Enlarged hemorrhoids cause unpleasant symptoms such as burning and itching on the anus. Those affected want to get rid of them as quickly as possible. There are different possibilities for this. Read more: What are hemorrhoids exactly? What kind of complaints do they trigger? How can hemorrhoids be treated and prevented?
Hemorrhoids: short overview
- Treatment: Depending on severity, ointment, zinc paste or vegetable ointments (witch hazel, aloe vera), cortisone ointment, local anesthetic, “sclerotherapy”, constriction (rubber band ligation), surgery
- Home remedies: anti-inflammatory and itch-calming sitz baths, flaxseed (to facilitate the bowel movement)
- Prevention: High-fiber diet, regular daily bowel movements, a few presses during bowel movements, adequate drinking, daily physical activity.
- Typical symptoms: Foreign body sensation, oozing, pain and / or itching in the anal area, light red blood on the chair or toilet paper
- investigations: physical examination with palpation of anal reflection (proctoscopy) and endoscopy (rectoscopy)
- complications: Skin irritation, anal eczema, anemia, fecal incontinence
Hemorrhoids: treatment
Everyone has hemorrhoids (also: hemorrhoids): The sponge-like, well-perfused vascular pad sits at the exit of the rectum. It seals together with the sphincter muscles the anus.
However, if the hemorrhoids are enlarged, they can cause discomfort. The patients complain for example about pain, itching and burning on the anus. Doctors then speak of one haemorrhoids, Colloquially, it simply means: someone has hemorrhoids.
There are several ways to treat such abnormally enlarged hemorrhoids. A role is played by the severity of hemorrhoidal disease:
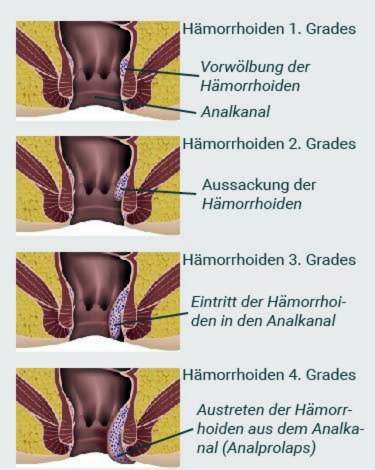
- Grade 1: The mildest and most common form are first degree hemorrhoids. They are not palpable and visible only in an anal canal mirroring (proctoscopy).
- Grade 2: Hemorrhoids of the second degree bulge outward when pressed and then retract by themselves back into the anal canal.
- Grade 3: Third-degree hemorrhoids also escape from the anus when pressed. But you have to push it back with your finger.
- Grade 4: Grade 4 hemorrhoids are permanently visible on the outside of the anus. They can not be pushed back into the anal canal. Often also protrudes some anal mucous membrane (anal prolapse).
Depending on the severity of Hämorrhoidalleidens different treatment options are considered. It is best to discuss with your doctor what kind of therapy is best for you. He will then transfer them to the right place. For which doctor is ultimately the right contact person for hemorrhoids, depends on the type of treatment. That can be about one proctologist, surgeon or gastroenterologist be.
The basis of every hemorrhoids treatment is one healthy diet and a controlled bowel movement, Both also help to prevent hemorrhoids. If necessary can also conservative measures how to use pain relieving ointments. For persistent complaints or severe Hämorrhoidalleiden is usually one surgery necessary.
Hemorrhoids treatment with drugs
Medicines are used in the treatment of hemorrhoids to relieve the symptoms. They can be helpful with any degree of hemorrhoids. There are various active ingredients available. Some have anti-inflammatory, some locally numbing.
Anti-inflammatory drugs
With Wundsalben or zinc paste can be treated well painful hemorrhoids. Also vegetable ointments or suppositories are available, for example preparations based on Hamamelis virginiana (Virginian witch hazel) or from Aloe vera, The preparations should help against hemorrhoidal complaints such as skin irritation and itching.
In addition, your doctor can give you cortisone-containing ointments prescribe. They contain, for example, prednisolone or hydrocortisone acetate. These drugs inhibit the immune system, which counteracts the inflammation of the anus. Only use cortisone-containing ointments for as long as your doctor has recommended. For a long time, they can lead to skin atrophy. In other words, the skin becomes irreversibly thinner and thus more vulnerable. In addition, cortisone ointments promote fungal infections in the gut.

Local anesthetics
Local anesthetics also help against itching and pain. These stun the affected area locally, so that the patients feel no more pain. Examples of local anesthetics are benzocaine, cinchocaine and lidocaine.
Like cortisone ointments, local anesthetics may only be used for a short time. The reason: you can cause allergies. If you have previously had any allergic reactions to local anesthetics, you should tell your doctor before you receive the hemorrhoid treatment.
Application of the drugs
The ointments can be placed directly in the anus using an applicator. Alternatively you can coat a compress with the ointment and use it as an insert.
Some agents are called Analtampons offered. These are suppositories, which are provided with a gauze strip. They remain in the anal canal and release their active ingredient there. Conventional suppositories, however, release their active ingredient in upper intestinal sections.
Be careful with laxatives!
The stool can be very painful in haemorrhoidal disease and cause bleeding in the anus. Use it anyway laxativeonly after consultation with your doctor. Some preparations only help in the short term against constipation and make the bowel sluggish with prolonged use. This creates a new blockage.
Soil, ice or constrict hemorrhoids
Mild hemorrhoids (especially grade 1) are often obliterated. To do this, the doctor injects substances that are dying in the area of a hemorrhoid, for example zinc chloride. Blood flow into the hemorrhoid is blocked, the tissue shrinks and solidifies. This method will sclerotherapy called. Properly performed, it is painless for the patient. To treat all enlarged hemorrhoids, but usually several interventions are necessary.
Hemorrhoids can also be left to soil by irradiating with infrared light. These Infrarotkoagulation but is considered less successful.
Another possibility is freezing the hemorrhoids with nitrous oxide or liquid nitrogen. Doctors speak of this Kryohämorrhoidektomie, Similar to infrared coagulation, the chances of success are not very high.
Better chances of success are the “binding” of the hemorrhoids: Rubber band ligation or Hemorrhoid ligation called. The doctor sucks individual hemorrhoids and laces them with rubber bands. The patient generally does not feel pain. Due to the interrupted blood supply, the tissue dies. The hemorrhoid falls off after one to two weeks. This can lead to bleeding. A hemorrhoid treatment by means of rubber band ligation is performed especially in second degree haemorrhoids (sometimes also 3rd degree).
Hemorrhoids operate
The last option of hemorrhoid treatment is the classic hemorrhoid surgery. The hemorrhoids are completely cut out. These hemorrhoidectomy is indicated if the symptoms can not be alleviated with other treatments (such as sclerotherapy). Hemorrhoids of the third and fourth degree often require surgery.
For the hemorrhoid surgery there are different techniques. The hemorrhoid tissue can be removed with the help of a pair of scissors, a scalpel or a laser. In some procedures, the surgical wound in the rectum is sutured partially or completely, in others, it remains open.
Modern procedures of hemorrhoids treatment
There are also some modern methods that can be used to remove hemorrhoids. They are considered more gentle than a classic hemorrhoidectomy. An example is the Forklift operation to Longo:
It is suitable for hemorrhoids of the third degree: These are hemorrhoids that have occurred from the anus (prolapse), but can still push back well. During surgery, a strip of the anal mucosa above the hemorrhoid is punched out with a special stapler. Then the affected hemorrhoids are “pulled” back into the anal canal and stapled to the edges of the wound.
The method is considered less painful than a hemorrhoidectomy. Patients usually need less painkillers afterwards and can leave the hospital sooner. But there are also disadvantages, including the increased risk of relapse: After a Longo operation, new hemorrhoids are formed faster and more frequently than after a hemorrhoidectomy.
Hemorrhoids: home remedies
As a hemorrhoid patient, you can also do a great deal against your condition yourself. For example, you can take sitz baths with anti-inflammatory tannins to relieve the itching and pain of the anus. To facilitate bowel movements, you can take flaxseed with plenty of fluid.
The various home remedies and advice sometimes suffice to make slight hemorrhoids disappear. But even with more advanced hemorrhoids they are useful: they can relieve the symptoms and support the medical treatment.
More home remedies and valuable advice on hemorrhoidal disease can be found in the article Hemorrhoids – home remedies.
Prevent hemorrhoids

The basic measures of hemorrhoid treatment are also valid if you want to prevent hemorrhoids: high-fiber diet and controlled bowel movement.
The most important tips for prevention and as a basic therapy for hemorrhoids are:
- Eat foods rich in fiber on a regular basis. This prevents constipation. A lot of fiber is in wholemeal bread, cereals, wheat bran, sesame, oatmeal, legumes, vegetables and fresh fruit (with shell).
- Drink at least 1.5 liters of fluid per day. Then the fiber in the intestine can well swell. Especially recommended are water and other non-calorific beverages such as unsweetened tea.
- Eat as little food as possible to promote constipation. These include, for example, white bread, chocolate, white rice and white noodles. Black tea also makes the bowel sluggish if it has been pulling for a long time.
- Move sufficiently and regularly. If you are overweight, you should lose some pounds.
- Take time for a bowel movement and always at the same time of the day (after breakfast, if possible). This is how you get used to your bowel in a controlled bowel movement.
- Do not press too hard during bowel movements.
- Do not use laxatives (even natural or herbal products) without consulting your doctor!
Hemorrhoids: symptoms
How do patients first become aware of possible hemorrhoids? Blood in the stool is often the first sign. Here, the color of the blood is crucial: Bleeding hemorrhoids give off bright red blood. It indicates bleeding from arterial vessels. Dark red blood usually comes from a venous vessel. Here you have to think of other diseases of the intestine.
Hemorrhoids often bleed after defecation, as increased blood accumulates in the vessels as a result of pressing. The blood may be on the top of the chair, sticking to the toilet paper or dripping into the toilet. Normally hemorrhage bleeding is weak. But they can be very strong, especially in advanced disease. Then you should definitely visit a doctor.
Advanced Hemorrhoid Symptoms
Hemorrhoids usually change their symptoms in the course of the disease: as occurs in advanced hemorrhoids Itching and burning on the anus on. Some patients also complain about it Foreign body sensation, wet, sore skin in the anal area or palpable protrusions, The latter are nothing but the hemorrhoids that have fallen out of the anal canal. Pain also often show up only in advanced hemorrhoids.
diarrhea is not a typical hemorrhoid symptom. Nevertheless, diarrhea-like complaints may occur during the course of the disease: sufferers often report mucous secretions from the intestine. Some patients also suffer from fecal incontinence, This means that stool or mucus goes off unchecked. The reason is that enlarged hemorrhoids can no longer fulfill their main task: the dense closure of the anus.
Loggerhead (outer) hemorrhoids
Real (internal) hemorrhoids arise from dilated arteries of the vascular pad, which is located inside the rectum near the exit (anus). To distinguish from it are so-called spurious (outer) hemorrhoids: These are protrusions around blood clots (thrombosis) in the venous system of the anus sphincter, which arise at the outer edge of the anus. They are sometimes confused with real hemorrhoids that bulge out of the anus. That is why they are called unclean and false or external hemorrhoids. The medically correct name is perianal.
Hemorrhoids: causes and risk factors
Basically, hemorrhoids are an extension of the arterial vessels of the hemorrhoidal pad. But how do hemorrhoids develop exactly?
There are now various theories about which factors favor their development vasodilation in the rectum. One of these factors is repeated strong pressing during bowel movements, Especially people with chronic constipation (Constipation) tend to. Therefore, they often suffer from hemorrhoids. A constipation usually arises through a low-fiber diet, lack of exercise and / or too low fluid intake.
As well as strong pressing during bowel movements also allows Lifting heavy loads increase the pressure in the abdomen. So if you have to haul large loads on a regular basis, this can also promote hemorrhoidal disease.
Another possible hemorrhoid cause is frequent diarrhea: If you constantly only low-viscosity chair settles, the sensitive closure system of the anus is not trained enough. As a result, the arteries in the hemorrhoidal pad can expand.
Hemorrhoids can also be caused by circumstances that hinder blood flow from the erectile tissue. These include pregnancy, overweight and sedentary activities.
A congenital weakness of the blood vessel walls may also promote the development of hemorrhoids. Such vessel wall weakness is also likely to increase the risk of hemorrhoids with age: the vessel walls become less elastic over the years.
By the way: There are also Hemorrhoids in childrenalthough much less common than in adults. One of the possible causes is the chronic constipation.
Hemorrhoids: pregnancy
Pregnancy is a known risk factor for hemorrhoidal disease. But how do hemorrhoids develop during pregnancy?
As mentioned above, one reason is the decreased blood flow out of the arteries of the hemorrhoidal pad: the adolescent child in the abdomen presses on the rectum of the mother. This blocks the blood circulation, which widens the vascular pad at the end of the rectum.
Also the hormonal change in the pregnancy favors hemorrhoids.
You can read more about hemorrhoidal disease in expectant mothers in the article Hemorrhoids – Pregnancy.
Hemorrhoids: examinations and diagnosis
Complaints such as burning and itching on the anus and blood in the stool are embarrassing for many people. They are reluctant to go to the doctor. It is very important to have the symptoms cleared up by a doctor. Often there are actually enlarged hemorrhoids behind it. Then the sooner they are recognized, the easier they can be treated.
Sometimes other diseases are the cause of the symptoms such as perianal thrombosis, anal abscess, herpes, eczema or fungal infections. In the worst case, colon cancer is behind it (blood in the stool!). Therefore, do not be afraid to visit your family doctor at an early stage if you suffer from the symptoms mentioned above.
Detailed conversation
The doctor will first talk to you in detail about your medical history to raise (anamnesis). For this he asks you the following questions:
- Since when are you having those complaints?
- Did you notice blood after stool?
- Do you feel pain or itching on the anus?
- Do you suffer from constipation?
- Do you eat a lot of fruits and vegetables?
- What do you do professionally (sedentary or physically active activity)?
investigations
Then follows the physical examination, The doctor scans the anal area and the anal canal with his finger (digital-rectal examination). So he can examine the anal sphincter muscles and the texture of the anal mucosa. The examination often provides clear evidence of hemorrhoids. For further examinations the general practitioner can refer you to a specialist, for example to a proctologist.
This will examine the rectum in more detail. He can do this Analkanalspiegelung (Proctoscopy) or one endoscopy of the rectum (Rectoscopy). In each case, a small tube of different lengths is introduced with a tiny camera in the rectum, so that the doctor can make a visual impression.
Sometimes a reflection of the entire colon is necessary (colonoscopy). Above all, it is used to rule out bowel cancer in the presence of blood in the stool.

Hemorrhoids: disease course and prognosis
Many sufferers ask themselves the question: “Are hemorrhoids dangerous?The answer is: Basically, hemorrhoids are not threatening and have a good prognosis, the sooner they are recognized, the better they can be treated, but the bigger the hemorrhoids are, the more difficult and time-consuming the therapy is to the doctor!
In the course of hemorrhoidal disease can complications occur. Enlarged hemorrhoids can too skin irritation to lead. These in turn favor anal eczema: The skin on the anus is red and inflamed, it is wet and itches. In addition, skin blisters and scab may form.
Strong, recurrent bleeding sometimes produces a persistent bleeding anemia (chronic anemia). As a result, patients often feel tired and tired or complain of dizziness.
Hemorrhoids can become trapped as they exit the anus. Doctors then speak of incarceration. She is very painful. As a result of the entrapment, the blood builds up in the blood vessels and the blood flow slows down. This can cause a hemorrhoid thrombosis form.
Enlarged hemorrhoids can no longer sufficiently fulfill their main task: ensuring the chair continence. This threatens a long-term illness one fecal incontinence: In those affected goes uncontrolled chair.
If there are already hemorrhoids, it may Anal come to pain or bleeding. Therefore, you should perform anal intercourse with hemorrhoids carefully and with enough lubricant. Even better: they do without it until the hemorrhoids have healed. Another important tip: Because of the risk of bleeding in hemorrhoids, always practice anal sex with a condom!
Hemorrhoid surgery: Possible complications
After surgery, complications can also occur. These include, for example, bleeding, pain and the formation of blood clots (thrombosis) on the anus. Also, infections, abscesses and a narrowing of the intestinal outlet (anal stenosis) are possible. Rarely can hemorrhoidsPatients no longer willingly control bowel movements after surgery (fecal incontinence).
Additional information
Book recommendation:
Freya Reinhard and Jens J. Kirsch: Hemorrhoids and the Diseased Rectum: Advice and Help for Concerned and Relatives. Diagnosis and treatment of disorders and diseases of the rectum, Kohlhammer, April 17, 2003.