The scaphoid fracture (scaphoid fracture) is the most common bone fracture of the carpal. The cause is usually a fall on the outstretched hand. Therapeutically, it is often sufficient to rest your hand with a plaster. In some cases, however, surgery is essential to avoid lasting damage. During the healing process of a scaphoid fracture, various complications may occur. Read all about the scaphoid fracture!
Puncture fracture: description
In German, the term “scaphoid” refers to two different bones. On the one hand the scaphoid of the carpal, but also the os naviculare of the tarsus. So if we talk about a scaphoid fracture, it can mean two different fractures. However, the scaphoid fracture of the carpal (scaphoid fracture) is much more common and is therefore usually equated with a scaphoid fracture. This text also mainly deals with the navicular fracture of the wrist.
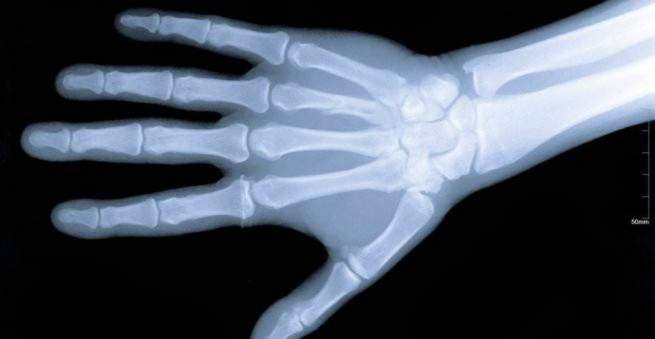
Puncture fracture: hand
The scaphoid bone is one of the eight carpal bones and part of the wrist. It forms with its lower edge the joint surface to the radius (radius), one of the two long forearm bones. If one falls with outstretched arm on the palm, the acting force of the fall over the carpal bones on the forearm is transferred. Often this leads to a rupture of the spine, but also the carpal root can be affected and then in two-thirds of all cases the scaphoid bone.
The navicular bone is a curved bone that can be divided into three sections: a proximal, a middle and a distal. The proximal portion forms part of the articular surface with the radius, the distal portion is the distal end of the patellar bone away from the forearm. Mostly it breaks in the middle, sometimes in the proximal and only very rarely in the distal area.
Since the blood supply differs greatly depending on the section, the exact description of the fracture line is important in order to select the best possible treatment. Overall, the more distal the fracture, the better the blood supply and thus the chance of recovery.
Puncture fracture: foot
The scaphoid of the foot (os naviculare) is a supporting element of the arch of the foot. In most cases, sports injuries lead to breakage, but also fatigue fractures caused by long-lasting strains – such as extended hikes and marches – are possible. Fatigue fractures are not easy to diagnose and are often overlooked. The consequences are long-lasting pain and delayed healing.
Puncture fracture: symptoms
The typical symptoms of a scaphoid fracture are pain, which mainly occurs on the back of the hand and on the side of the thumb. The wrist is swollen and hurts especially when it is moved, which leads to a restraint.
In addition, the so-called Tabatière is very sensitive to pressure. Tabatiere is the area on the back of the wrist, above the wrist crease, between the two tendons, which spread the thumb. A pressure pain there is a typical sign of a fractured navicular bone, even if the fracture is not clearly visible on the x-ray.
Patients with a scaphoid fracture usually hold their hands close to the body and avoid any form of vibration. Even gripping movements are difficult and very painful. Puncture fracture on the dominant hand often restricts patients, as many everyday movements, such as brushing teeth, are much more difficult with the other hand.
Puncture fracture: causes and risk factors
The cause of a scaphoid fracture is in most cases a fall on the outstretched hand. The scaphoid bone is exposed to many shear forces. Typical sports that lead to a scaphoid fracture because they are often associated with corresponding falls are, for example, snowboarding or inline skating.
Although the bone structure is more pronounced in men, they are six times more likely to be affected by a fractured scaphoid bone than women. The reason for this is the different risk tolerance between the sexes. If you crash more often, you are more likely to pull a broken-bone fracture.
Puncture fracture: examinations and diagnosis
In the physical examination of a scaphoid fracture in particular the typical pain in the Tabatière and the rest of attention.
In the so-called Watson shift test, the examiner moves his hand slowly towards the thumb. When the scaphoid bone is broken, he feels a small “click” over the bone and the patient reports a stabbing pain in his wrist.
Particularly important for a reliable diagnosis are apparatus tests. In the X-ray, however, the assessment of the pelvic bone is not easy, so especially fresh fractures are often overlooked. To be on the safe side, you make four pictures in different positions. If the diagnosis is still unclear, a computed tomography (CT) may be necessary. In a CT fine shots of the wrist are created. In this way, a possible break line can be tracked and evaluated accurately.
Puncture fracture: treatment
A scaphoid fracture can be treated conservatively, ie without surgery, or surgically. The doctor’s treatment depends on the individual case and depends mainly on the part of the scaphoid bone that breaks. The longer healing process of conservative therapy must be weighed against the risks of surgery.
Puncture fracture: Conservative treatment
If the fragments of the scaphoid bone have not slipped against each other and the fracture line is not too close to the forearm bone, a conservative therapy is possible. In this case, you can only treat the scaphoid fracture with a plaster. After about two to three weeks, the doctor uses a new X-ray image to check how the healing process is progressing. Since a scaphoid fracture heals only slowly – especially if it is not operated on – the hand usually has to be immobilized for two to three months.
Puncture fracture: operative treatment
If the fragments of the navicular bone are separated, or if the fracture is close to the forearm articular surface, it is unlikely that it will be properly dissected without surgery, and surgery will be required. In this operation, the two fragments are screwed together. This is followed by a four-week plaster. The healing process is generally a little faster during an operation. The screw remains in the wrist for the most part in most cases.
Puncture fracture: Disease course and prognosis
The scaphoid fracture healing time depends on the location of the fracture within the bone and whether the wrist is adequately sedated. In addition, a bone fracture heals faster the younger the patient is. A general statement about the healing time is therefore not possible because it depends on many individual factors.
In all scaphoid fractures there is a risk of a so-called pseudarthrosis. This term describes an incomplete bone healing, in which a bone is not healed months after the break and the fragments can be moved against each other. Since this risk is relatively high in the scaphoid fracture, the operation is the best therapy in case of doubt, despite the possible risks.
If a pseudarthrosis occurs in the course of healing, a major surgery must be performed. Here, a part of the scaphoid bone is removed and replaced with bone material from another area of the body (for example, from the pelvis). This is followed by a three-month rest position.
In young patients, favorable Bruchverlauf, and consistent immobilization of the healing process is often unproblematic. In unfavorable cases, one can scaphoid fracture however, represent a very long limitation. Persistent pain in the wrist after a fall should therefore always be taken seriously and clarified by a doctor so as not to unnecessarily delay the start of therapy.