Fibromyalgia is one of the pain syndromes. Typical are deep muscle aches in different parts of the body. There are also exhaustion, concentration and sleep problems. The causes of the disease are not yet known, but possible is a disturbed pain processing. The treatment is difficult because common painkillers fail. Find out here about symptoms, therapy and possible triggers of fibromyalgia!
Brief Overview Fibromyalgia
- symptoms: Deep muscle aches, abnormal sensations, painful pressure points, fatigue, irritable bowel symptoms, depression, anxiety
- Painkiller: Opioids, cortisone or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs such as acetaminophen, ibuprofen, acetylsalicylic acid have little or no effect
- Treatment: Exercise, heat therapy, psychotherapy, antidepressants, relaxation procedures
- Nutrition: predominantly vegetable based, especially a lot of vegetables, low meat, low alcohol
- Causes: Triggers still largely unknown, possibly disturbed pain processing, genetic causes, altered nerve fibers, mental trauma
- Diagnosis: Exclusion of other causes, review of specific pain points, pain questionnaires
- Forecast: incurable but manageable, does not leave lasting physical damage
Fibromyalgia – Symptoms
The term “fibromyalgia” stands for fiber-muscle pain. This already describes the central symptom of the disease. Most are persistent, deep muscle pain, accompanied by abnormal sensations. So far, they can not be explained by pathological processes. Other main symptoms include sleep disorders and fatigue. Frequently, fibromyalgia is also associated with emotional complaints such as depression or anxiety.
Main symptom pain
The main symptom of fibromyalgia is diffuse and chronic pain. Often the sufferers describe it as a deep muscle pain that can cause stiffness, burning sensation, tapping, numbness and tingling. Sometimes joints or muscles feel swollen.
The pain can focus on specific areas. Especially affected are neck, back, arms, legs and chest. He can also occur in other parts of the body.
Variable pain intensity: Pain levels and intensity are affected by weather, temperature, time of day, stress levels and physical activity. In some patients the pain is particularly intense in the morning. He then improves during the day. Warmth and moderate activity usually ameliorate fibromyalgia symptoms.
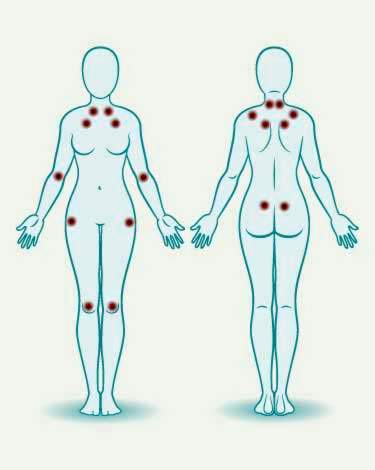
Painful pressure points (tender points): It is typical for patients with fibromyalgia that they are particularly sensitive to pressure at certain body points. In total, there are 18 of these so-called tender points.
A headache: In addition to muscular pain, people with fibromyalgia also commonly experience headaches or migraines. Also irritable bowel symptoms with frequent abdominal pain diarrhea or constipation are common. Others again suffer from pain that resembles a urinary tract infection.
Painful face: A special variant of fibromyalgia manifests as a so-called temporomandibular joint syndrome, in which the face and jaw ache. The latter can move the persons only to a limited extent, which causes them problems with chewing.
Main symptoms of fatigue and sleep disorders
More than 90 percent of fibromyalgia patients suffer from fatigue and fatigue. Often, sleep disorders are added – their sleep is easy and they often wake up. In addition, they often suffer from sleep apnea. Breathing misfires occur during snoring during the night. Sleep is then less restful and the risk of cardiovascular disease increases.
Fatigue in fibromyalgia: Sleep disorders can lead to a chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS). Fatigue is the term for chronic fatigue. In fact, most fatigue sufferers meet the criteria for fibromyalgia. Conversely, more than two-thirds of those with fibromyalgia suffer from CFS.
Restless Legs Syndrome: A disease that is also common in fibromyalgia patients is Restless Legs Syndrome. Affected suffer at rest with agonizing pulling or tingling in the legs. The symptoms can only be relieved by exercise. This too can cause significant sleep disturbances and subsequent fatigue. For patients with symptoms of fibromyalgia, it should therefore be investigated whether there is no additional restless legs syndrome.
Fibromyalgia: mental symptoms
Fibromyalgia is often associated with mental illness. Particularly common are depressive symptoms such as nervousness, inner restlessness, depression and loss of drive. About 30 percent of people with fibromyalgia suffer from a true depression. Others develop fibromyalgia as well as an anxiety disorder.
Hypersensitivity and regulatory disorders:People with fibromyalgia are often particularly sensitive to stimuli such as odors, noise or light. Further fibromyalgia symptoms occur as a result of disturbed body regulation. Such vegetative symptoms include increased tremor (tremor), excessive sweating (hyperhidrosis), reduced salivation, and cold fingers. Also, irritable bowel syndrome with seizures and diarrhea is common in people with fibromyalgia symptoms.
Severities of fibromyalgia
How strong and diverse the fibromyalgia symptoms are in a patient is very different. Therefore, doctors also classify the disease in different degrees of severity.
Afflicted with lighter forms have next to the pain in different parts of the body little or no other physical and mental discomfort. They often experience prolonged periods without complications and are hardly impaired in their quality of life at work and in their free time.
Others have other physical and mental fibromyalgia symptoms in addition to the chronic pain. They are moderately or even significantly impaired in their everyday lives.
Fibromyalgia therapy
The triggers and disease mechanisms of fibromyalgia are yet to be known. A fibromyalgia therapy is therefore not aimed at curing the disease, but at the improvement of the symptoms.
But that is difficult in many cases. Therefore, it is all about the best way to deal with the disease and to achieve the highest possible quality of life, even if the pain does not disappear.
movement therapy
The most important building block of fibromyalgia treatment is exercise. Physicians recommend the patients two to three times a week endurance training in low to medium intensity.
The goal is to stay in the so-called aerobic range, where the body does not consume more oxygen than it just absorbs. A good indication is that you have enough air during the workout to be able to talk easily.
Among the suitable sports in fibromyalgia include
- hike
- swim
- To go biking
- To dance
- ergometer
- Aqua Jogging
- flex
In addition to cardiovascular fitness, sufferers should specifically train the function of their joints and muscles, flexibility, strength and coordination. Experts recommend this
- Water aerobics (two to three times a week)
- Dry gymnastics (two to three times a week)
- Function training (twice a week)
Physical therapy
A heat treatment can improve the symptoms. In most patients, cold worsens the symptoms. But some patients also benefit from a whole-body cold therapy. They spend a few minutes in a cold chamber with extremely low temperatures.
Also soothing in many patients is a so-called balneotherapy with medical baths. Massages, however, are not recommended for fibromyalgia treatment.
psychotherapy
How much pain is perceived depends on the inner attitude towards the symptoms. As part of a cognitive behavioral therapy, patients learn to reassess the pain. He is still there, but no longer in the center of consciousness.
To do this, the therapist, in collaboration with the patient, also discovers patterns of thought and perception that negatively influence the course of the disease. If they break through, this can significantly change the perception of pain.
relaxation techniques
Stress increases the discomfort of people with fibromyalgia. Therefore, relaxation techniques are important elements of fibromyalgia therapy. These include autogenic training and progressive muscle relaxation according to Jacobsen. Also Far Eastern relaxation techniques such as Tai Chi, Qi Gong and Yoga can help.
Medical therapy
In more severe cases, medications can be an important complementary component of fibromyalgia therapy.
antidepressants
Many patients with fibromyalgia develop mental comorbidities such as anxiety or depression. In addition to cognitive behavioral therapy, medications can help.
Antidepressants act on the messenger metabolism in the brain. Not only do they reduce depressive symptoms through this mechanism of action, they also relieve pain and fatigue and promote general well-being. Therefore, they can also help patients with severe fibromyalgia who do not have depressive symptoms.
It prescribes drugs from the drug class of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and tricyclic antidepressants, especially those with the drug amitriptyline.
Tricyclic antidepressants not only relieve muscle pain, they also improve sleep. However, such medications should only be taken permanently if they are effective.
anticonvulsants
Another important group of drugs for fibromyalgia therapy are the so-called anticonvulsants. They have been developed to treat nerve pain and epilepsy, but can also relieve pain and improve sleep as part of fibromyalgia therapy.
Pregabalin, for example, blocks certain messengers that are responsible for the transmission of pain. Such medications can help especially patients with severe pain in the foreground of the disease. Possible side effects include dizziness, weight gain and edema in the arms and legs.
Ineffective painkillers
Although pain is the main symptom of fibromyalgia, most common analgesics for fibromyalgia therapy are not recommended – they have little or no effect.
Fibromyalgia is not associated with inflammatory changes. For this reason, one does not use any anti-inflammatory analgesics such as ibuprofen, acetylsalicylic acid and acetaminophen and no cortisone.
Similarly, opioid painkillers for fibromyalgia therapy are usually unsuitable. Most do not work, except Tramadol, which also has an antidepressant effect. This medication is also prescribed especially for patients with pronounced pain symptoms.
Alternative healing
Since conventional therapy is often inadequate, many patients turn to alternative therapies. These include methods of traditional Chinese medicine such as acupuncture, but also osteopathy.
Other fibromyalgia patients rely on homeopathy. Depending on the type of symptoms, different homeopathic remedies may be considered. For example, Rhus Toxicodendron is said to relieve pain.
Trained patients
At the beginning of fibromyalgia therapy, training can be very helpful. In their framework, patients learn to live as best they can with the disease. For example, people who suffer from fibromyalgia need more relaxation, sleep, but also exercise than healthy people.
Rehabilitation measures
Some people with fibromyalgia suffer so much from ailments such as pain, heavy fatigue or depression and fears that they are often absent from the workplace. In extreme cases, they may even have to take early retirement.
With such severe impairments and performance losses, a rehabilitation therapy can be useful, in which many approaches of fibromyalgia therapy are bundled available.
Individual concepts
Fibromyalgia treatment should be tailored as individually as possible to the patient. Experts have identified three groups of patients:
- Patients with anxiety and depression in the foreground of the complaints
- Patients who suffer from the pain in particular
- Patients who are so severely limited by fatigue, pain or mental health problems that they are often absent at work or even threatened with early retirement.
For the success of therapy, it is crucial that the patient actively supports all measures. That is why it is important for the patient and the doctor to plan the procedure together. This also includes the gradual use of treatment options. It depends on the type of symptoms, the severity and the course of the disease.
Fibromyalgia: diet
A special diet is not recommended for fibromyalgia. However, many patients report that their symptoms improve when they consume certain foods more often or avoid others.
A lot of fruits and vegetables: Fruits and vegetables contain many antioxidants. They catch aggressive oxygen molecules in the body called free radicals. In fibromyalgia, many of these could circulate in the body. Therefore, a plant-rich diet could have a positive effect on the disease process.
Little meat: Meat contains a lot of arachidonic acid, which promotes inflammatory processes. People with fibromyalgia can also meet their protein needs through dairy or vegetable protein sources such as soy and other legumes.
Stimulants only in moderation: Alcohol, chocolate and coffee as well as nicotine increase muscular restlessness. Therefore, they should not be consumed too much. Instead, green tea is recommended, which has a strong antioxidant effect.
For more information on how to best feed on fibromyalgia, see the article Fibromyalgia – Nutrition.
Fibromyalgia: causes and risk factors
The causes of fibromyalgia are still not fully understood. In most cases, there is no clear trigger of pain sickness. It is not an inflammatory rheumatic disease of the muscles or joints and also not wear-related pain.
Although those affected feel pain in muscles and connective tissue. On radiographs or CT scans, however, there are no pathological changes even after years. Current laboratory tests, for example on rheumatoid factors, remain fruitless.
Disturbed pain processing
The most important hypothesis on the causes of fibromyalgia is currently that patients’ central nervous pain perception has changed. The threshold of pain perception is lower than usual, so that the brain already perceives light stimuli as pain and attaches greater importance to it.
Genetic predisposition
Genetic changes that result in increased sensitivity to pain have not yet been identified, but could be a cause of fibromyalgia. This suggests that family members of fibromyalgia patients have an eightfold increased risk of the disease.
Altered nerve fibers
Studies by the University of Würzburg have for the first time provided a true organic finding in fibromyalgia. The researchers found that the small nerve fibers in the muscle tissue of patients with fibromyalgia were altered. Whether this applies to all patients with fibromyalgia is still open.
Psyche, stress and trauma
Since there is usually no organic explanation for the pain, those affected were long regarded as imaginary patients. Or it was falsely assumed that her symptoms are a purely psychosomatic expression of depression.
This hypothesis has since been refuted, even though the psyche may well play a central role in the onset of the disease. Thus, stress as well as physical or emotional injuries (trauma) can promote the development of fibromyalgia. It often appears in periods of high stress. Also, people who have been maltreated or sexually abused in childhood or as adults are more likely to develop fibromyalgia.
In addition, the high burden associated with a serious course of illness can actually foster anxiety and depression.
Unhealthy lifestyle
An unfavorable lifestyle can also promote the disease. These include smoking, obesity and low physical activity.
Middle age, female gender
Fibromyalgia can occur at any age. However, it is most common between the ages of 20 and 50 years. 80 percent of the patients are female.
Secondary fibromyalgia
In some cases fibromyalgia seems to develop in the course of another disease. In contrast to a primary fibromyalgia, in which no other diseases are considered as a cause, this is called a secondary fibromyalgia. Diseases that promote fibromyalgia include:
- rheumatic diseases
- Infectious diseases, mostly viral infections with Epstein-Barr virus, hepatitis viruses and HI viruses.
- certain tumor diseases
- Disorders of hormone balance
Fibromyalgia: examinations and diagnosis
If a fibromyalgia syndrome is suspected, the family doctor is the first contact person. If necessary, he or she will treat the disease in collaboration with specialist colleagues, specialized pain therapists, neurologists, psychotherapists and physiotherapists.
Often it takes a long time until the diagnosis of fibromyalgia is made, since the disease is very diverse and difficult to grasp. The affected people are often mistaken for years from doctor to doctor. They suffer from the fact that their symptoms can not be assigned to a diagnosis. This creates uncertainty, delays the treatment and thus worsens the prognosis.
anamnesis
The basis of the medical examination is the conversation. This allows the complaints to be more accurately determined and arranged. Typical questions of the doctor are:
- How does your pain feel?
- Where exactly are the pain?
- Is a rheumatic disease known to you?
- Is your everyday life affected by the symptoms?
- Do you suffer from sleep disorders?
- Do you have gastrointestinal discomfort?
- Is your mood impaired?
Fibromyalgia is a so-called exclusion diagnosis. This means that all other possible illnesses must first be ruled out before a fibromyalgia diagnosis can be made.
Cornerstone of the diagnosis
For the diagnosis, the pain in different parts of the body must exist for at least three months. The doctors also evaluate different pain scales and questionnaires.
In addition, the so-called tender points play a central role in the clarification. These are certain pressure points that typically cause pain in patients with fibromyalgia. If the patient responds to pressure with pain at eleven out of 18, this is an indication of a fibromyalgia syndrome. Conversely, there are also pressure points that should not be painful during the test.
Pain diary as a diagnostic aid
The doctor will ask the patient to keep a pain diary in which, in addition to the type, duration and location of the pain, he also records conspicuous abnormalities. These include, for example, gastrointestinal complaints and urinary problems.
Similarly, mental stress such as concentration or sleep disorders and lack of drive should be recorded and discussed. Such concomitant symptoms are typical of the fibromyalgia syndrome.
Online tests
Various online questionnaires on the fibromyalgia self-test can be found on the internet. However, they are not very meaningful because the diagnosis is very difficult and requires a lot of experience. In addition, the tests sometimes include only individual symptom areas, such as the pain.
Attention likelihood of confusion!
The symptoms of fibromyalgia patients also occur in other diseases. This includes:
- Rheumatoid arthritis (RA)
- Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)
- Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) disease
- Polymyalgia Rheumatica (PMR)
- Hyperthyroidism and other hormonal diseases
- muscle inflammation
- Neurological disorders of the central or peripheral nervous system
In order to exclude or detect them as the cause of the complaints, the doctor performs a series of examinations. This includes
- X-ray, CT or MRI
- Blood test, including the so-called rheumatoid factors
If one discovers no pathological changes in these examinations, this speaks for a fibromyalgia.
Mental pain
There is also a risk of confusion with the “persistent somatoform pain disorder” and the “chronic pain disorder with mental and somatic factors”. In these, the pain is caused by severe mental stress – which does not mean that they are mere imagination. This is not the case with fibromyalgia, although mental stress can worsen the symptoms.
Fibromyalgia: disease course and prognosis
Fibromyalgia is not curable so far. However, it does not cause lasting damage to the muscles and joints, so that the patient is neither threatened with disability nor their life expectancy is shortened.
The aim of the therapy is to reduce the symptoms as much as possible. The treatment is not always easy, but there are many methods of modern pain therapy available. Success requires close collaboration between patient and doctor.
If the symptoms can not be sufficiently alleviated, the suffering is high. The consequences are frequent sick leave. Some patients, in their distress, are considering applying for recognition as severely disabled or even retiring due to their fibromyalgia.
However, getting a pension actually granted is difficult, as the severe symptoms have so far hardly been proven by hard evidence. Those affected should turn to self-help groups and fibromyalgia organizations on this matter.
It is important to get the complaints under control as quickly as possible. An early start of treatment within two years of the onset of symptoms largely relieves up to 50 percent of those affected from their pain. On the other side of the age of 60, the symptoms of a fibromyalgia syndrome often improve on their own.
Additional information
Self-help groups & clubs
- German Fibromyalgia Association (DFV) e.V.
- Fibromyalgia League Germany (FLD)
Books
- Fibromyalgia. Compact Guide: Coping with chronic pain successfully (Dr. med. Eberhard J. Wormer, Mankau Verlag, 2017)
- The Fibromyalgia Guide: Living a good life despite constant pain. The Guide to the German Fibromyalgia Association e. V. (Holger Westermann, 2017)
- Fibromyalgia – starting afresh every day, Deutsche Rheumaliga, 2016
guidelines
- Abstract of the guideline “Definition, Pathophysiology, Diagnosis and Therapy of the Fibromyalgia Syndrome”, Deutsche Schmerzgesellschaft e.V., 2017
- Long version of the guideline “Definition, Pathophysiology, Diagnosis and Therapy of the Fibromyalgia Syndrome”, Deutsche Schmerzgesellschaft e.V., 2017
- Patient Guideline “Definition, Pathophysiology, Diagnosis and Therapy of the Fibromyalgia Syndrome”, Deutsche Schmerzgesellschaft e.V., 2017
- Patient Guideline “Fibromyalgia syndrome: the most important in brief”, German Pain Society e.V., 2017