However, complications are also possible, especially in people with a weakened immune system and in children. These patients have an increased risk that the skin fungus infection extends to organs inside the body.
To prevent a (re) skin fungal infection, you should take some tips:
- Pay particular attention to hygiene in areas with a high risk of infection (such as swimming pool, sauna, tanning salon).
- Change socks and underwear daily and wash at least 60 degrees Celsius.
- Avoid lightly breathable shoes and always keep the skin dry on vulnerable parts of the body (skin folds, toe gaps, etc.).
- Pets such as dogs, cats and horses can transmit skin fungi to humans. That’s why you should go to the vet skin fungus examine and, if necessary, treat with appropriate antimycotics.
Additional information
guidelines:
- Guideline “Tinea of the Free Skin” of the German Dermatological Society (2008)