Hand-foot-and-mouth disease is a mostly harmless but highly contagious viral disease. Especially children are affected. The disease is transmitted via body fluids, stool or contaminated objects. Typical symptoms include painful blisters on the hands, feet and around the mouth. The hand-foot-mouth disease usually heals without consequences after ten days at the latest. Read all important information about hand-foot-and-mouth disease: symptoms, cause, diagnosis, treatment and possible complications.

Quick Overview
- What is Hand-Foot-Mouth Disease? A highly contagious viral disease, which occurs mainly in (small) children and people with immunodeficiency. It is sometimes called “mouth and mouth disease” or “hand-foot-mouth rash.”
- Infection: about droplet infection or smear infection
- symptoms: First flu-like symptoms, then red spots and blisters on the hands, feet and in the mouth area. Often, the infection also runs asymptomatic.
- Diagnosis: Often the doctor already recognizes the disease by the typical symptoms and by using the information from the anamnesis interview. In severe or unclear cases, further examinations (blood, stool) are useful.
- Treatment: Relief of discomfort through analgesic tinctures, calf wrap for fever reduction etc.
- Forecast: The hand-foot-mouth disease heals in most cases by itself and without complications. Rarely, complications develop through the spread of infection to internal organs (e.g., meningitis = meningitis).
Hand-foot-and-mouth disease: infection
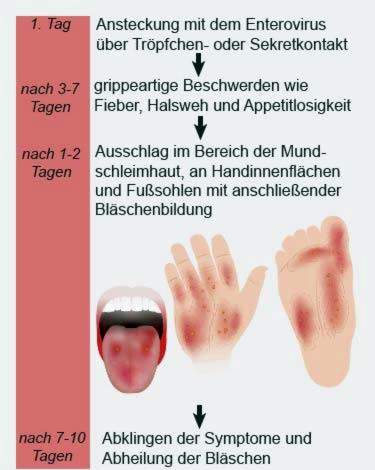
The triggers of hand-foot-and-mouth disease (various enteroviruses) are present everywhere (ubiquitous) in the environment and are highly contagious. The disease will transmitted from person to person: This can be done directly via body fluids such as nasal and pharyngeal secretions, saliva or secretions of the typical skin blisters. In case of coughing or sneezing, infected persons can distribute tiny saliva droplets in the environment that can transmit the pathogen to healthy people (droplet infection). Also, when touching the bubbles seeket infection is possible.
In addition, the hand-foot-and-mouth disease is over contact infection transferable: The virus-containing secretion droplets can contaminate objects and surfaces such as cutlery or door handles, which thus become a source of infection for healthy people. In addition, infected people excrete the viruses through the stool. If they do not (properly) wash their hands after a bowel movement, they can also contaminate taps, door handles, etc. in this way.
The incubation period The hand-foot-and-mouth disease, ie the time between the infection and the appearance of the first symptoms, is on average three to ten days. Sometimes, however, the infection is already noticeable (at the earliest one day after the infection) or much later (up to one month later).
Duration of the risk of infection
In the first week of the disease, patients are the most infectious. In this phase, the viruses multiply particularly strong, so that they are also released in large numbers to the environment (secretions, stool).
However, there is also a certain risk of infection even if the symptoms of hand-foot-and-mouth disease (rash, etc.) have already subsided. Infected people sometimes excrete the pathogens for weeks with the stool. After the toilet or the diaper change you should therefore wash your hands thoroughly!
Many infected (especially adults) show no disease symptoms. But they are still contagious!
Hand-foot-and-mouth disease: symptoms
The term “hand-foot-mouth disease” already gives an idea of which parts of the body show the characteristic symptoms of the disease. First, however, she expresses herself in flu-like complaints such as fever, poor performance, throat and body aches and loss of appetite.
About one to two days later develop in the mouth (tongue, gums, oral mucosa) and around the mouth (perioral) painful red dotsthat after a short time to small Vesicles or superficial ulcers (canker sores) become.
Around the same time as the red spots in the mouth area or less hours later, it develops on the hands and feet rash: Mostly it shows in the form of many red patches of different shape and size, which usually do not initially itch. However, this can change if bubbles form on the reddened areas. Typically, the palms and soles are affected by this rash. But it can also develop elsewhere (back of the hand, buttocks, genital area, knees, elbows, etc.).
Some sufferers lose their fingernails and toenails around four to eight weeks after the disease subsides.
The skin blisters in hand-foot-and-mouth disease but a secretion containing many of the triggering viruses. As a result, the patient transmits the virus to other parts of his body, but also – by touching objects – to other people. Thorough hygiene is therefore very important during the illness!
Not always, however, sufferers have (such) complaints. Doctors assume that the symptoms described only occur in about 20 percent of cases. Four out of five people have no symptoms. Especially in adults, the symptoms of hand-foot-and-mouth disease are often very low. That’s why they often do not notice anything about the infection. The same applies to children over the age of ten. Nevertheless, there is a risk of infection for others.
So if you suspect that you have the condition, for example because you notice some (nonspecific) symptoms, then you should avoid staying in the presence of small children during the illness.
Hand-Foot-Mouth Disease: Pregnancy & Newborn
In general, there is no reason to worry if a pregnant woman is diagnosed with hand-foot-and-mouth disease: the infection is usually mild or completely symptom-free (asymptomatic) during pregnancy.
If the pregnant woman develops the symptoms of hand-foot-and-mouth disease shortly before or after birth, she can transmit the infection to the newborn. For most babies the disease is mild. Rarely, the infection spreads to internal organs (such as liver, heart) and can then be very difficult. This risk is highest in newborns during the first two weeks of life.
Hand-foot-and-mouth disease: treatment
The hand-foot-mouth disease can not be treated causally, that is: There are no drugs against the triggering viruses. But that is not necessary because the disease is usually harmless. The treatment is limited to alleviating the symptoms. So you can, for example, a analgesic and antipyretic drug give, for example, with the active ingredient paracetamol.
Acetylsalicylic acid (ASA) is also a popular pain and fever remedy. However, it is not suitable for children: With them, the drug in conjunction with a viral infection can cause serious complications such as the Reye syndrome.
For painful blisters in the mouth, the doctor can make a mild, analgesic tincture to dab or rinse. This usually contains the active ingredients chlorhexidine or lidocaine. Also different Plant-based remedies (Chamomile, lemon balm, thyme) can relieve symptoms of hand-foot-and-mouth disease.
Despite the painful blisters in the mouth, patients should drink enough. Otherwise there is a risk of dehydration, especially in children.
antibiotics are generally not effective in viral infections because they only help against bacteria. In some cases, however, a bacterial infection (superinfection) may develop in addition to viral hand-foot-and-mouth disease. Then an antibiotic treatment may be necessary.
Hand-foot-mouth disease: home remedies
Not only with conventional medical measures, but also with home remedies can do something against the symptoms of hand-foot-and-mouth disease. Some examples of suitable ones home remedies:
- With fever, home remedies like calf wrap can help.
- The blisters in the mouth often make chewing and swallowing painful. Recommended are then chilled or lukewarm meals, which do not have to be chewed (such as yogurt, pudding, soup) and drinks such as chamomile or chanterelle tea.
- You can dab the painful blisters in your mouth with a cotton swab dabbed in honey. That can have a soothing effect.
Hand-foot-mouth disease: homeopathy
Some people also try the healing process of hand-foot-mouth disease homeopathyto support. So for example Rhus toxicodendron help against the vesicular rash. Generally feverish infections will be around Apis and belladonna recommended. An experienced doctor or homeopath can advise you on the selection, use and dosage of homeopathic remedies for hand-foot-and-mouth disease.
The concept of homeopathy and its specific effectiveness are controversial in science and not clearly proven by studies.
You really never have any peace of mind before hand-foot-and-mouth disease: you can all year round occur, with emphasis in late summer and fall. In addition, the responsible ones Pathogen spread everywhere, It is about different enteroviruses, especially Coxsackie A viruses and the Enterovirus A71.
Especially children under the age of ten fall ill with hand-foot-and-mouth disease. Adults can also be affected. Especially when someone falls ill in kindergarten, kindergarten or school, it usually does not take long for the highly contagious disease to spread.
Particularly endangered are people with one immune deficiency, The cause of this immune deficiency may be another disorder (such as HIV) or immunodeficiency therapy (for example, taking immunosuppressants). Due to the defensive weakness, the pathogens of hand-foot-and-mouth disease can in the worst case cause meningitis or damage organs such as the liver and heart.
Hand-foot-and-mouth disease is often mistakenly referred to as foot-and-mouth disease. However, this disease occurs only in cattle, sheep and pigs and has no relation to hand-foot-mouth disease. Nevertheless, the latter is often called “wrong foot-and-mouth disease”.
Hand-Foot-Mouth Disease: Examinations & Diagnosis
If you suspect hand-foot-and-mouth disease in yourself or your child, your pediatrician is the right person to talk to. He will first discuss all relevant information with you medical history (Medical history). Possible questions of the doctor are:
- What symptoms occur (fever, sore throat, loss of appetite, rash, etc.)?
- Did you or did your child have contact with other children with hand-foot-and-mouth disease (kindergarten, nursery, etc.)?
- Are you taking or taking medication for your child?
- Against which diseases are you or is your child vaccinated? Do you have the vaccination certificate with you?
The last question has the background that rashes also occur in other typical “teething troubles”. In contrast, if vaccinated, the doctor can exclude such diseases as the cause of the symptoms with high security.
After the anamnesis interview follows one physical examination, The doctor looks, among other things, where a rash has formed and how it looks exactly.
Based on the information from the anamnesis interview and the physical examination, the hand-foot-and-mouth disease can usually be clearly diagnosed. Further investigations As a rule, they are only necessary if the clinical picture is very severe or if the symptoms can not be unequivocally attributed to hand-foot-and-mouth disease. Then, for further clarification, the doctor may, for example, have a blood or stool sample of the patient examined in more detail. Less often, he takes a sample of the nerve water (CSF) and sends it to the laboratory for analysis.
There are some diseases that can cause similar symptoms in the mouth area as hand-foot-mouth disease. These include tonsillitis, glandular fever and herpes.
Hand-Foot-Mouth Disease: Course & Prognosis
The hand-foot-and-mouth disease usually resolves after seven to ten days without complications. Newborns, infants, and immunocompromised individuals can develop complications as the virus spreads throughout the body. Possible consequences are, for example, a meningitis (meningitis) or damage to the heart or liver.
Diseased children should not visit community facilities (kindergarten, school, etc.) until the symptoms have completely resolved. For siblings, the same thing applies if they also show possible signs of hand-foot-and-mouth disease.
Once you have the disease, it is immune to the triggering specific type of virus. However, if you are infected with another type of hand-foot-mouth disease, a new disease is possible.
Hand-foot-mouth disease: prevention
There is no vaccine against hand-foot-and-mouth disease in this country. To prevent infection or transmission of the pathogen, you should pay attention to a very thorough hygiene. First and foremost, wash your hands regularly with soap. This is especially true after sneezing or coughing, after going to the toilet, after the diaper change and before and after the meal preparation.
If a family member becomes ill, it is highly recommended to clean potentially contaminated items and surfaces such as doorknobs and toilets. Close contact with the patient (hugging, kissing, etc.) should be avoided as much as possible. This helps to be infected with the Hand, foot and mouth disease submissions.
Additional information
guidelines:
- RKI Guidebook “Hand-Foot-Mouth Disease” by the Robert Koch Institute (2017)